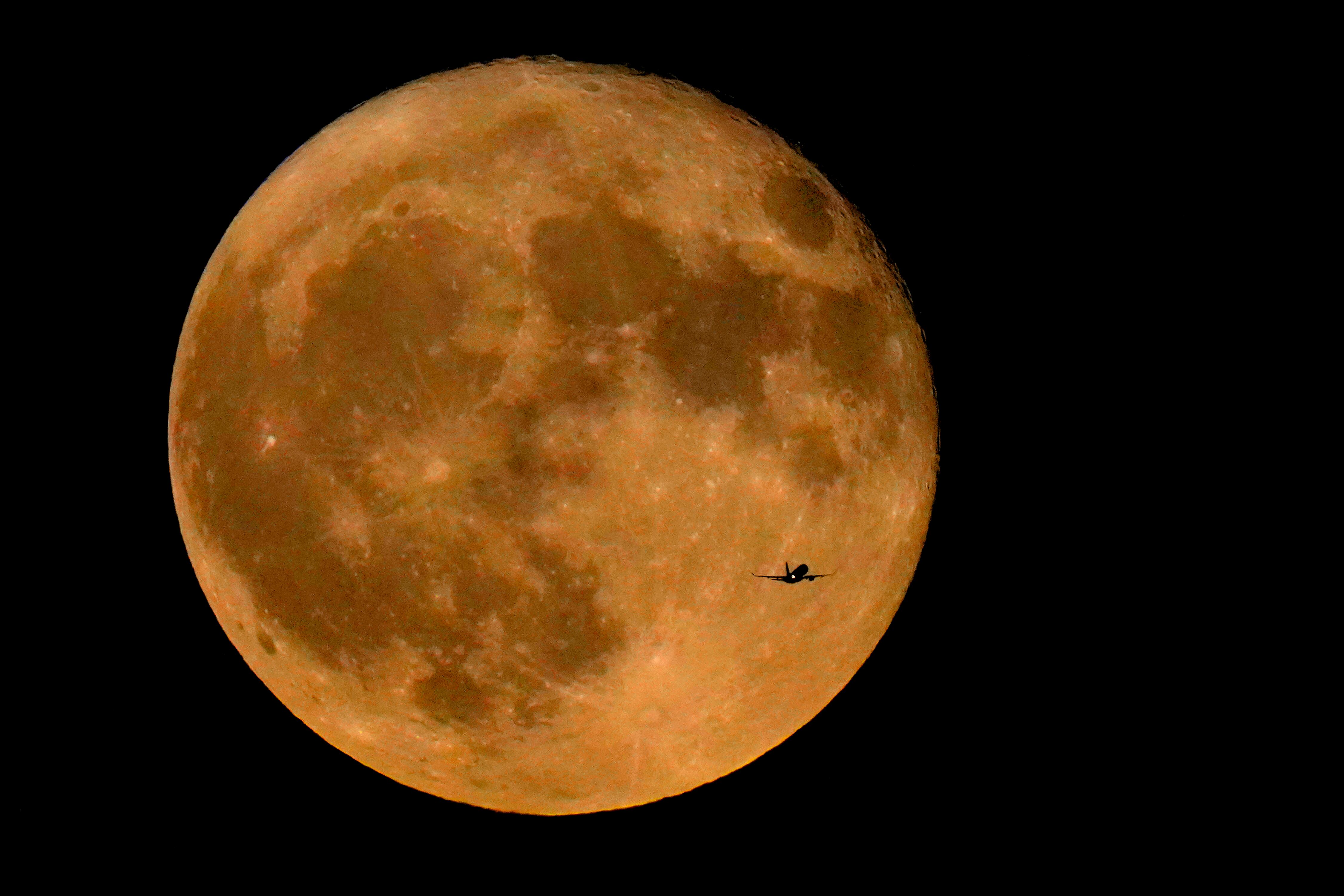
The cosmos is offering up a double feature in August: a pair of supermoons culminating in a rare blue moon.
Catch the first show Tuesday evening as the full moon rises in the southeast, appearing slightly brighter and bigger than normal. That’s because it will be closer than usual, just 222,159 miles (357,530 kilometers) away, thus the supermoon label.
The moon will be even closer the night of Aug. 30 — a scant 222,043 miles (357,344 kilometers) distant. Because it’s the second full moon in the same month, it will be what's called a blue moon.
“Warm summer nights are the ideal time to watch the full moon rise in the eastern sky within minutes of sunset. And it happens twice in August,” said retired NASA astrophysicist Fred Espenak, dubbed Mr. Eclipse for his eclipse-chasing expertise.
The last time two full supermoons graced the sky in the same month was in 2018. It won’t happen again until 2037, according to Italian astronomer Gianluca Masi, founder of the Virtual Telescope Project.
Masi will provide a live webcast of Tuesday evening’s supermoon, as it rises over the Coliseum in Rome.
“My plans are to capture the beauty of this ... hopefully bringing the emotion of the show to our viewers,” Masi said in an email.
“The supermoon offers us a great opportunity to look up and discover the sky,” he added.
This year’s first supermoon was in July. The fourth and last will be in September. The two in August will be closer than either of those.
Provided clear skies, binoculars or backyard telescopes can enhance the experience, Espenak said, revealing such features as lunar maria — the dark plains formed by ancient volcanic lava flows — and rays emanating from lunar craters.
According to the Old Farmer’s Almanac, the August full moon is traditionally known as the sturgeon moon. That’s because of the abundance of that fish in the Great Lakes in August, hundreds of years ago.
Cheddar's Need2Know Podcast for Tues., June 16, 2020.
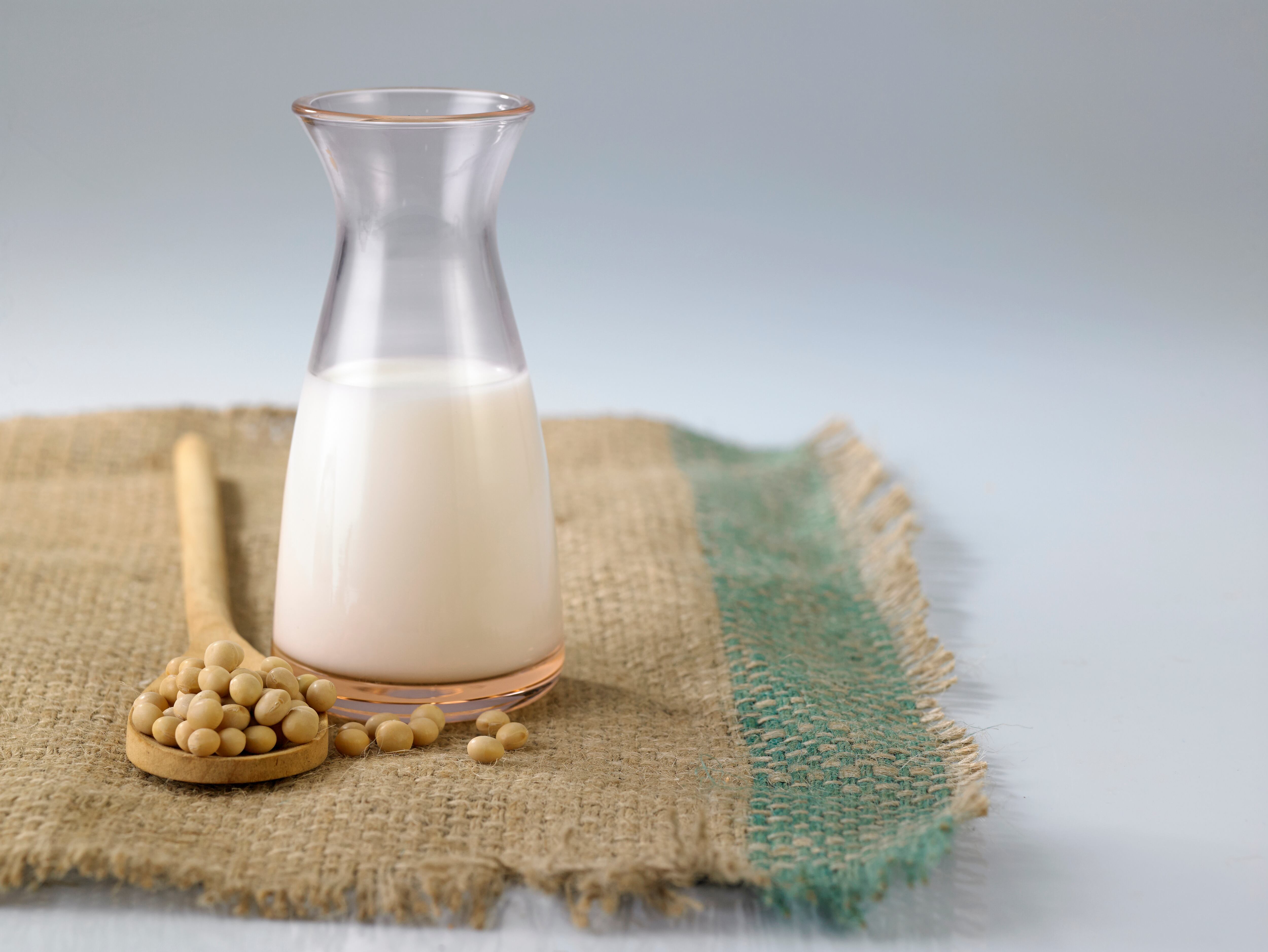
From milk to canned tuna to shampoo, soy is in a good majority of our day-to-day products. It’s added to around 60% of the nation’s processed foods. Soy has been known to provide some real health benefits, like high protein. But there are legitimate health and environmental consequences that raise the question: why do we use so much soy? And should we?
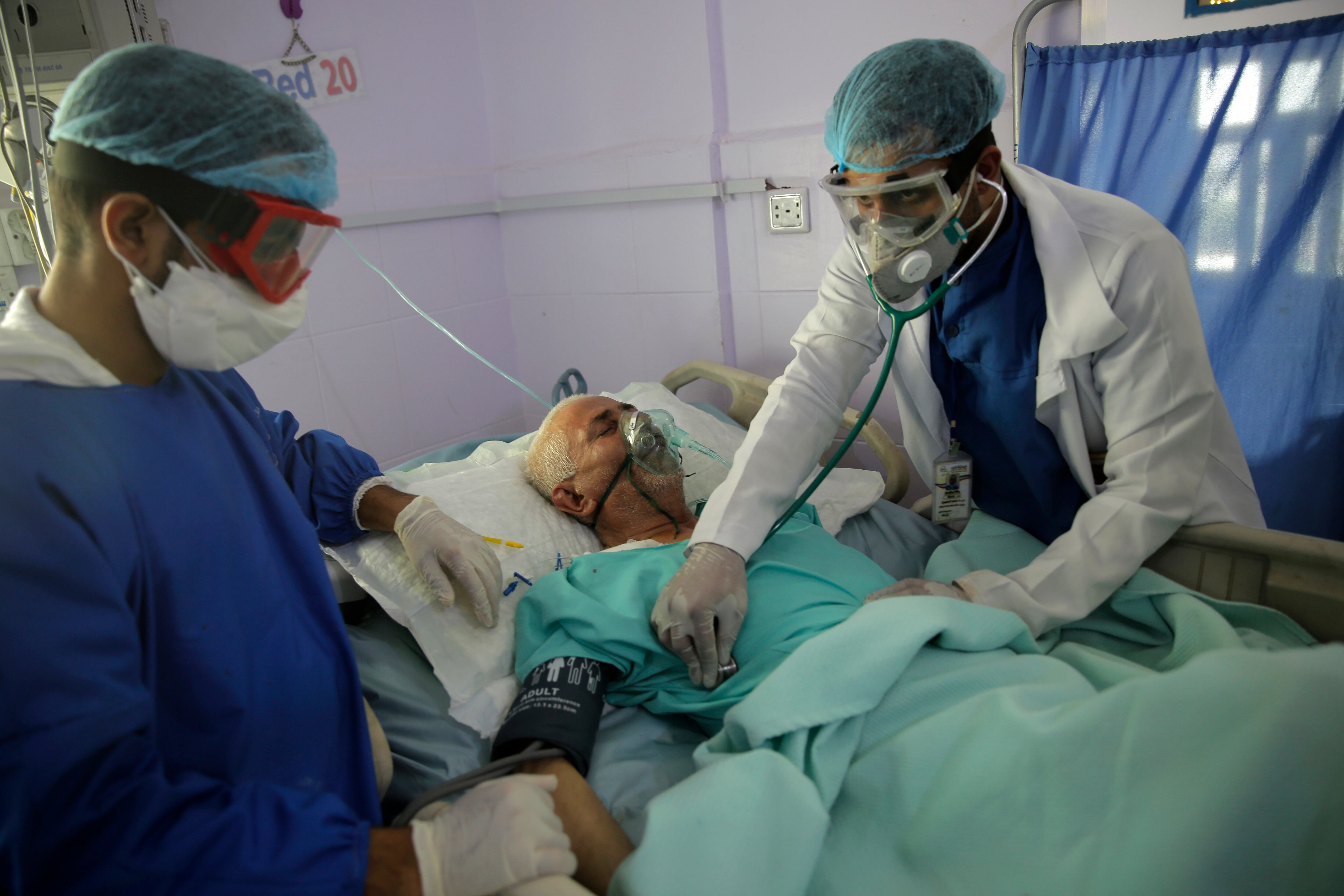
Researchers in England say they have the first evidence that a drug can improve survival from COVID-19. The drug is a cheap, widely available steroid called dexamethasone.
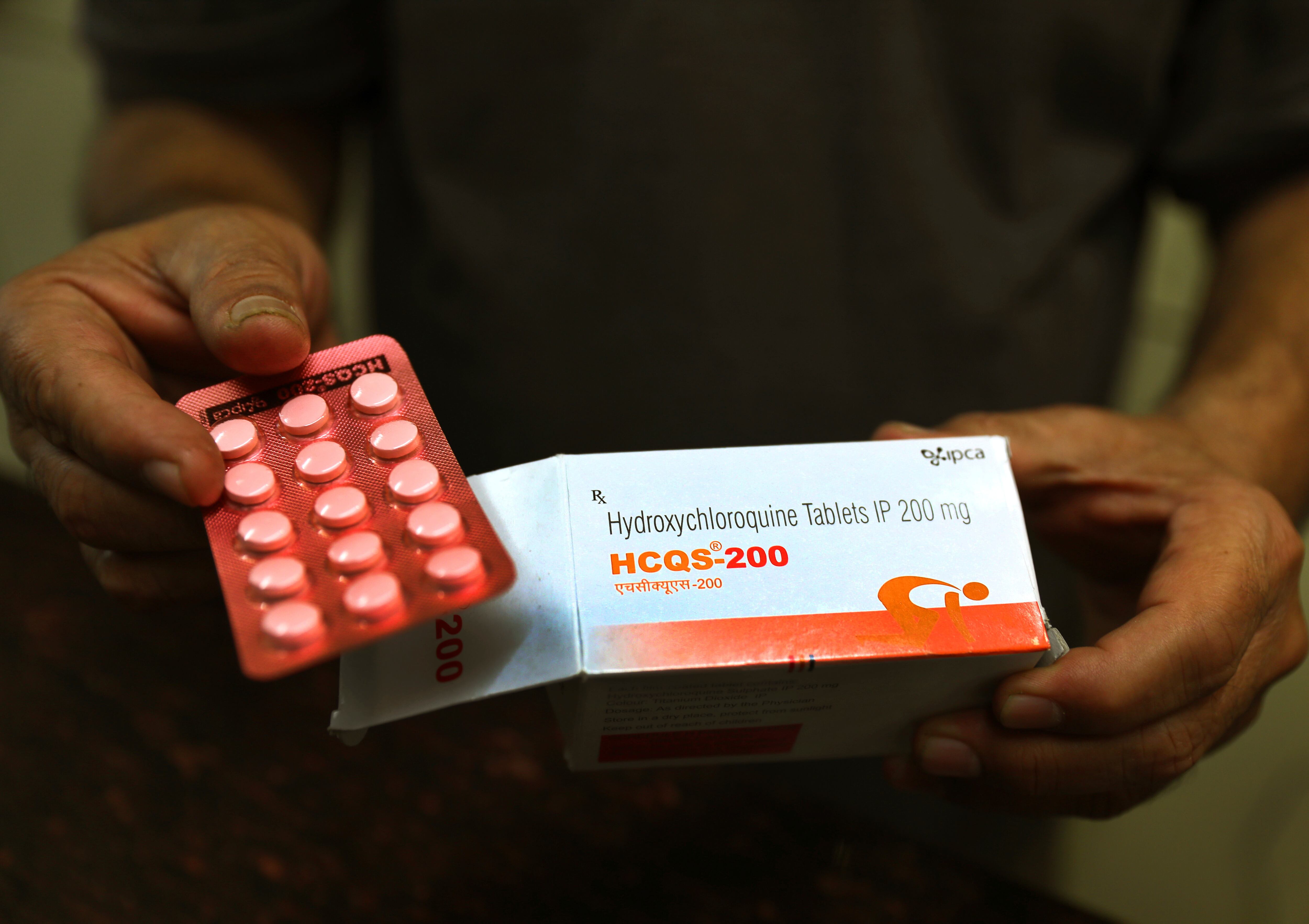
The Food and Drug Administration said Monday that the drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are unlikely to be effective in treating the coronavirus.
As the number of coronavirus cases continues to rise in the U.S., Johnson & Johnson's chief scientific officer Dr. Paul Stoffels told Cheddar the company has an accelerated plan to create a vaccine.
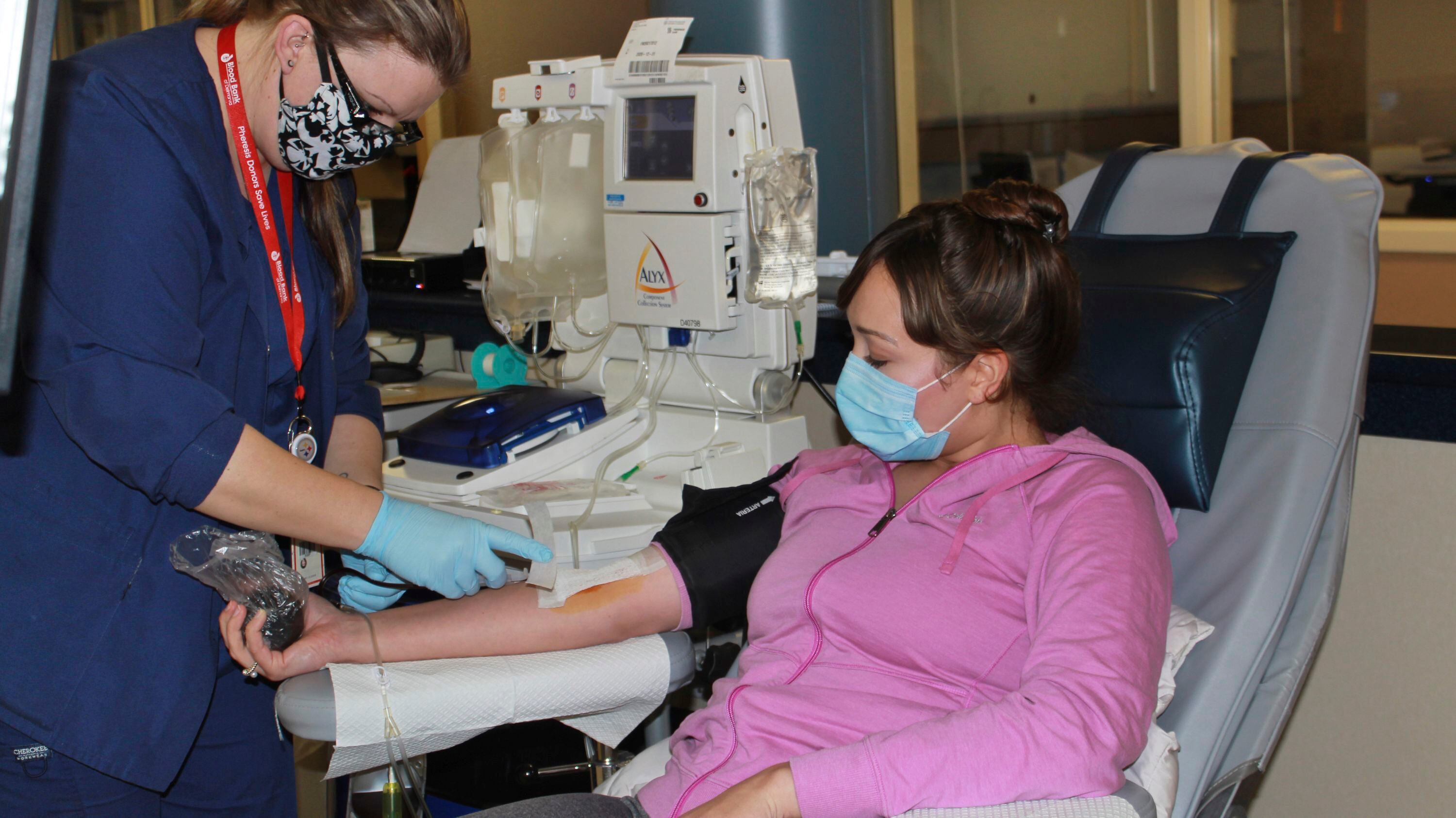
Scientists are beginning a new study to tell if the blood plasma of COVID-19 survivors might help prevent infection in the first place.
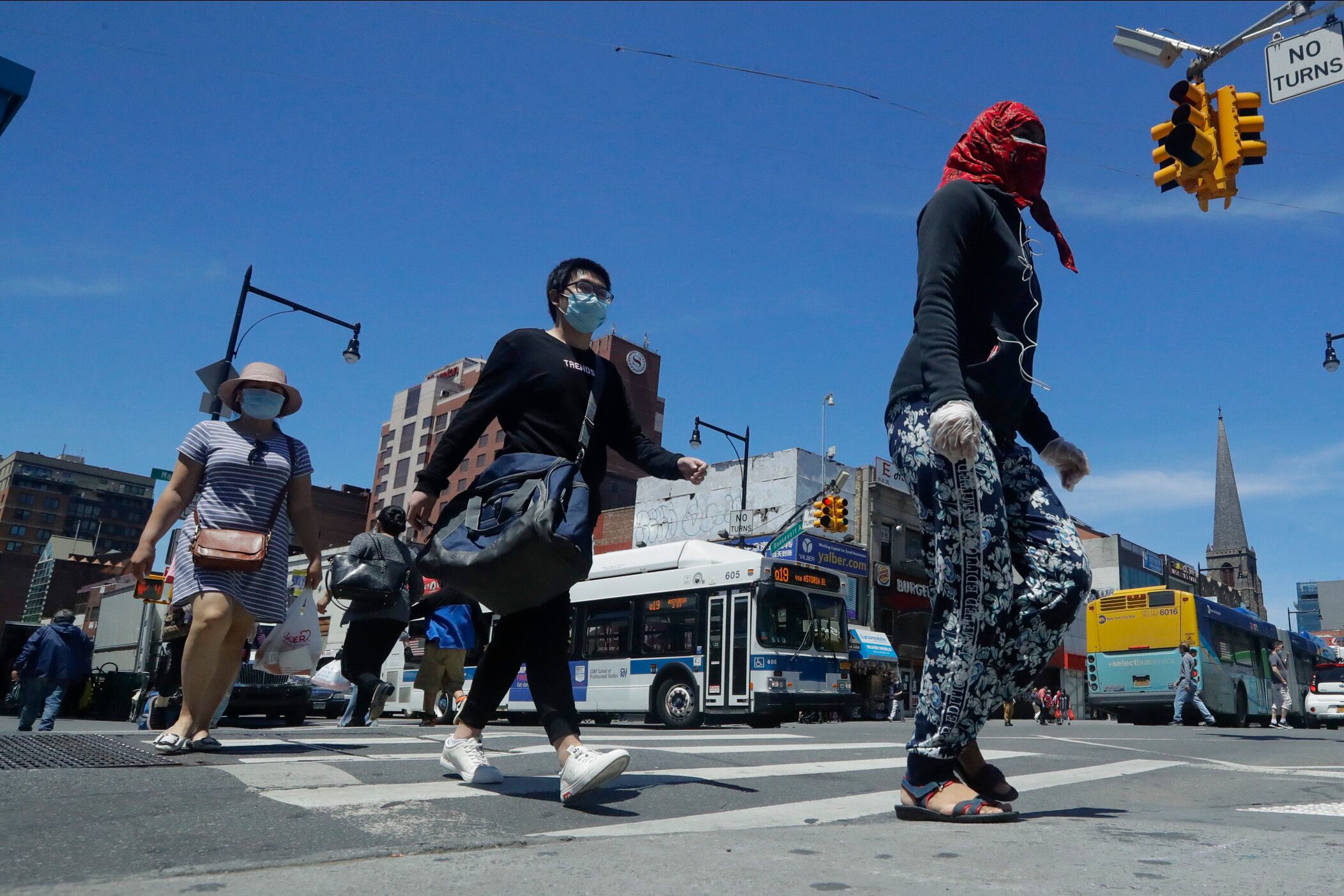
Coronavirus cases are rising in nearly half the U.S. states. And while many are chalked up to increased testing or to small, local outbreaks, others are more alarming.
If you lived in a big city in the 90s, you're probably one of the unlucky people who was kept up at night on a regular basis by errant car alarms. But today, those in that same big city hear alarms far less often than you did. So where did car alarms go? How have they evolved, and did we ever need them to begin with?
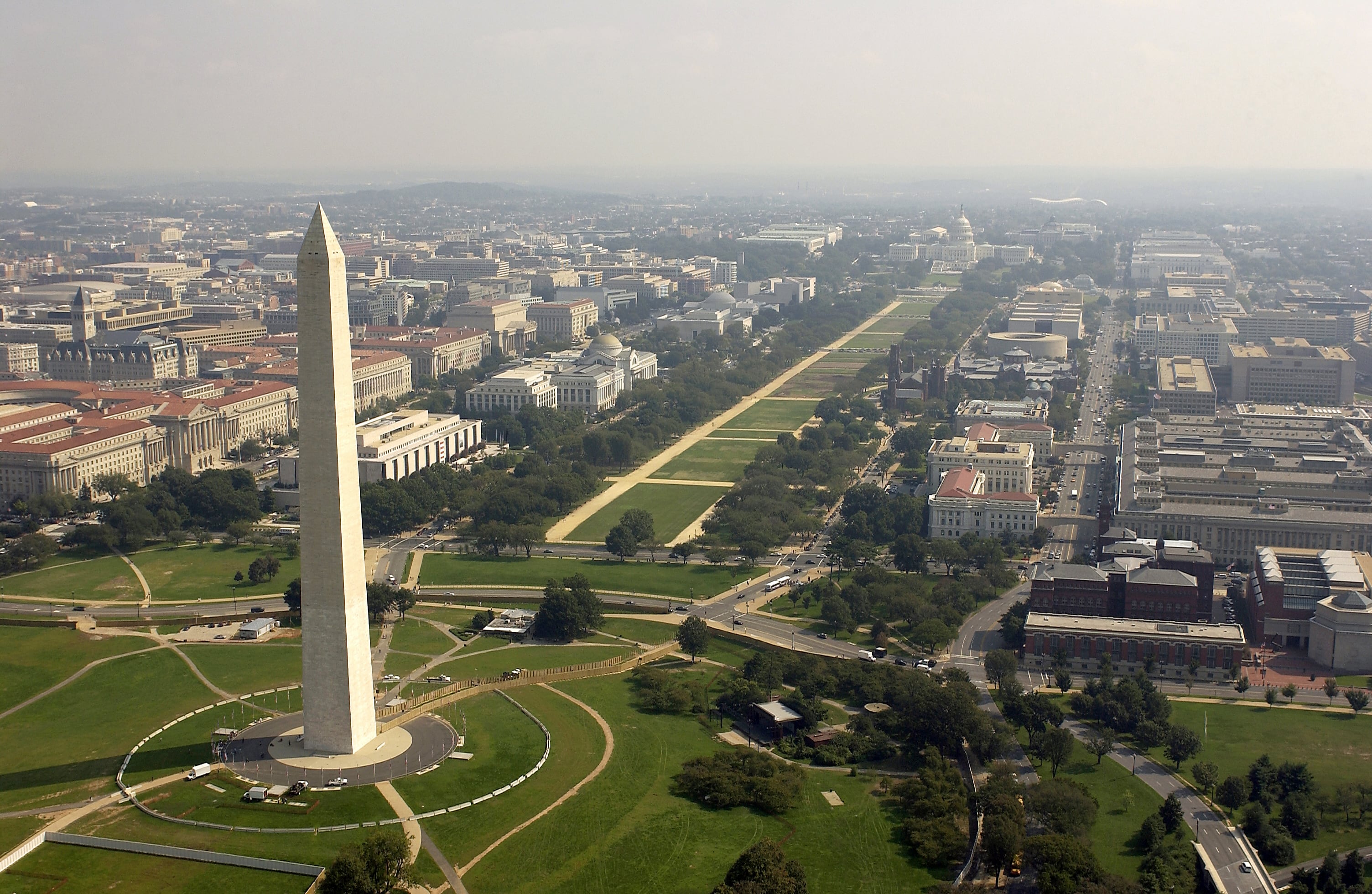
The skyline of Washington D.C. is stunted. You've probably heard that D.C. can't build skyscrapers taller than the U.S. Capital Building or the Washington Monument. But those are both myths from a bygone era. Cheddar tells the real story.
A top World Health Organization expert has tried to clear up “misunderstandings” about comments she made that were widely understood to suggest that people without COVID-19 symptoms rarely transmit the coronavirus.