Industrial conglomerate 3M Company is partnering with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to develop a cheaper, quicker COVID-19 test.
Right now, test results can take anywhere from a few hours to a week. Quest Diagnostics, for instance, said the average turnaround time at its labs is currently seven days.
3M's new test would function more like a pregnancy strip, a rapid paper-based test that could be mass-produced and quickly distributed at the point of care.
"In terms of patient experience, what we're looking to do is create that low-cost, highly-accurate, simple-to-use test that would be accessible to a lot of people," Dr. John Banovetz, chief technology officer for 3M, told Cheddar.
The antigen-based test, which looks at proteins on the virus, would offer a "preliminary view" of a patient's coronavirus status — though ideally, patients would follow up with a doctor, he added.
"Our goal would be a point-of-care test, so maybe it's taken in a doctor's office. Maybe you pick it up at the pharmacy," Banovetz said.
The goal is to start producing tests by the end of summer or early fall. Once manufacturing is rolling, 3M could produce millions of tests per day, according to the company.
As cases surge across the country and many anticipate a second wave in states where the infection rate has dropped off, calls for more testing are growing.
More than 41 million tests have been reported to the CDC, with a 9 percent positivity rate, but the U.S. continues to lag behind other countries by some measures.
In the meantime, the Trump administration is relying on the private sector to meet the demand for tests, putting pressure on companies such as 3M to come up with a solution.
"We're going as quick as we can right now," he said. "Our focus is trying to get that accuracy up and in a way that we know that we can mass-produce it. That's really where 3M can help contribute to this, our ability to be able to commercialize and bring to market new ideas and innovations."
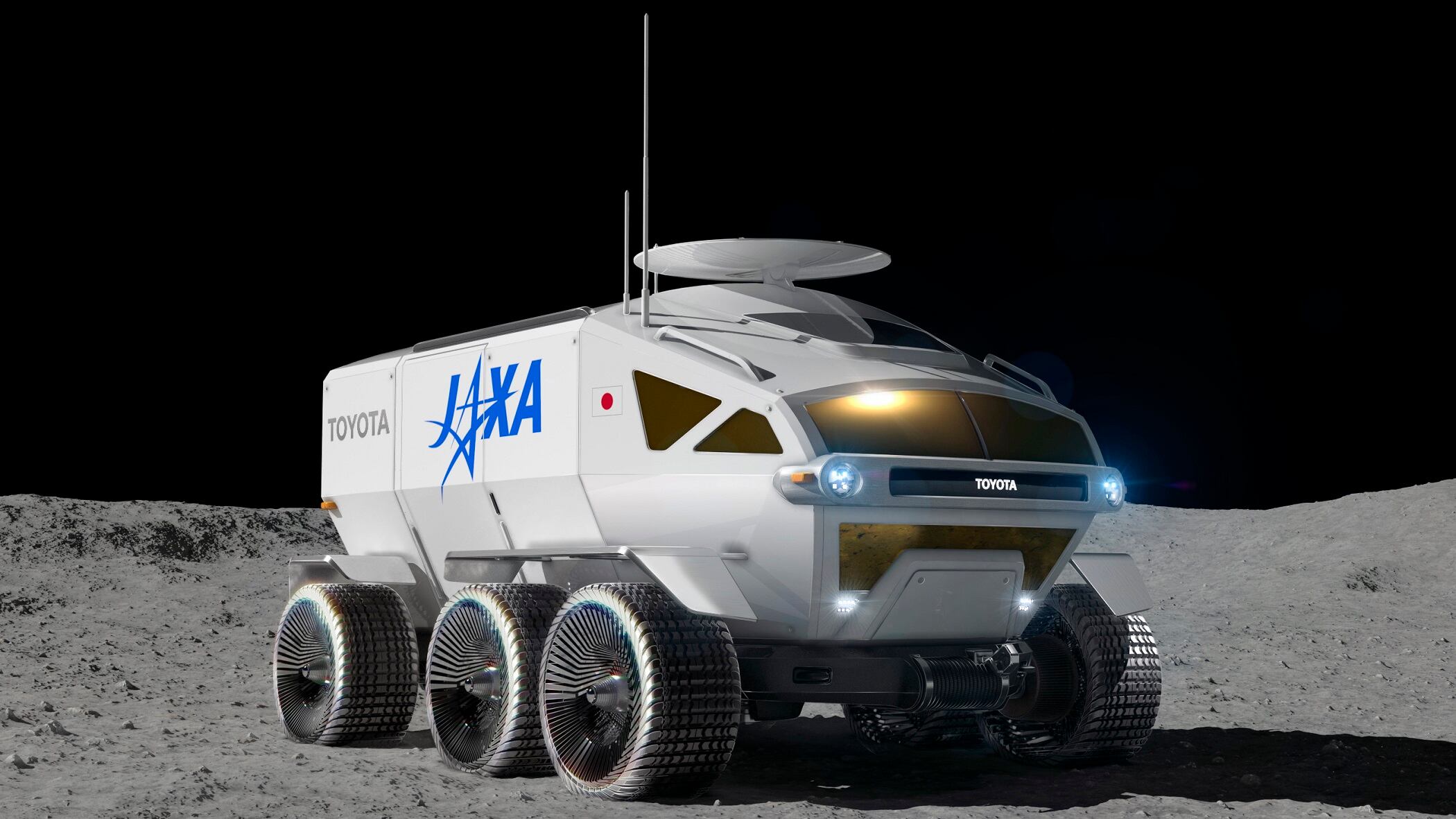
Toyota says it's working with Japan’s space agency on a vehicle to explore the lunar surface, with ambitions to help people live on the moon by 2040 and eventually live on Mars.
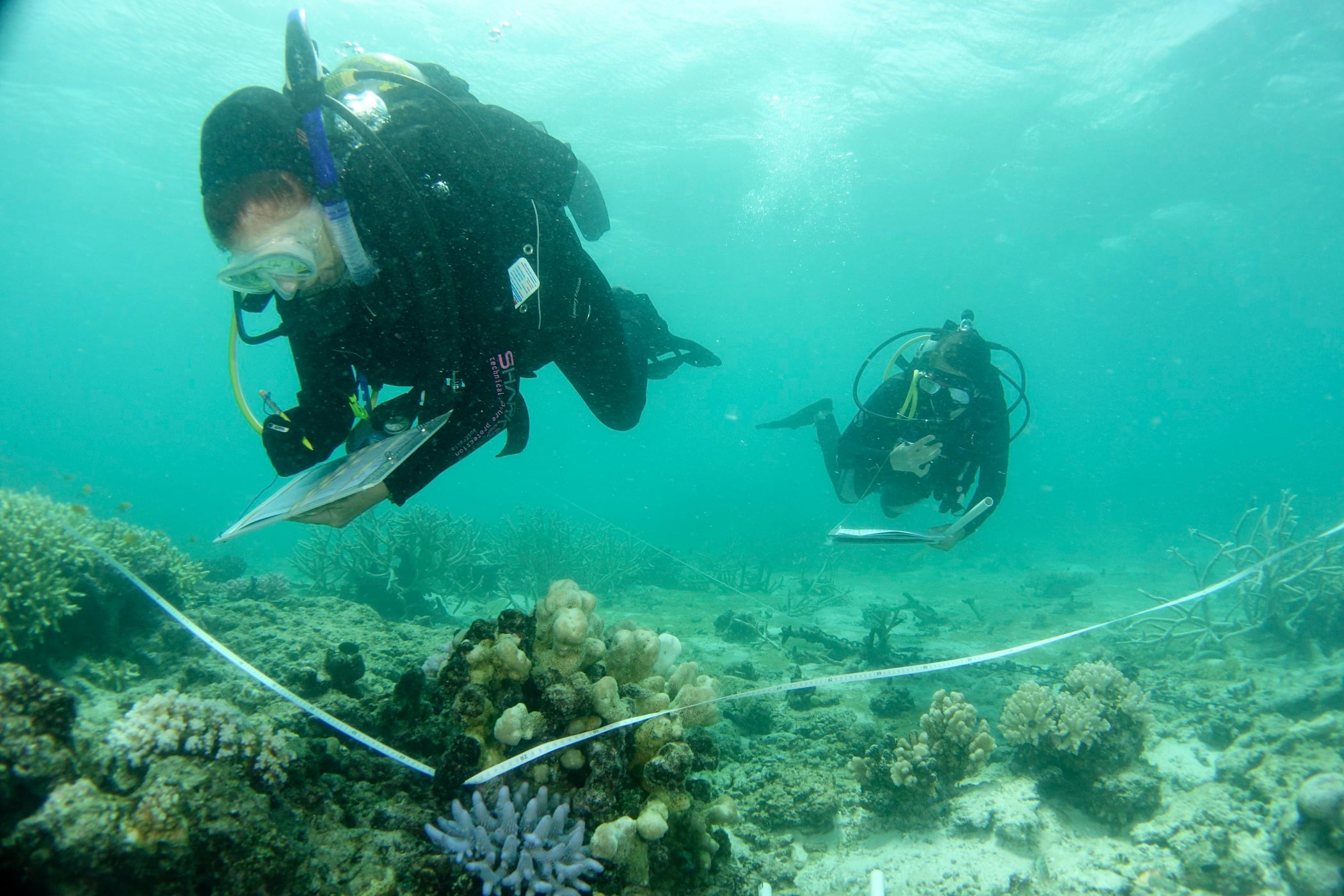
he Australian government has pledged to spend another 1 billion Australian dollars ($704 million) over nine years on improving the health of the Great Barrier Reef after stalling a UNESCO decision on downgrading the natural wonder’s World Heritage status.
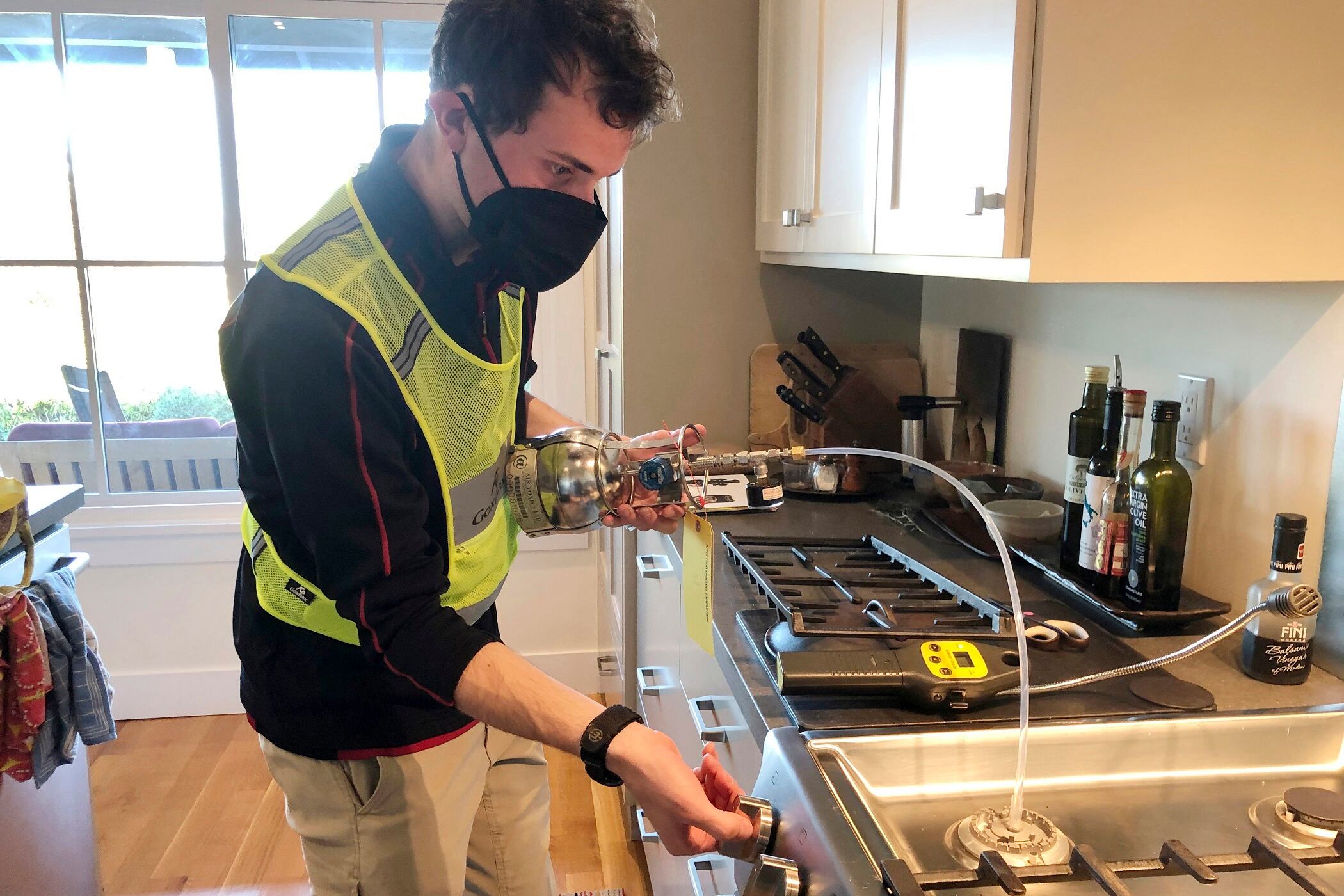
The study by California researchers that was published in Thursday’s journal Environmental Science & Technology found that more than 2.6 million tons of methane leaks into the air from gas stoves in the United States even when they aren't running.
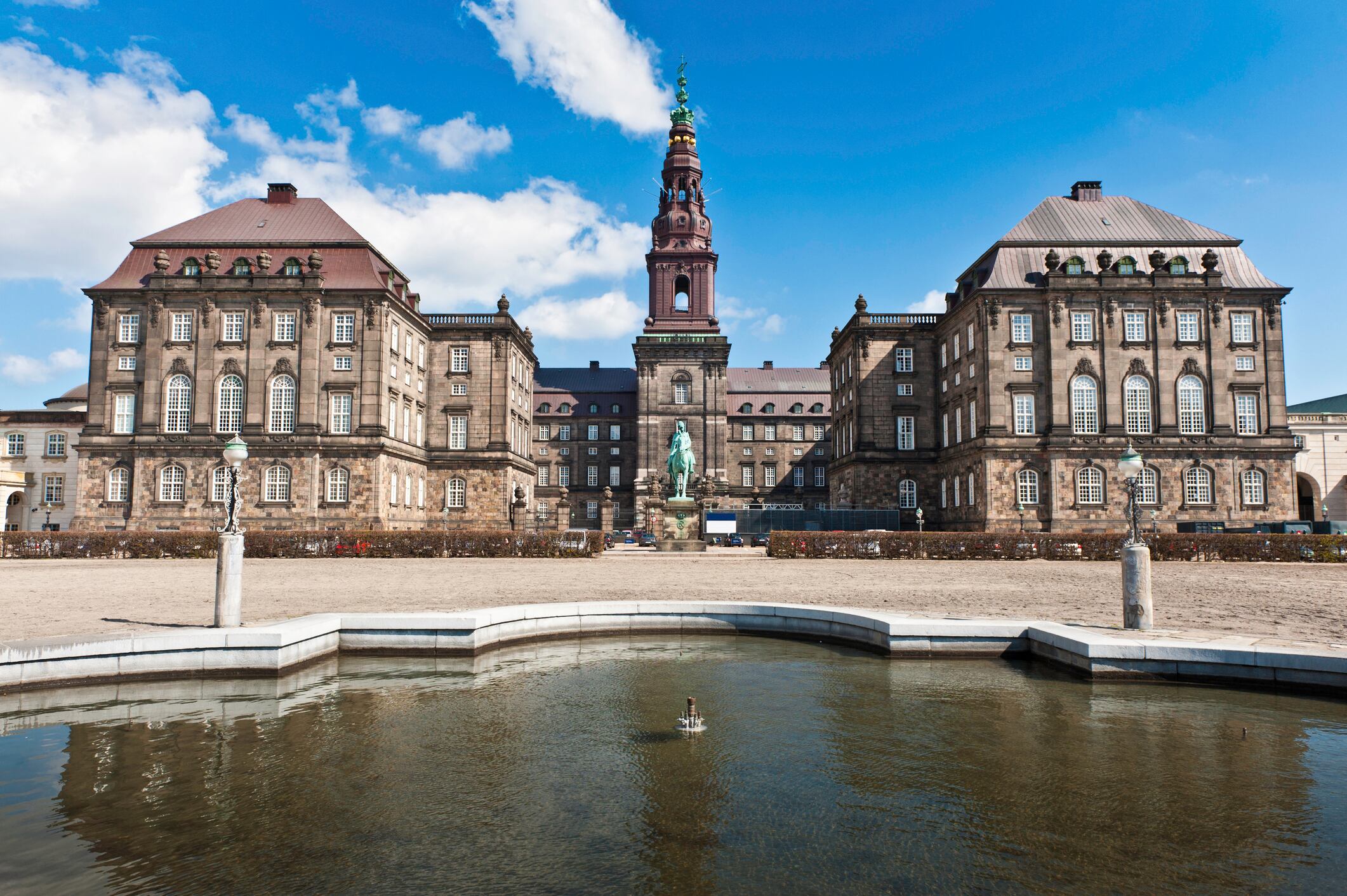
Denmark’s government says it will scrap most pandemic restrictions next week, even as neighboring Sweden has extended its own measures for another fortnight.
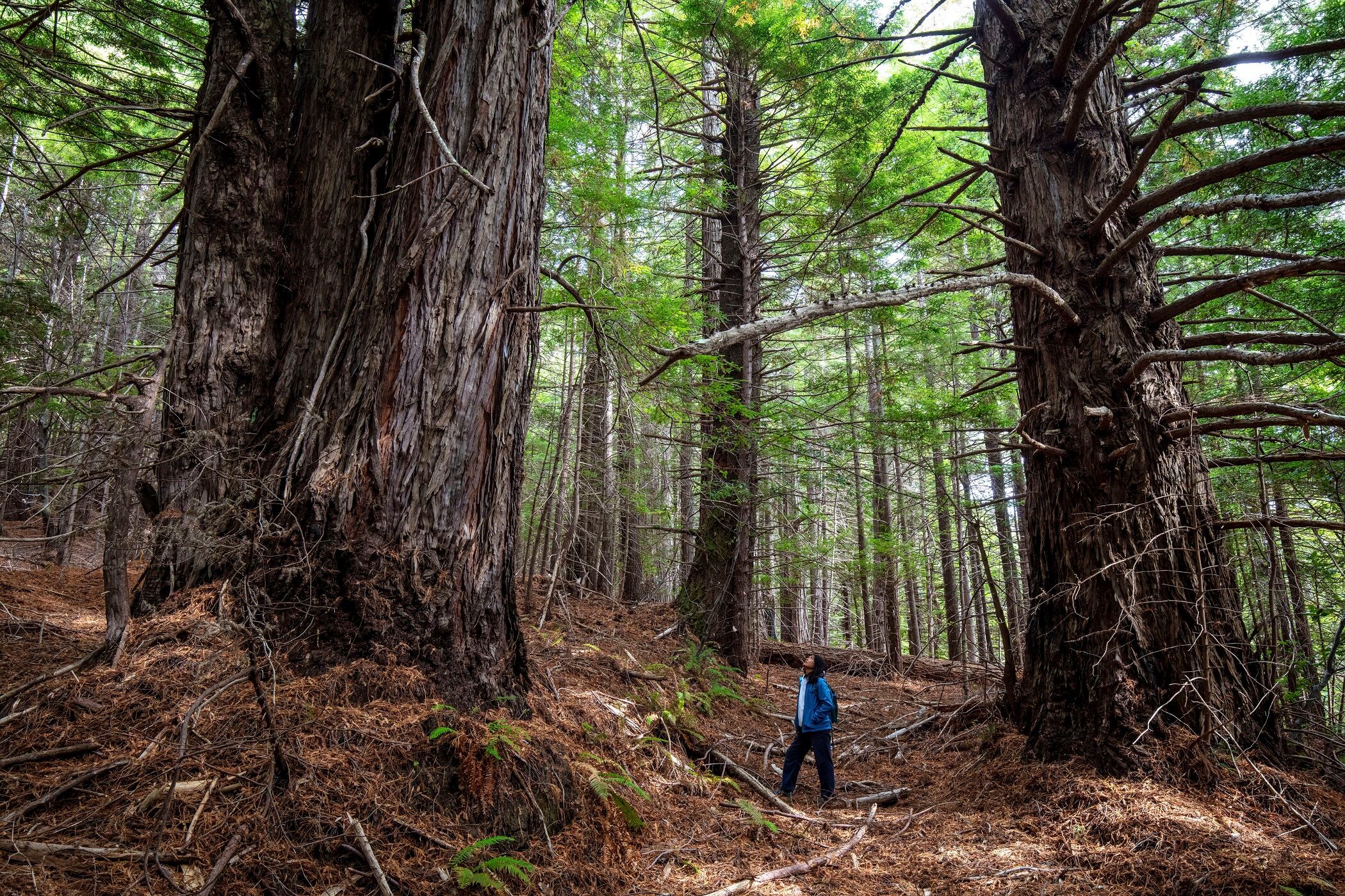
A conservation group is turning over a historic redwood grove on the Northern California coast to descendants of the original Native American inhabitants.
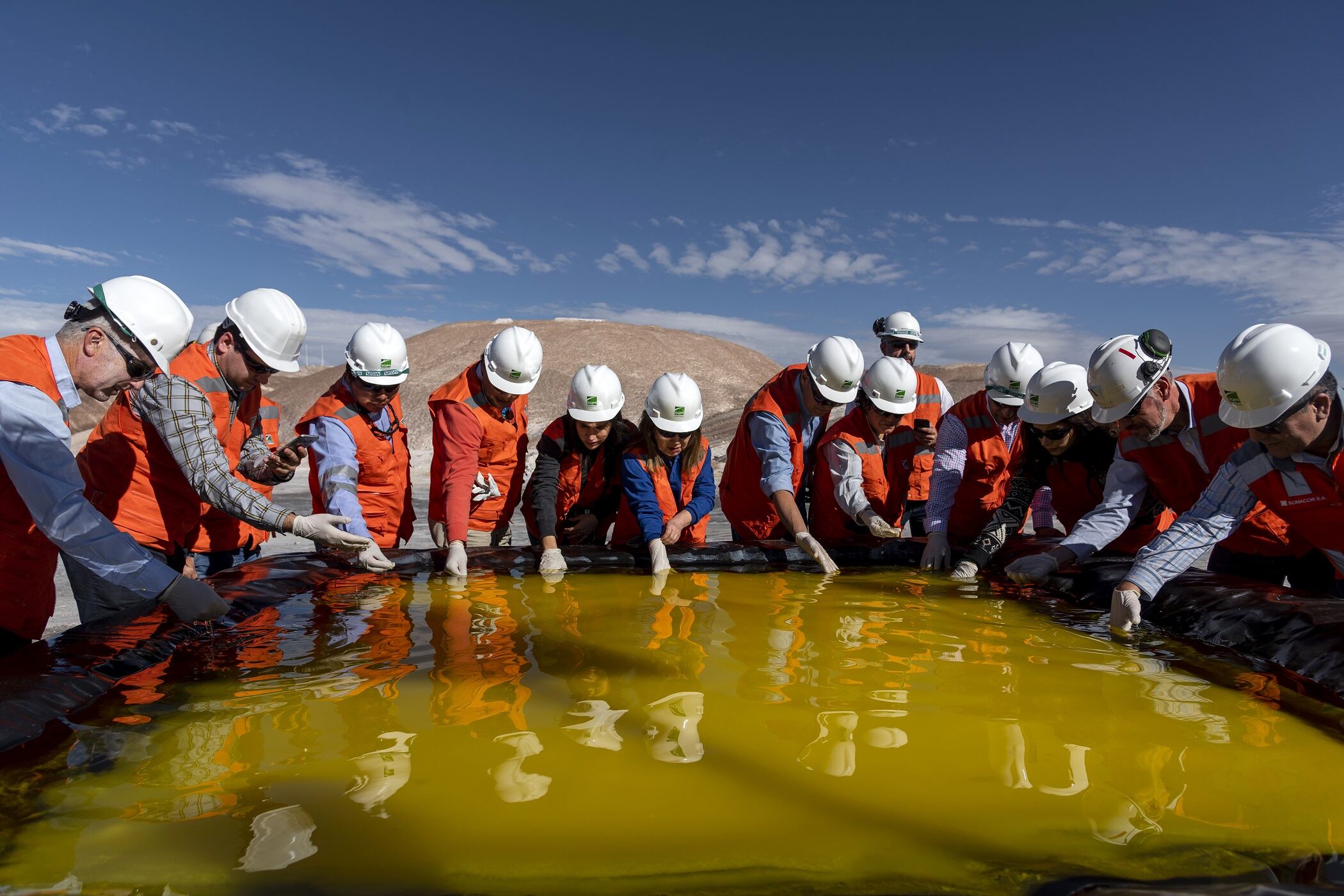
Arguably the biggest challenge to the rise of electric vehicles is their outsized demand for rare earth minerals. Cheddar's Alex Vuocolo does a deep dive into the struggle over securing supply chains for a green tech future.
New research suggests giving extra cash to low-income mothers can change their infants’ brain development.
Pfizer and BioNTech have begun studying a COVID-19 vaccine tweaked to match to the omicron variant in healthy adults.
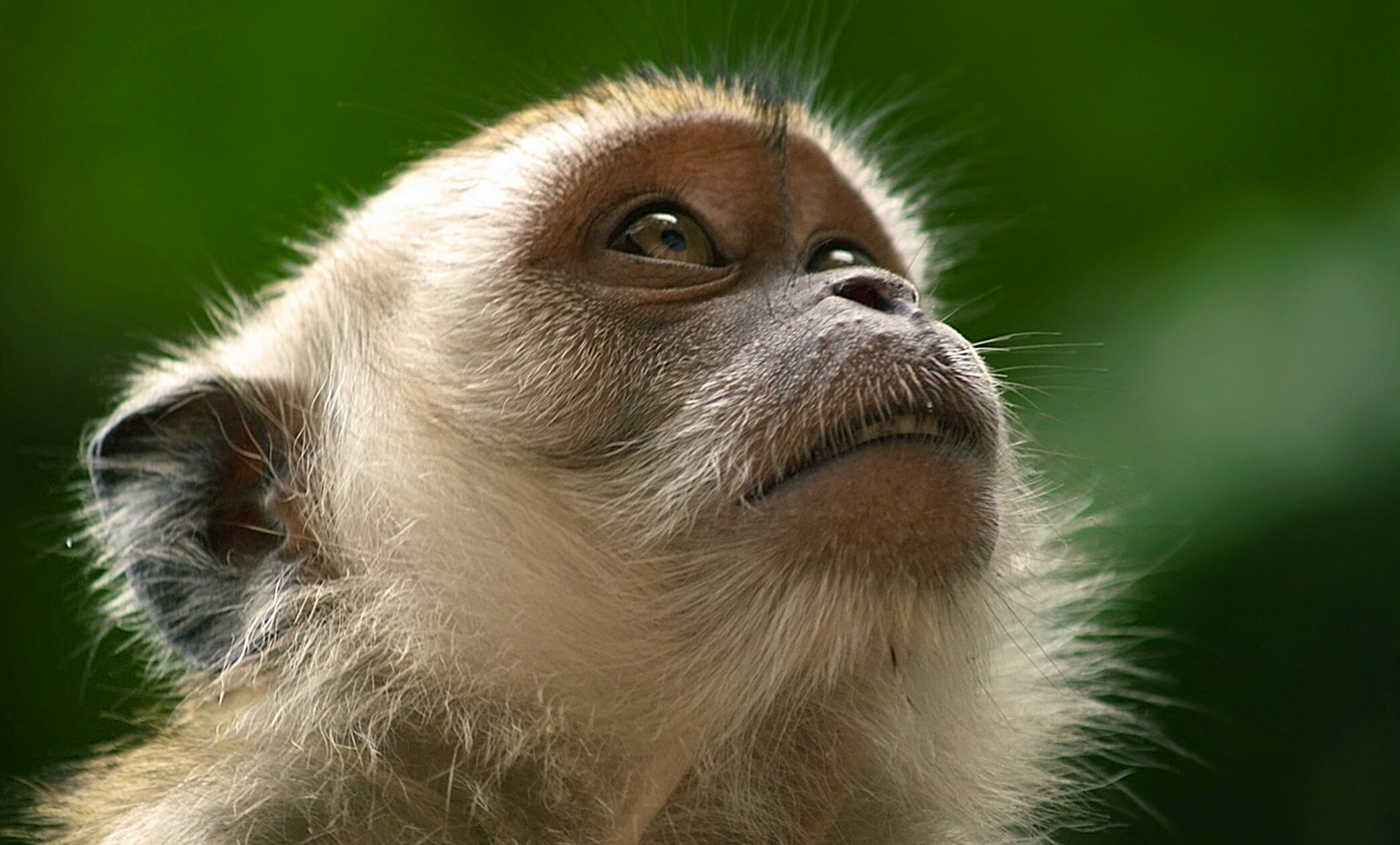
Federal authorities say the last of the escaped monkeys from a Pennsylvania highway crash of a truck towing a trailer load of the animals has been accounted for.
They say life is about the journey, not the destination — and how you get there makes all the difference. Americans shunned train stations, roadways, and airports amid the coronavirus pandemic, never realizing things could be fundamentally different when they return. In this episode, we're exploring the evolving world of transportation, from how we get around to how goods get to us.