By Angie Wang and Jay Reeves
Updated 3:00 pm ET
Forecasters ran out of traditional names for storms Friday, forcing them to begin using the Greek alphabet for only the second time since the 1950s, with more than two months left in the record-shattering hurricane season.
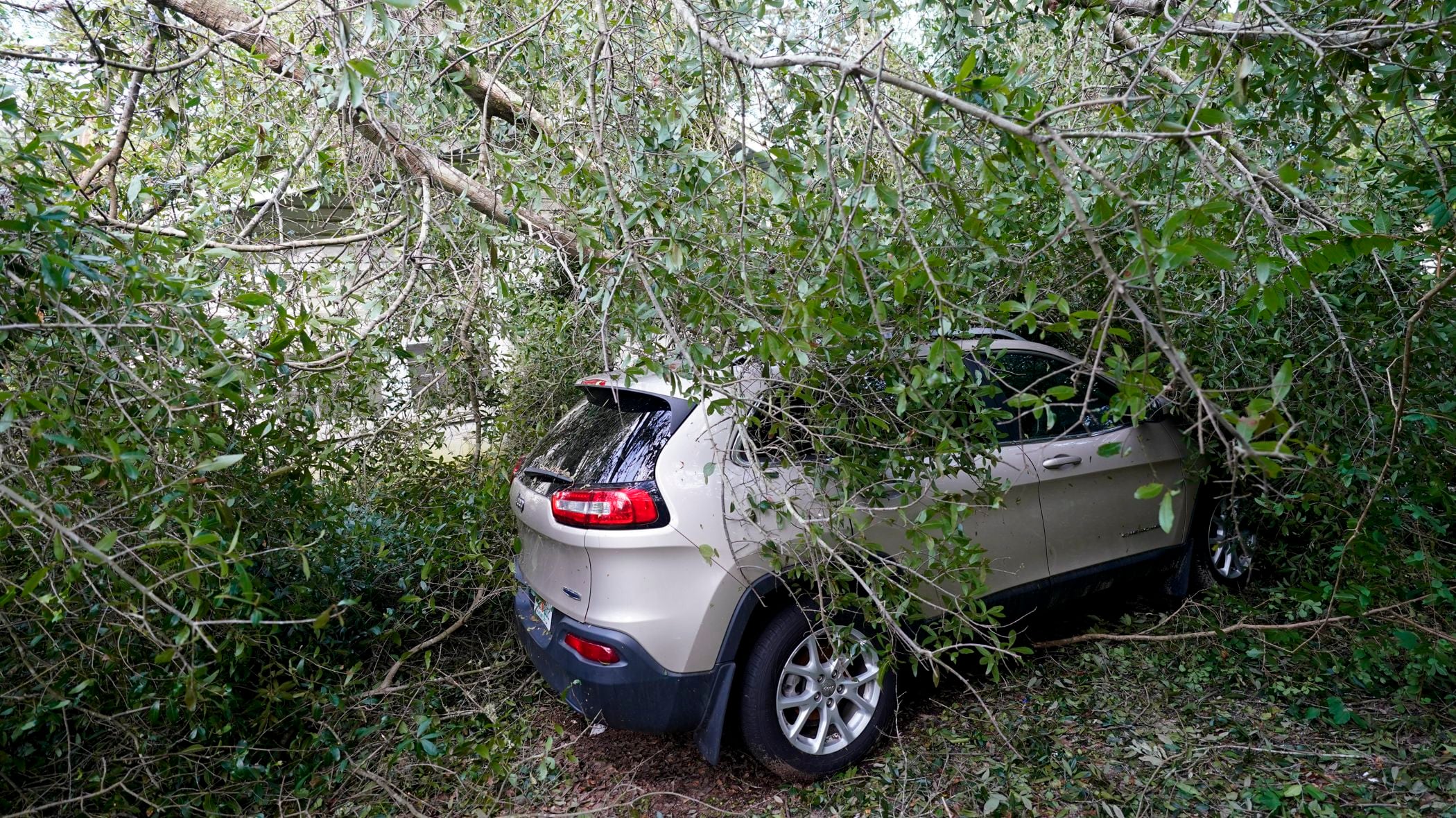
Meanwhile, hundreds of thousands of people were still without power along the Alabama coast and the Florida panhandle in the aftermath of Hurricane Sally. Officials continued to assess millions of dollars in damage that included a broken bridge in Pensacola and ships thrown onto dry land.
In Loxley, Alabama, Catherine Williams lost power and some of her roof to Sally. The storm also destroyed three pecan trees in her yard that she used to try to make ends meet.
“There’s no food, no money. I took my last heart pill today,” said Williams, who has been laid off twice from her job as a cook because of the economic problems caused by COVID-19. She hoped that the Red Cross would soon show up at her home.
Two people in Alabama were reported killed — a drowning and a death during the cleanup in Baldwin County. In Florida, authorities were looking for a missing kayaker who was feared dead in Escambia County.
The supercharged Atlantic hurricane season has produced so many named storms that scientists ran out of traditional names as Tropical Storm Wilfred developed in the eastern Atlantic. It was only the second time that has happened since forecasters standardized the naming system in 1953. Wilfred was weak and far from land.
Two hours after Wilfred took shape, the National Hurricane Center moved to the Greek alphabet when Subtropical Storm Alpha formed just off the coast of Portugal. Next up is Beta and so on. Forecasters are watching at least two other systems, including one that is a tropical depression in the western Gulf of Mexico.
The only time the hurricane center dipped into the Greek alphabet was the deadly 2005 hurricane season, which included Hurricane Katrina's strike on New Orleans. The prior record for the earliest 21st named storm was Wilma on Oct. 8, 2005, according to Colorado State University hurricane researcher Phil Klotzbach.
The onslaught of hurricanes has focused attention on climate change, which scientists say is causing wetter, stronger, and more destructive storms.
In Pensacola, Mamie Patterson was cleaning the yard of her cousin who was recovering from heart surgery after they lost power in a low-income neighborhood in Pensacola.
Patterson’s mother uses an oxygen machine that they took to an uncle’s home to charge because he had power. She saw utility trucks all over the city and wondered when power would be restored in her neighborhood, where several inches of water was standing in streets more than 48 hours after the storm.
“We feel a lot forgotten back here,” she said. “I hate to say it, but it’s the ghetto neighborhoods. We don’t have lights.”
Elsewhere in the city, Karen Robinson sat on the steps of her first-floor apartment and rattled off a list of belongings ruined by 4 feet (120 centimeters) of water from Sally — clothes, shoes, furniture, and food.
It took months to recover from a 2015 flood after a heavy rainstorm sent nearly the same amount of water from a creek into the 200-unit complex. She was concerned because hurricane season runs until the end of November.
“This could happen again. That’s the problem,” Robinson said as men tossed soggy items out of an apartment window nearby.
In Louisiana, about 41,000 people remain without power around Lake Charles, where Hurricane Laura made landfall on Aug. 27. On Oak Island, North Carolina, which was ground zero for Hurricane Isaias on Aug. 3, some rental homes finally reopened by Labor Day.
“It wasn’t pretty. We had piles of sand everywhere, piles of debris everywhere, but the roads were open,” Mayor Ken Thomas said.
With the dunes that provide some protection to the island gone, Thomas said people will be nervous for the rest of the storm season.
“There’s a hurricane for everyone out there,” he said.
Escambia County, which includes Pensacola, estimated that Sally caused at least $21 million in damage to public infrastructure such as roads and drainage. It will likely cost an additional $8 million to restore the sand washed away at Pensacola Beach, officials said.
The year-old Three Mile Bridge that connects Pensacola to the beaches was heavily damaged in at least two places, and authorities do not know how much money or time it will take to fix.
Back in the Atlantic, Hurricane Teddy was a powerful Category 4 storm about 850 miles (1,370 kilometers) southeast of Bermuda. The island was hit directly by Hurricane Paulette on Monday, and forecasters said a hurricane watch for Teddy may be issued soon.
___
Associated Press writers Bobby Caina Calvan in Tallahassee, Florida; Jeff Martin in Marietta, Georgia; and Jeffrey Collins in Columbia, South Carolina, also contributed to this report.