Dina Fine Maron, Editor of Health & Medicine at Scientific American, joins Cheddar to discuss some of the biggest changes to science regulations we'll see in 2018. From food labels to nonaddictive cigarettes, people need to be aware of what might affect their everyday lives.
A revamped nutrition label was slated to debut in July of 2018, however the Trump administration is giving companies a longer window. Major companies now have until 2020 and smaller companies have until 2021. The new labels will have more detail on added sugar and calorie count. However, critics say the delay could be a major blow to the public's health.
Plus, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration aims to create a nonaddictive cigarette with lower nicotine levels. It hopes this will help smokers quit. However, the agency opened up the conversation to the public for input which will ellicit some strong views from the tobacco industry.
Cheddar's Need2Know Podcast for Tues., June 16, 2020.
From milk to canned tuna to shampoo, soy is in a good majority of our day-to-day products. It’s added to around 60% of the nation’s processed foods. Soy has been known to provide some real health benefits, like high protein. But there are legitimate health and environmental consequences that raise the question: why do we use so much soy? And should we?
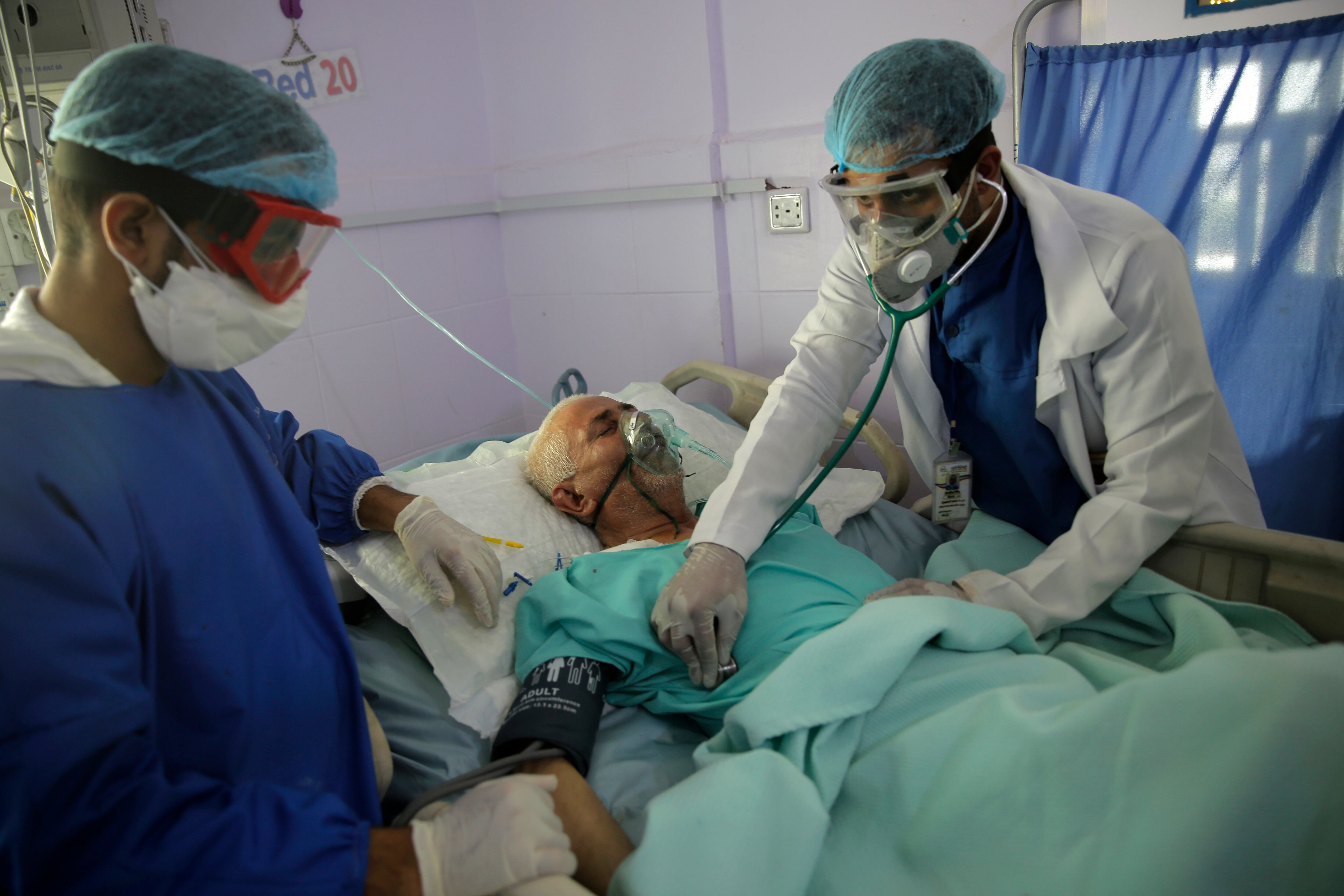
Researchers in England say they have the first evidence that a drug can improve survival from COVID-19. The drug is a cheap, widely available steroid called dexamethasone.
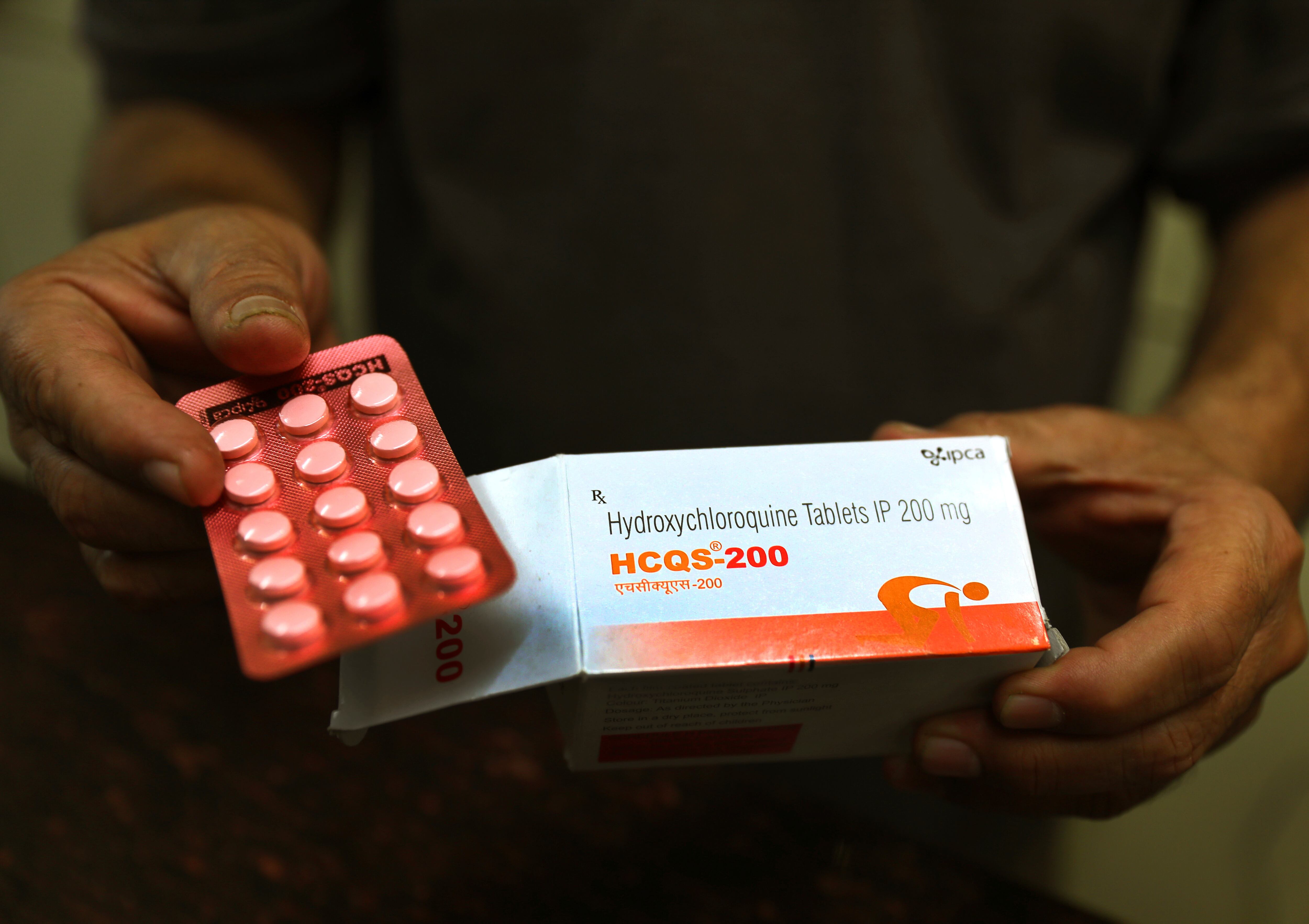
The Food and Drug Administration said Monday that the drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are unlikely to be effective in treating the coronavirus.
As the number of coronavirus cases continues to rise in the U.S., Johnson & Johnson's chief scientific officer Dr. Paul Stoffels told Cheddar the company has an accelerated plan to create a vaccine.
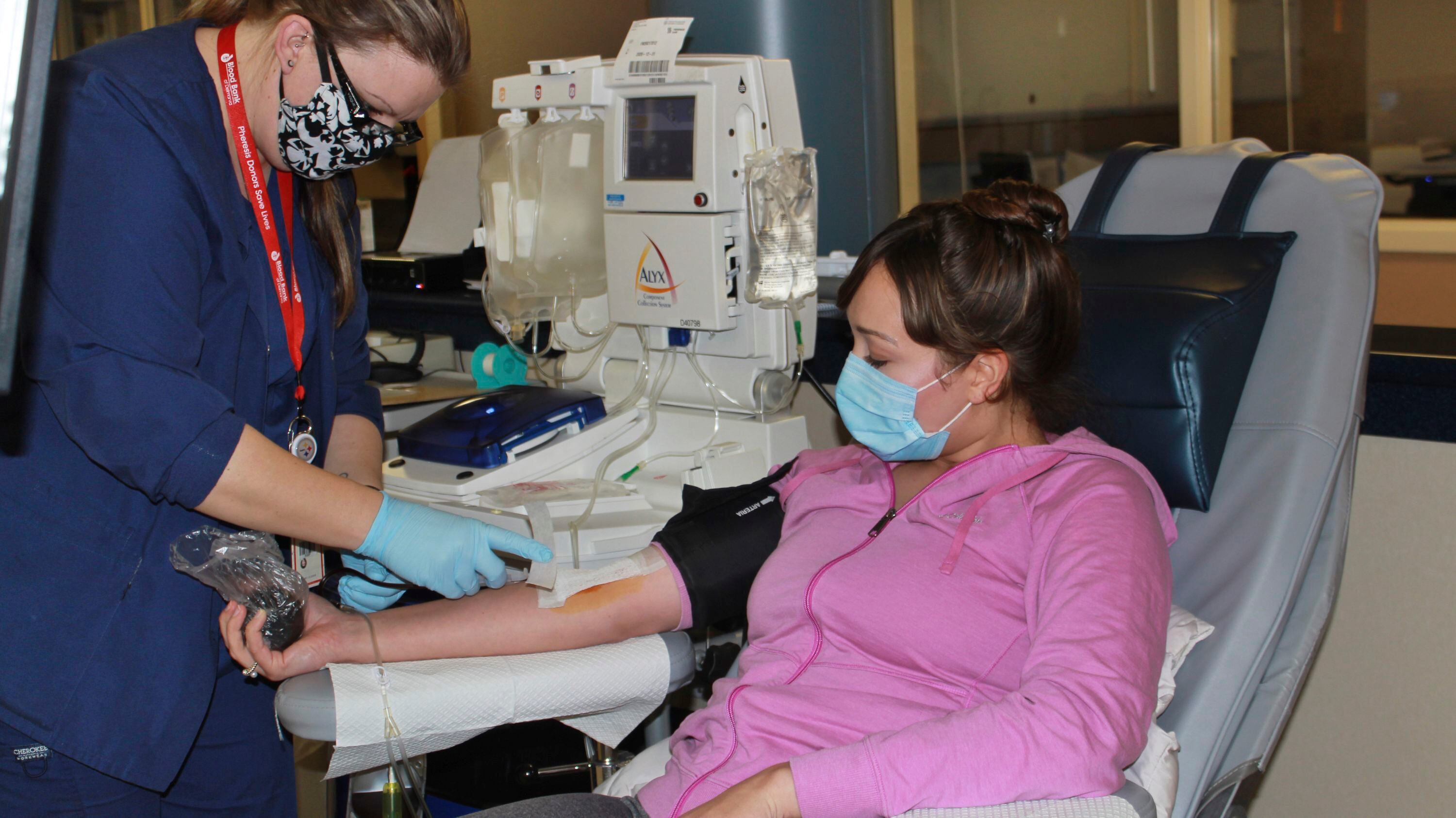
Scientists are beginning a new study to tell if the blood plasma of COVID-19 survivors might help prevent infection in the first place.
Coronavirus cases are rising in nearly half the U.S. states. And while many are chalked up to increased testing or to small, local outbreaks, others are more alarming.
If you lived in a big city in the 90s, you're probably one of the unlucky people who was kept up at night on a regular basis by errant car alarms. But today, those in that same big city hear alarms far less often than you did. So where did car alarms go? How have they evolved, and did we ever need them to begin with?
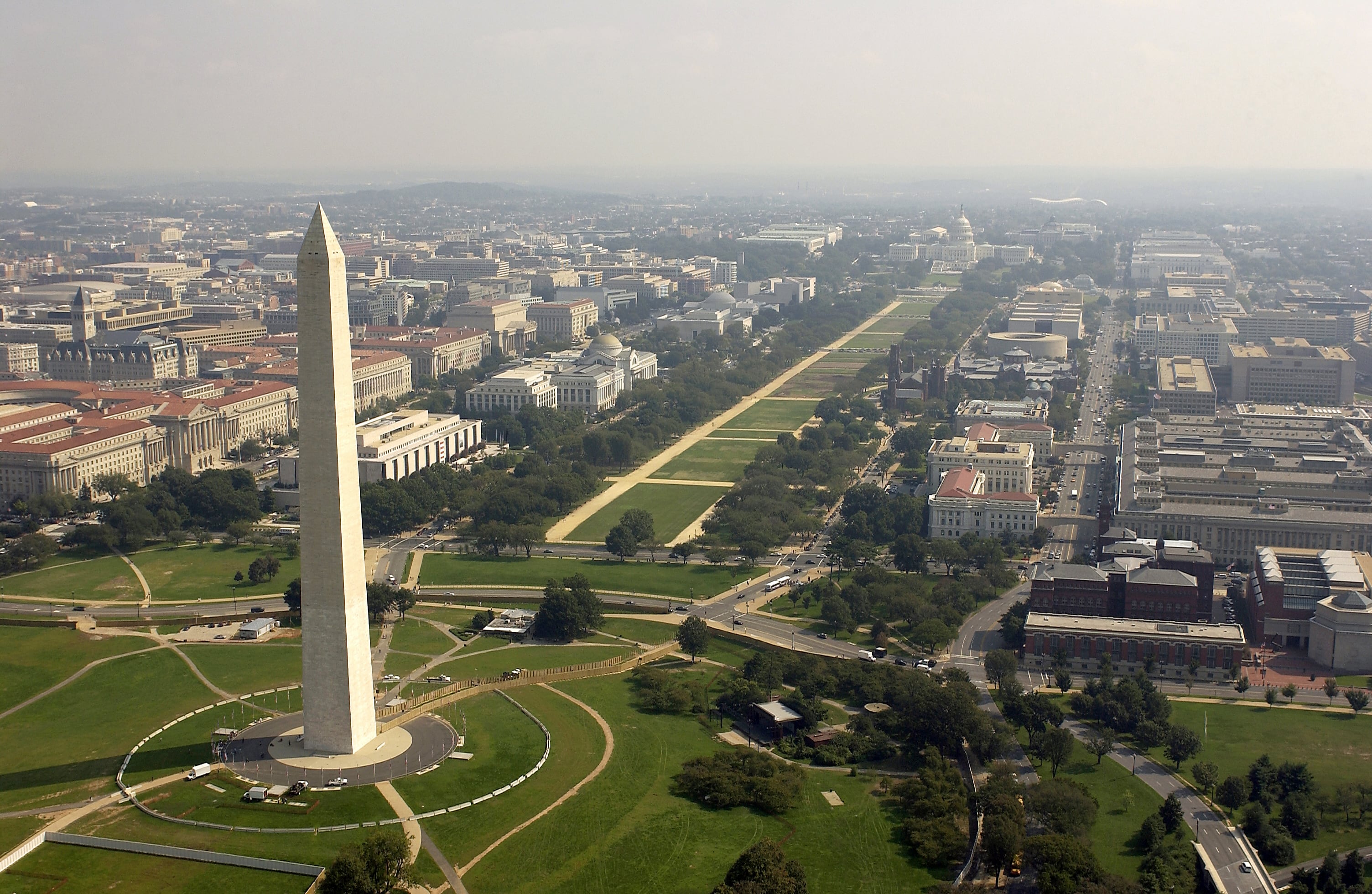
The skyline of Washington D.C. is stunted. You've probably heard that D.C. can't build skyscrapers taller than the U.S. Capital Building or the Washington Monument. But those are both myths from a bygone era. Cheddar tells the real story.
A top World Health Organization expert has tried to clear up “misunderstandings” about comments she made that were widely understood to suggest that people without COVID-19 symptoms rarely transmit the coronavirus.