Industrial conglomerate 3M Company is partnering with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to develop a cheaper, quicker COVID-19 test.
Right now, test results can take anywhere from a few hours to a week. Quest Diagnostics, for instance, said the average turnaround time at its labs is currently seven days.
3M's new test would function more like a pregnancy strip, a rapid paper-based test that could be mass-produced and quickly distributed at the point of care.
"In terms of patient experience, what we're looking to do is create that low-cost, highly-accurate, simple-to-use test that would be accessible to a lot of people," Dr. John Banovetz, chief technology officer for 3M, told Cheddar.
The antigen-based test, which looks at proteins on the virus, would offer a "preliminary view" of a patient's coronavirus status — though ideally, patients would follow up with a doctor, he added.
"Our goal would be a point-of-care test, so maybe it's taken in a doctor's office. Maybe you pick it up at the pharmacy," Banovetz said.
The goal is to start producing tests by the end of summer or early fall. Once manufacturing is rolling, 3M could produce millions of tests per day, according to the company.
As cases surge across the country and many anticipate a second wave in states where the infection rate has dropped off, calls for more testing are growing.
More than 41 million tests have been reported to the CDC, with a 9 percent positivity rate, but the U.S. continues to lag behind other countries by some measures.
In the meantime, the Trump administration is relying on the private sector to meet the demand for tests, putting pressure on companies such as 3M to come up with a solution.
"We're going as quick as we can right now," he said. "Our focus is trying to get that accuracy up and in a way that we know that we can mass-produce it. That's really where 3M can help contribute to this, our ability to be able to commercialize and bring to market new ideas and innovations."
A new U.N. biodiversity report card highlights the decline over the past 10 years in fragile ecosystems such as coral reefs and tropical forests.
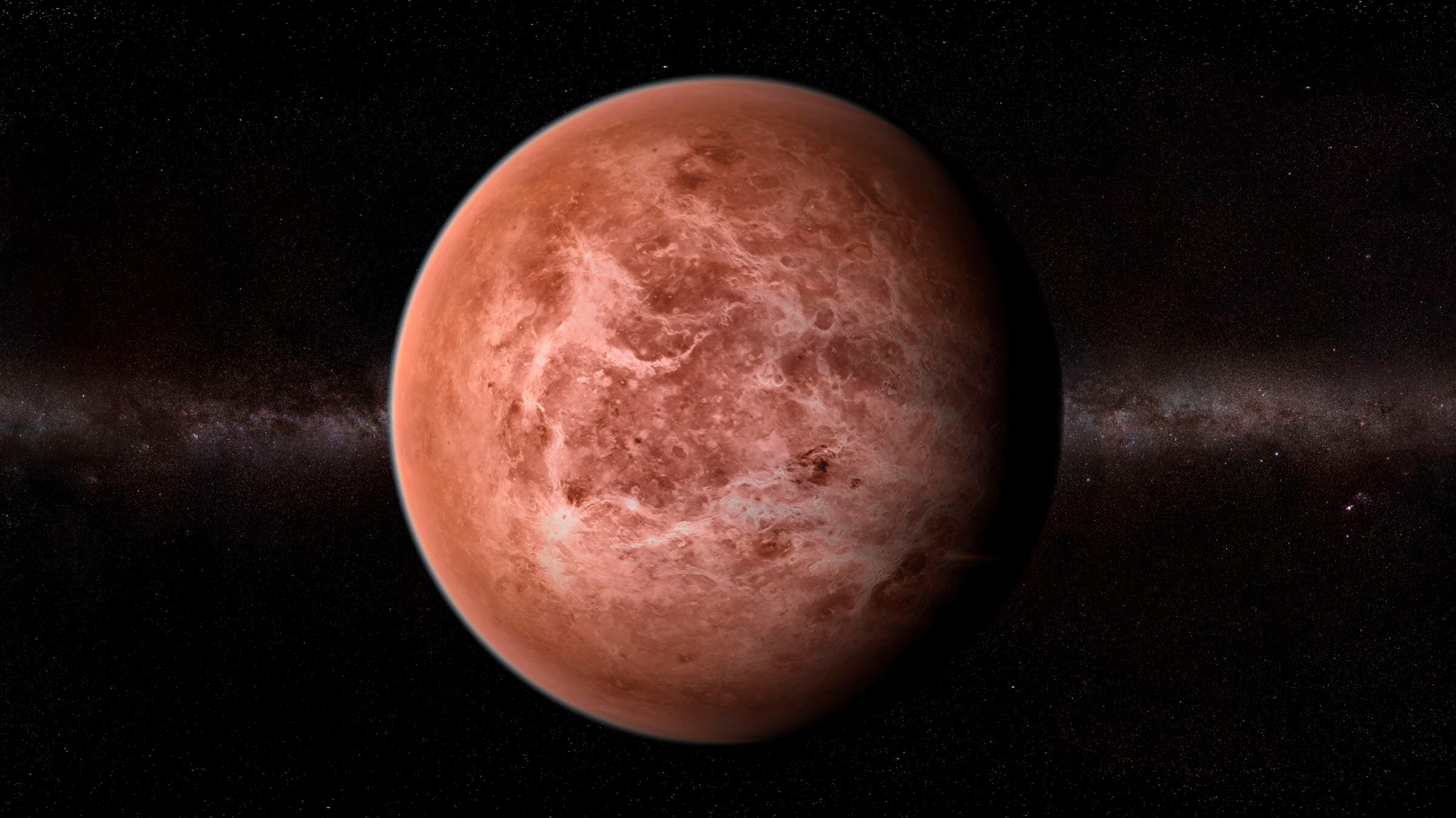
Astronomers looking at the atmosphere in neighboring Venus see something that might just be a sign of life. In a study published Monday, they say they found the chemical signature of a noxious gas called phosphine.
As people seek new ways to cope and treat psychiatric disorders like depression and anxiety, Ketamine is growing in popularity as doctors describe improvements in patients. Cheddar's Chloe Aiello reports.
Figuring out best practices when it comes to preventing airborne transmission is inherently challenging though, especially when it comes to the technical aspects of retrofitting ventilation systems.
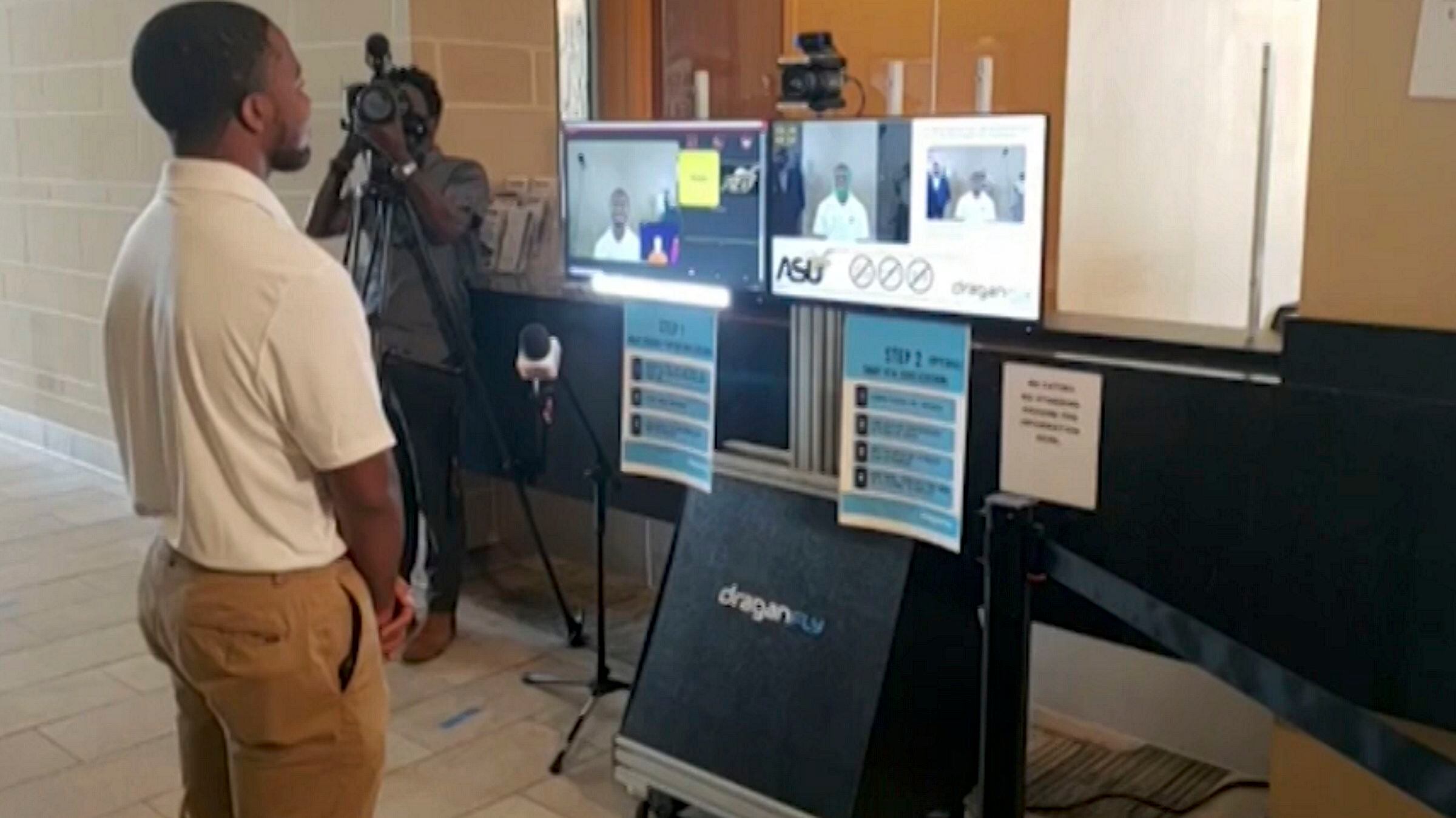
Alabama State University has managed to keep COVID-19 infections at zero despite rising cases on college campuses. University president, Quinton Ross, Jr, joined Cheddar to discuss new technology that scans for coronavirus symptoms.
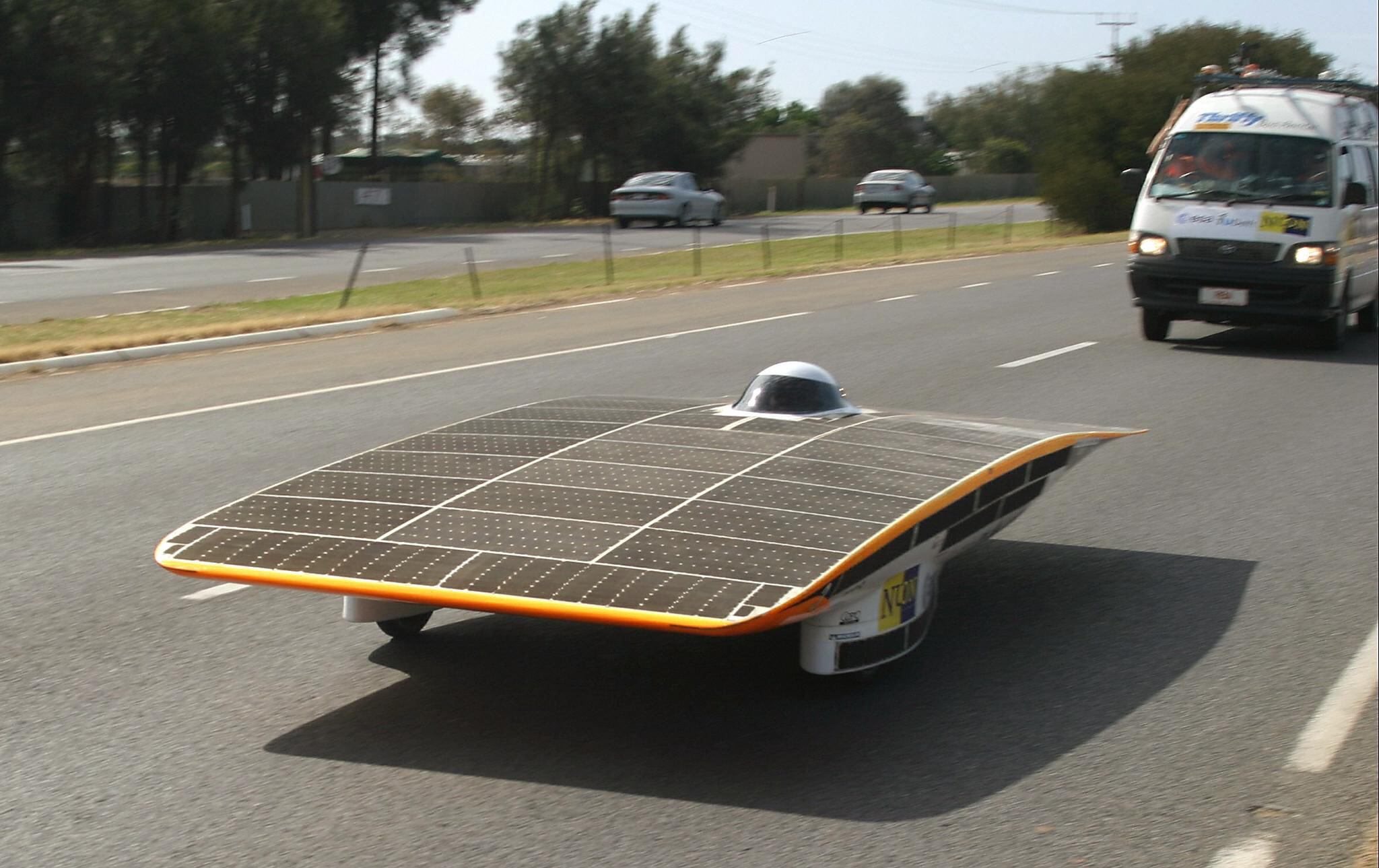
In the 1980's and 90's, the solar car was deemed the future of transportation. Yet, just as quickly as it arrived, the solar car disappeared. But today, as the problems caused by our reliance on fossil fuels have grown, so has a demand for alternative sources of energy for our vehicles. While electric cars are rapidly gaining a larger share of the automotive market, this technology still relies on electricity from a grid often fueled by petroleum or coal. And this is why some companies today are again trying to harness the most powerful energy source we know: the sun.
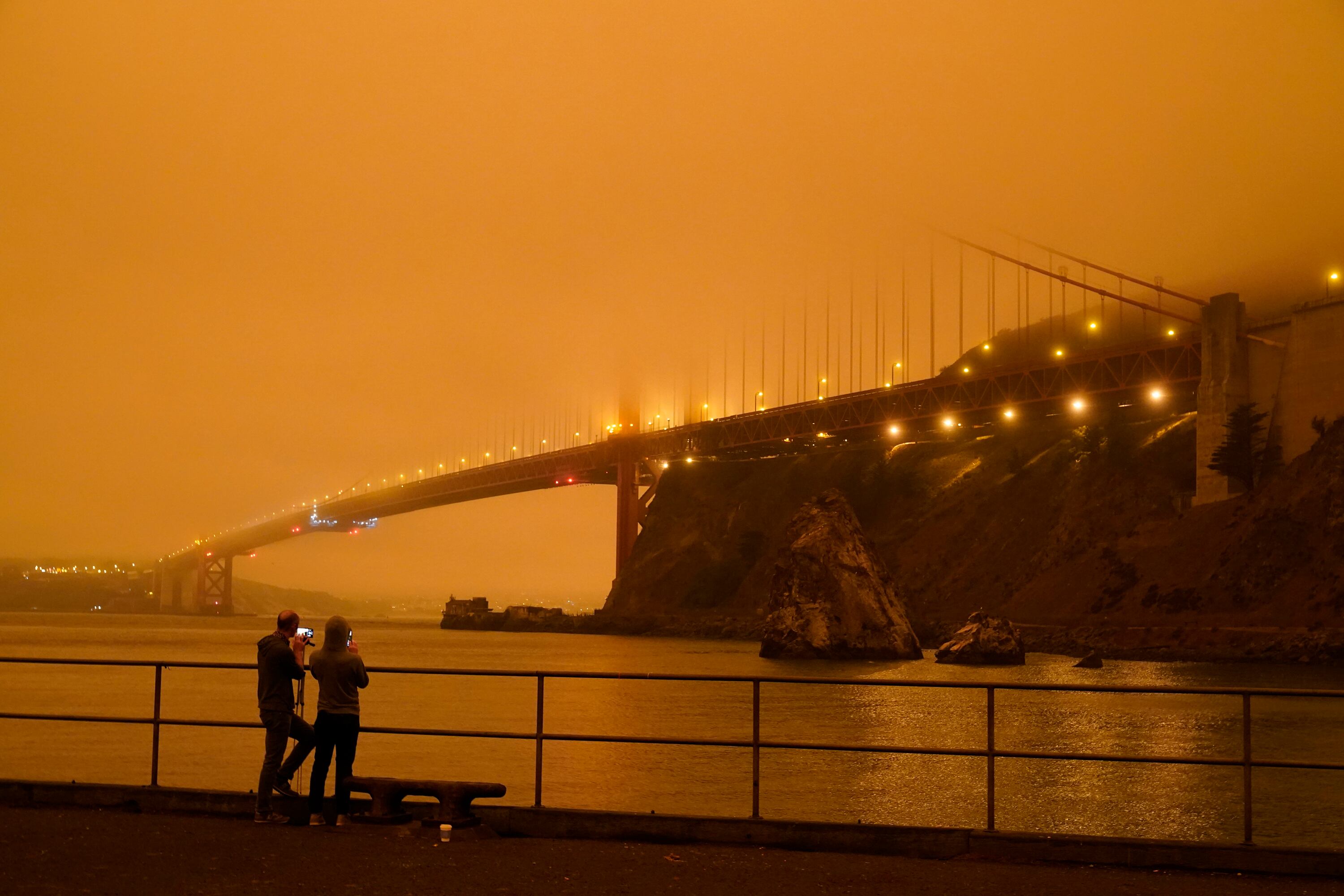
Wildfires are raging unchecked across parts of the western United States as winds sweep the region.
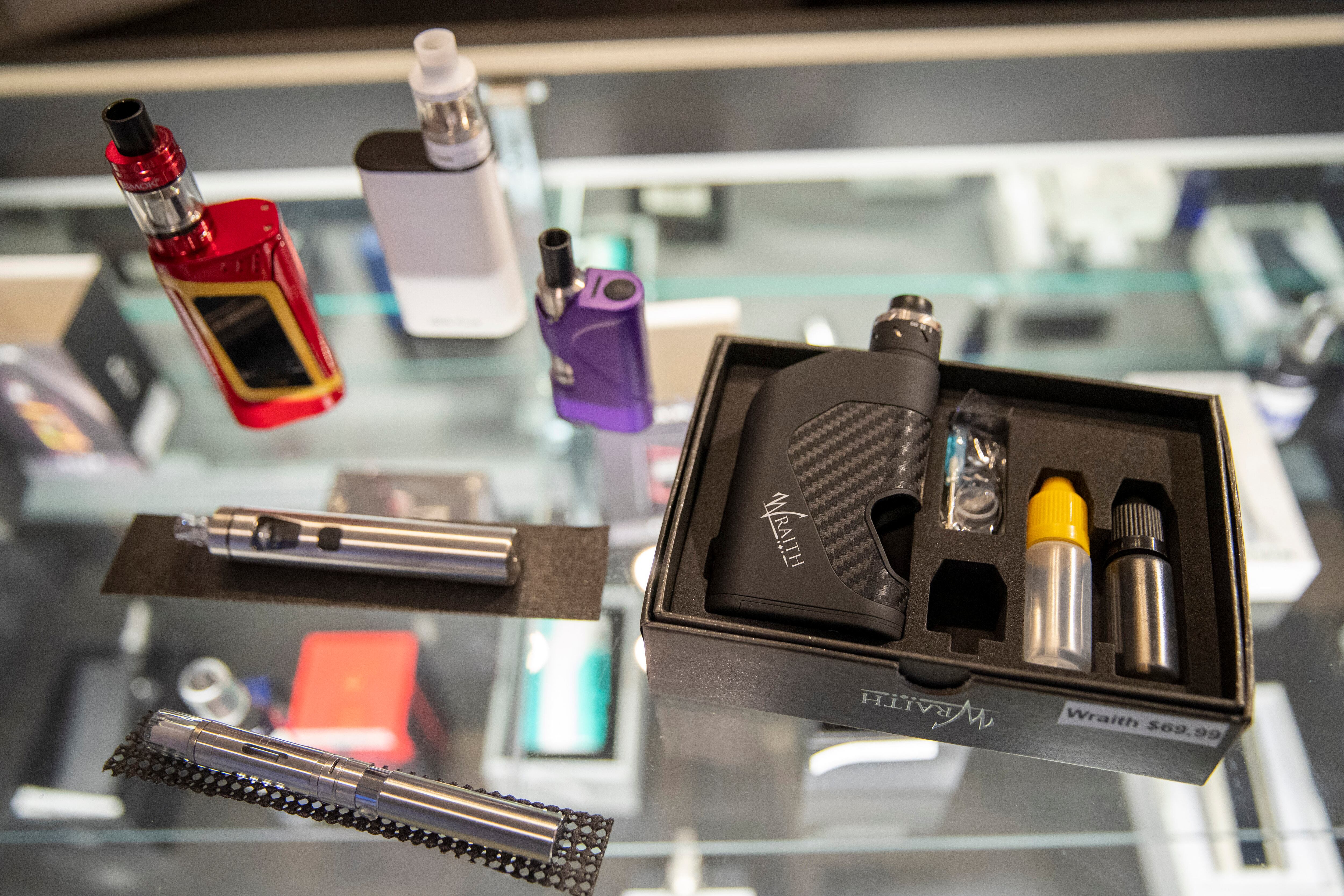
A new federal report shows vaping rates among U.S. teenagers fell dramatically this year.
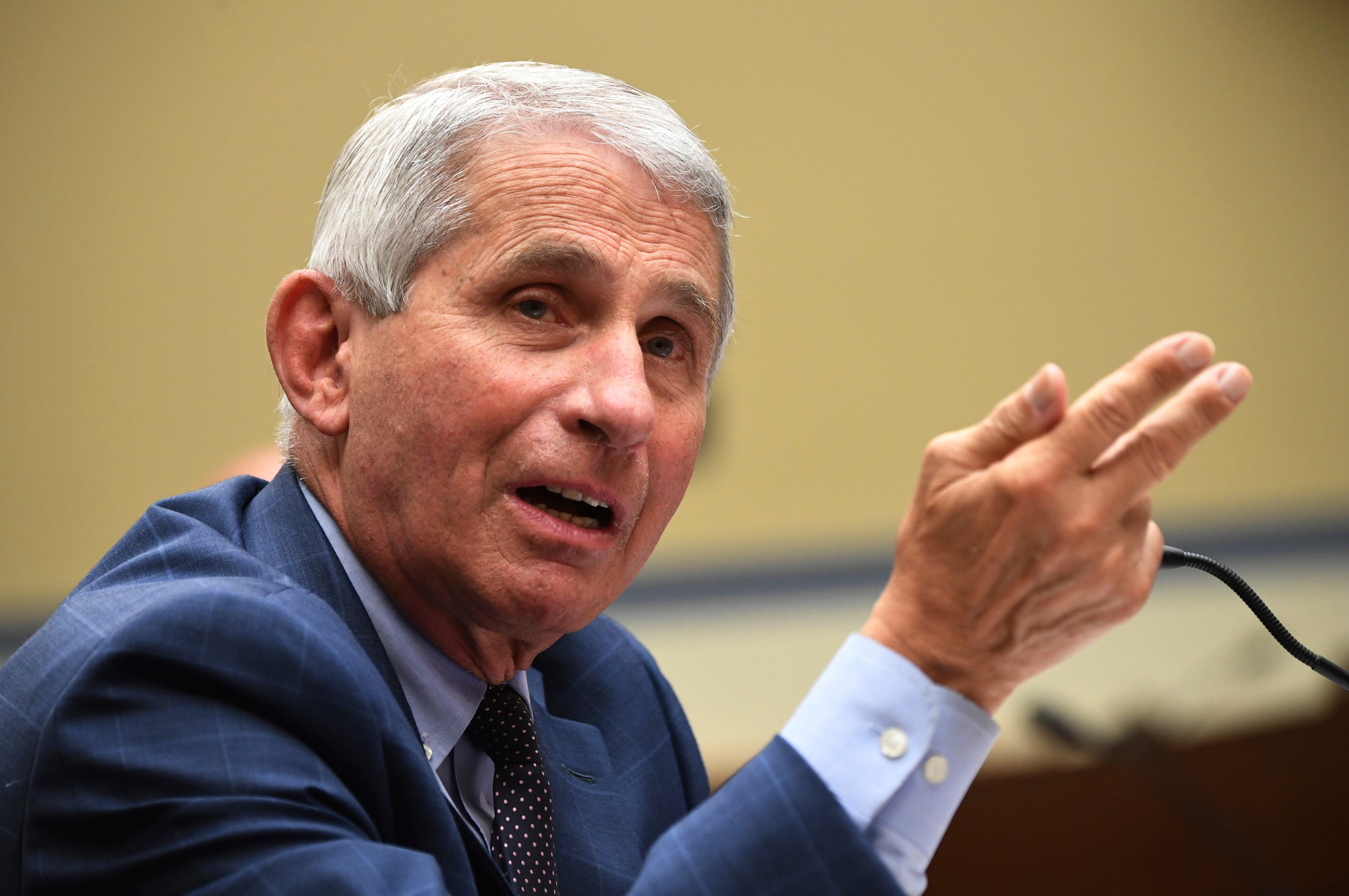
Dr. Anthony Fauci says AstraZeneca's suspension of its COVID-19 vaccine study shows “one of the safety valves” built into the research to spot any potential problems.
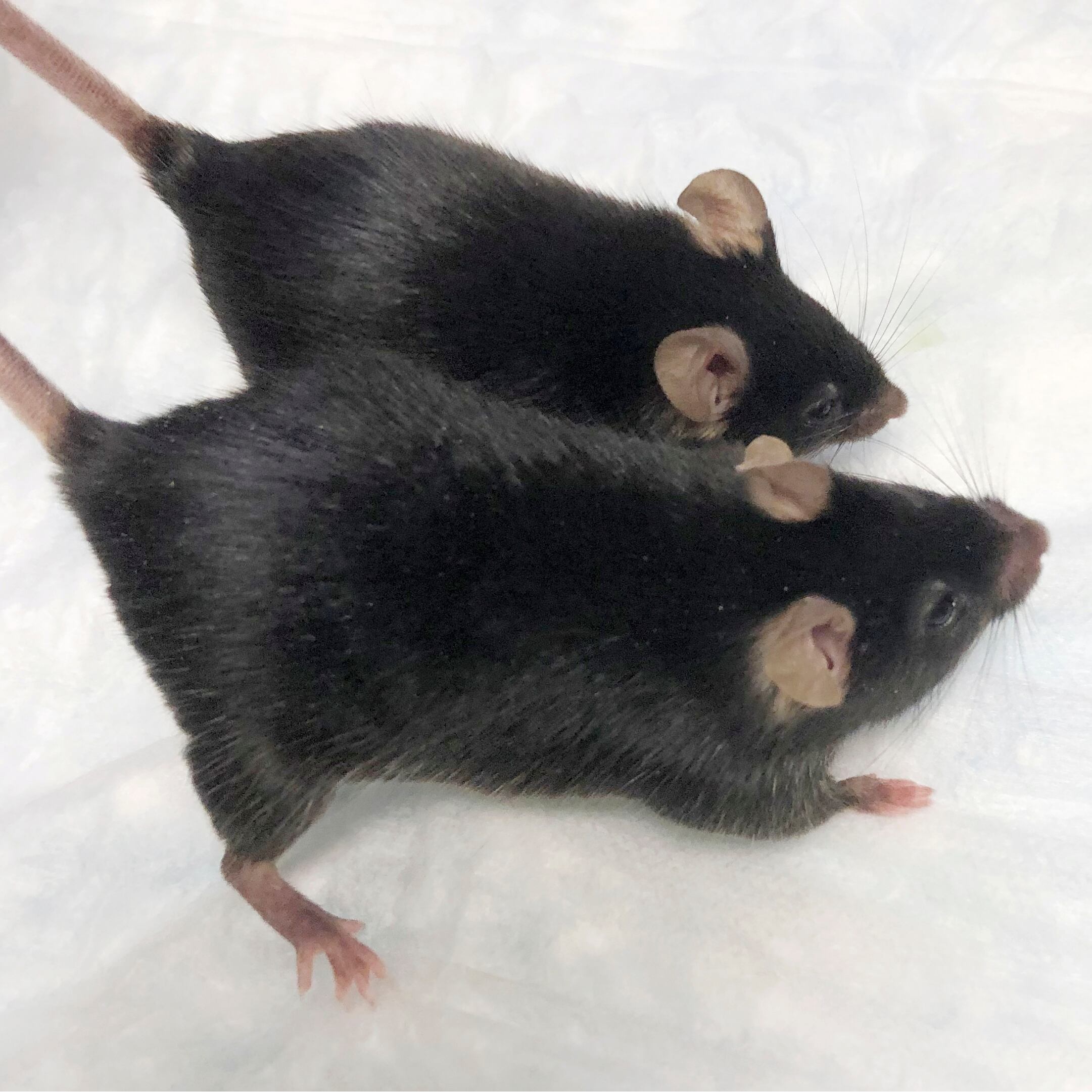
Scientists who sent bulked-up, mutant “mighty mice” to the International Space Station say the animals held onto their muscle during the monthlong flight.