By Marcia Dunn
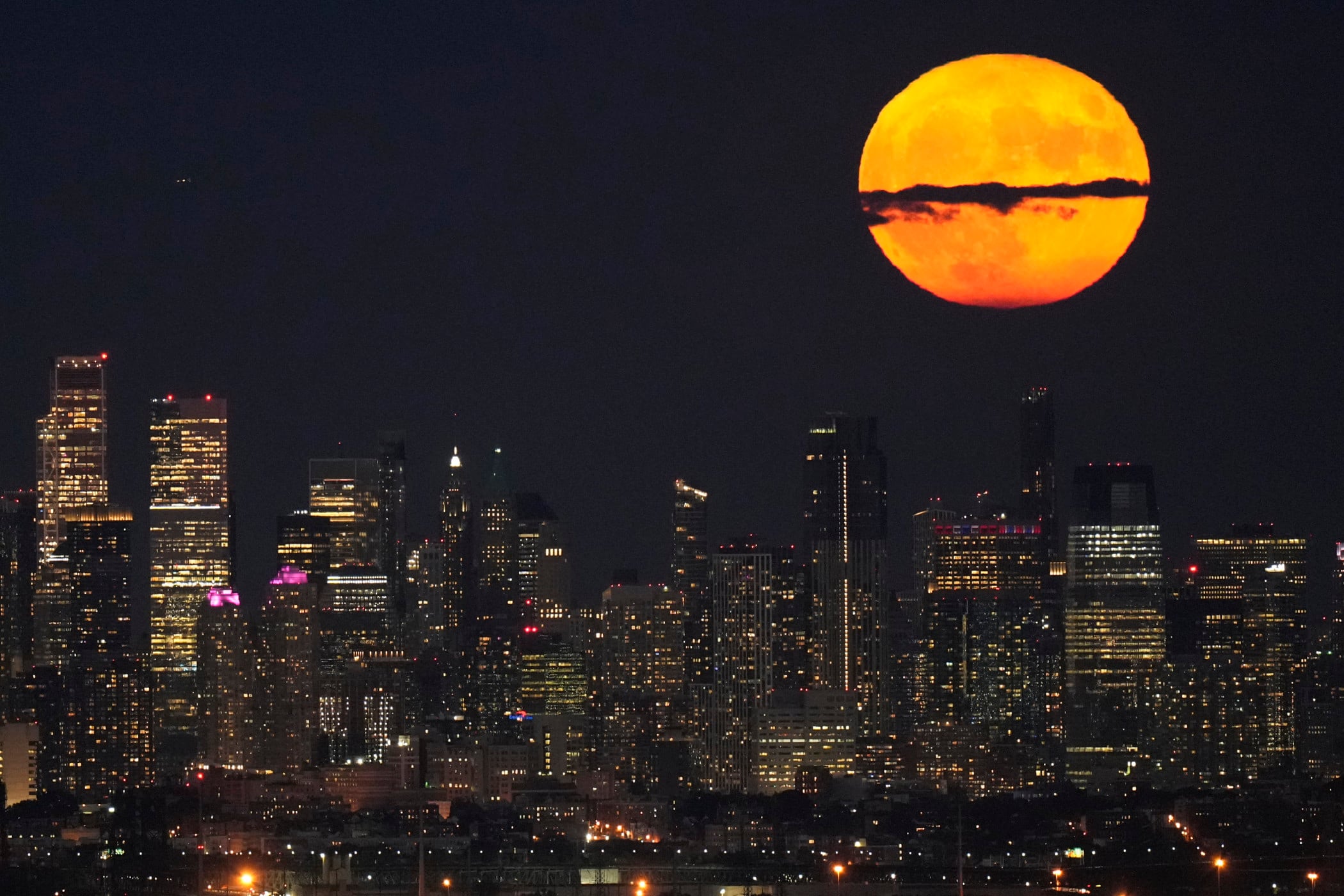
Stargazers are in for a double treat on Aug. 30: a rare blue supermoon with Saturn peeking from behind.
The cosmic curtain rises Wednesday night with the second full moon of the month, the reason it’s considered blue. It’s dubbed a supermoon because it’s closer to Earth than usual, appearing especially big and bright.
This will be the closest full moon of the year, just 222,043 miles (357,344 kilometers) or so away. That’s more than 100 miles (160 kilometers) closer than the Aug. 1 supermoon.
As a bonus, Saturn will be visible as a bright point 5 degrees to the upper right of the moon at sunset in the east-southeastern sky, according to NASA. The ringed planet will appear to circle clockwise around the moon as the night wears on.
If you missed the month’s first spectacle, better catch this one. There won’t be another blue supermoon until 2037, according to Italian astronomer Gianluca Masi, founder of the Virtual Telescope Project.
Clouds spoiled Masi's attempt to livestream the supermoon rising earlier this month. He’s hoping for clearer skies this time so he can capture the blue supermoon shining above St. Peter’s Basilica at the Vatican.
Weather permitting, observers don’t need binoculars or telescopes — “just their own eyes." said Masi.
“I’m always excited to admire the beauty of the night sky,” he said, especially when it features a blue supermoon.
The first supermoon of 2023 was in July. The fourth and last will be in September.
A new U.N. biodiversity report card highlights the decline over the past 10 years in fragile ecosystems such as coral reefs and tropical forests.
Astronomers looking at the atmosphere in neighboring Venus see something that might just be a sign of life. In a study published Monday, they say they found the chemical signature of a noxious gas called phosphine.
As people seek new ways to cope and treat psychiatric disorders like depression and anxiety, Ketamine is growing in popularity as doctors describe improvements in patients. Cheddar's Chloe Aiello reports.
Figuring out best practices when it comes to preventing airborne transmission is inherently challenging though, especially when it comes to the technical aspects of retrofitting ventilation systems.
Alabama State University has managed to keep COVID-19 infections at zero despite rising cases on college campuses. University president, Quinton Ross, Jr, joined Cheddar to discuss new technology that scans for coronavirus symptoms.
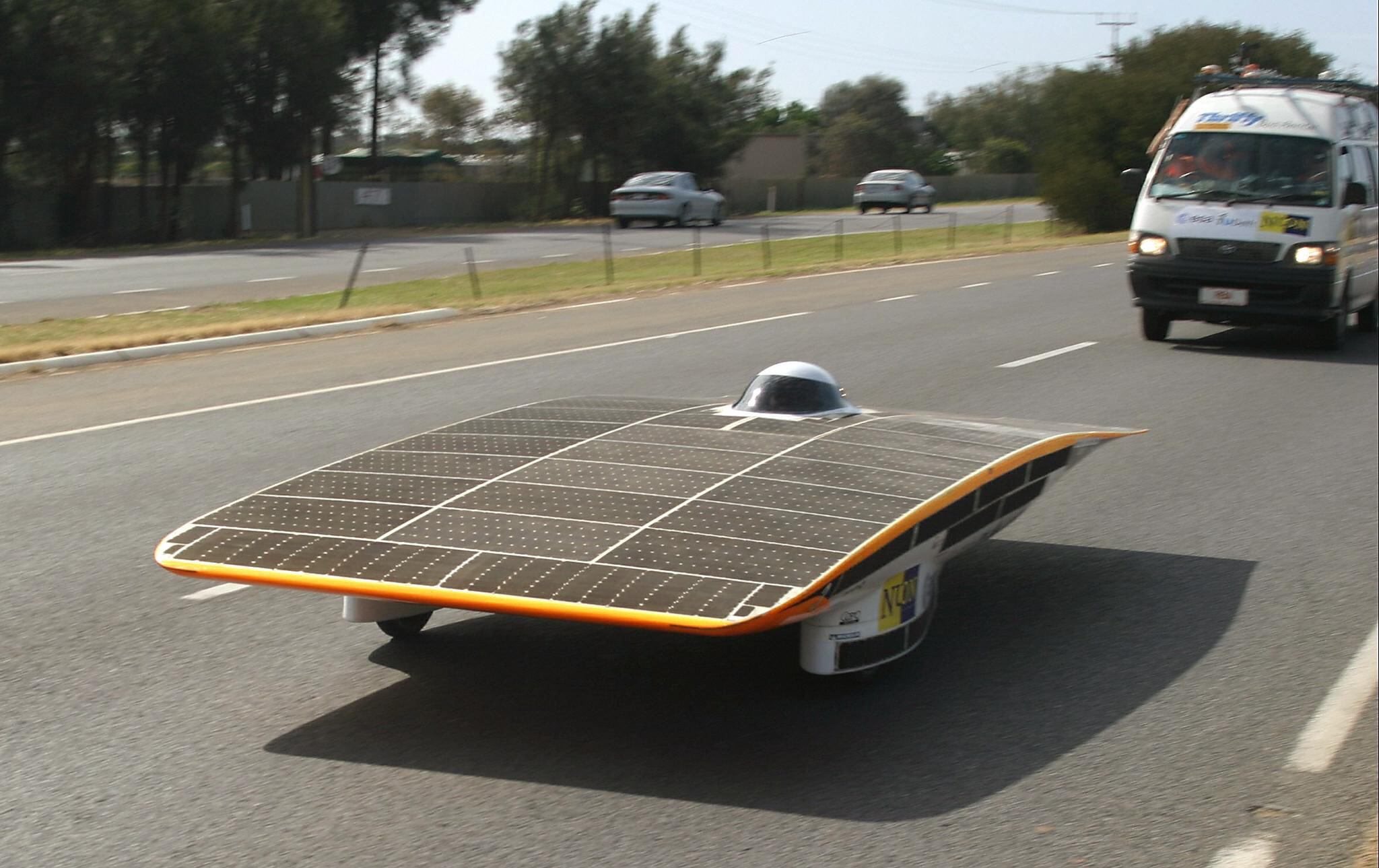
In the 1980's and 90's, the solar car was deemed the future of transportation. Yet, just as quickly as it arrived, the solar car disappeared. But today, as the problems caused by our reliance on fossil fuels have grown, so has a demand for alternative sources of energy for our vehicles. While electric cars are rapidly gaining a larger share of the automotive market, this technology still relies on electricity from a grid often fueled by petroleum or coal. And this is why some companies today are again trying to harness the most powerful energy source we know: the sun.
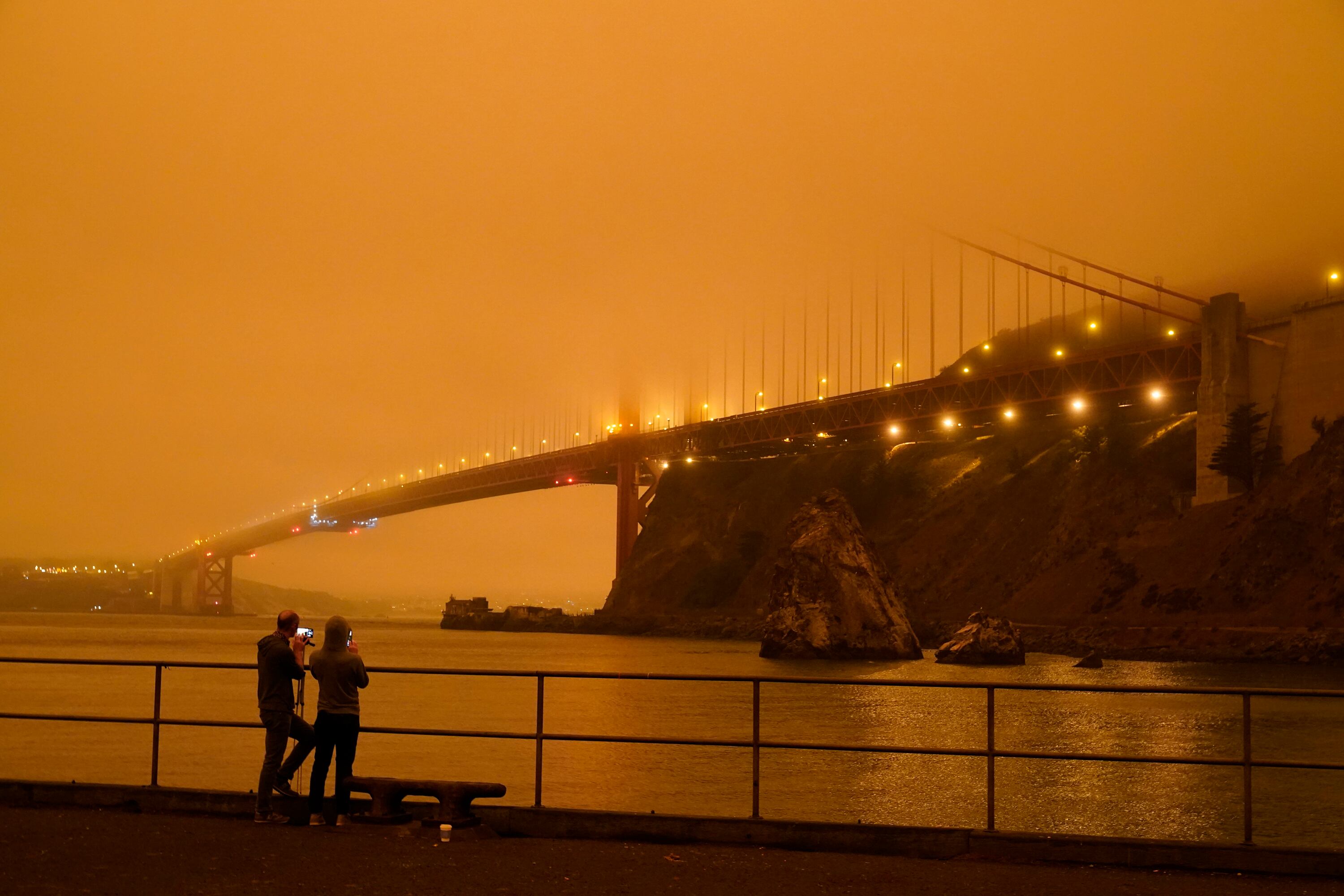
Wildfires are raging unchecked across parts of the western United States as winds sweep the region.
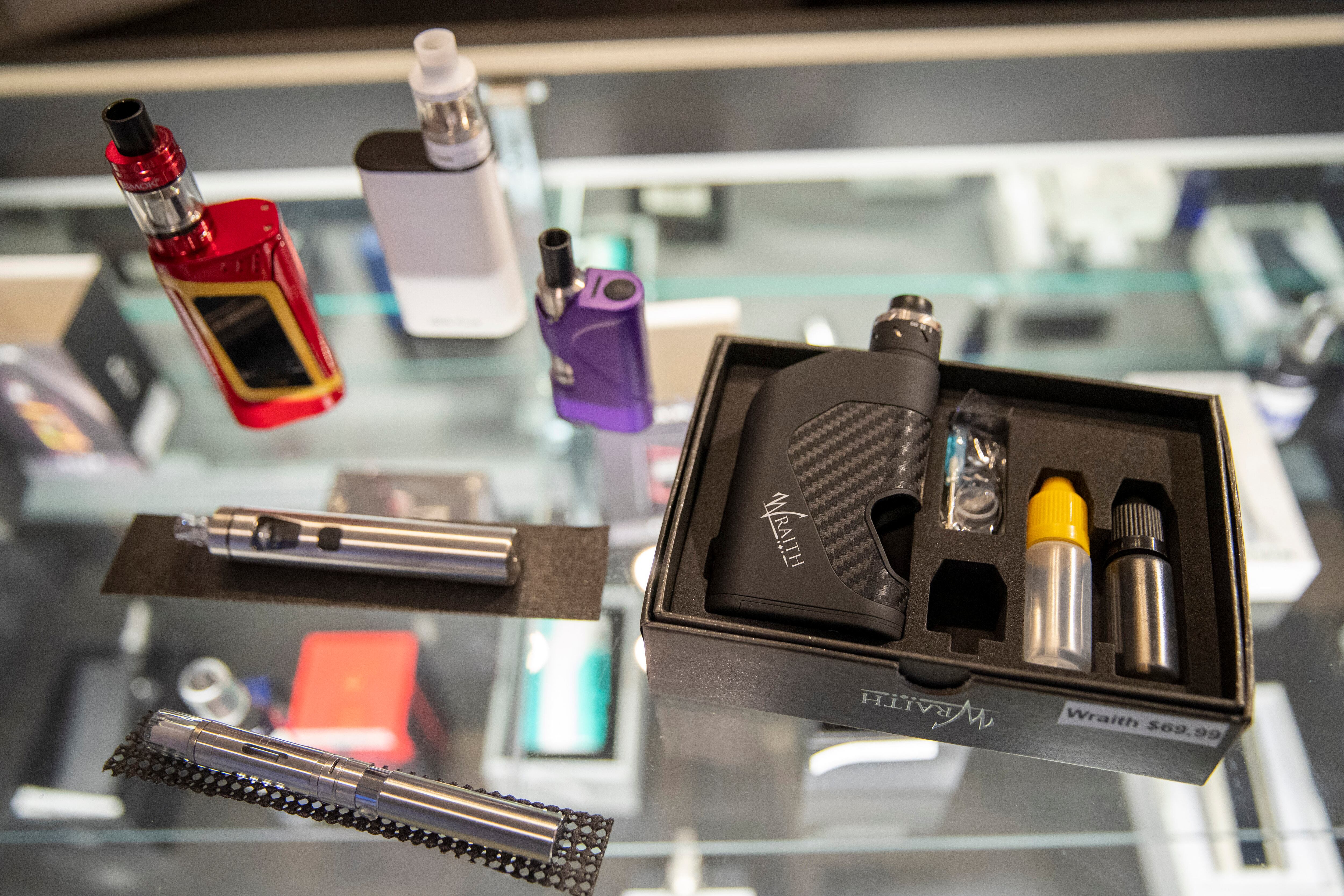
A new federal report shows vaping rates among U.S. teenagers fell dramatically this year.
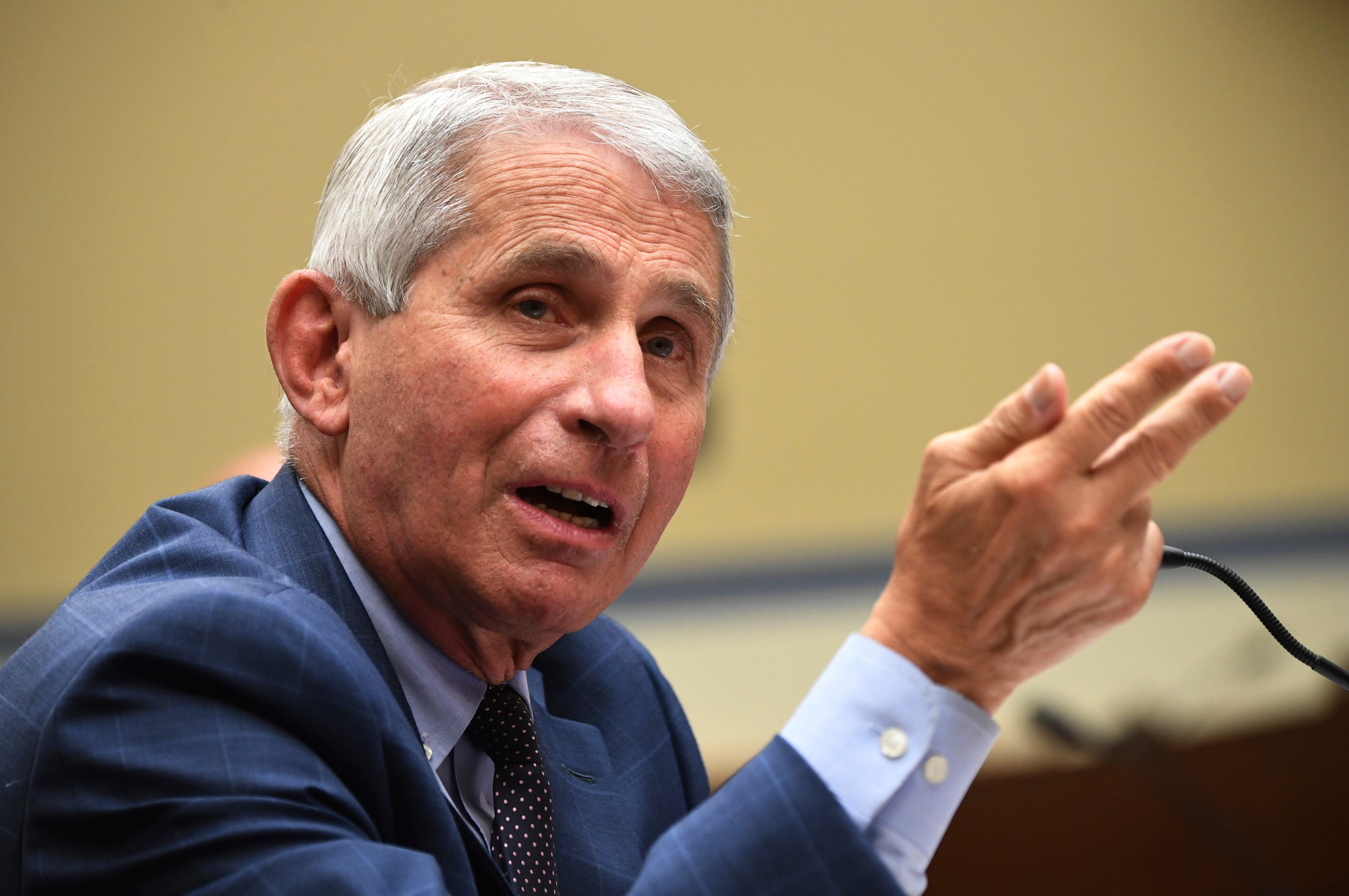
Dr. Anthony Fauci says AstraZeneca's suspension of its COVID-19 vaccine study shows “one of the safety valves” built into the research to spot any potential problems.
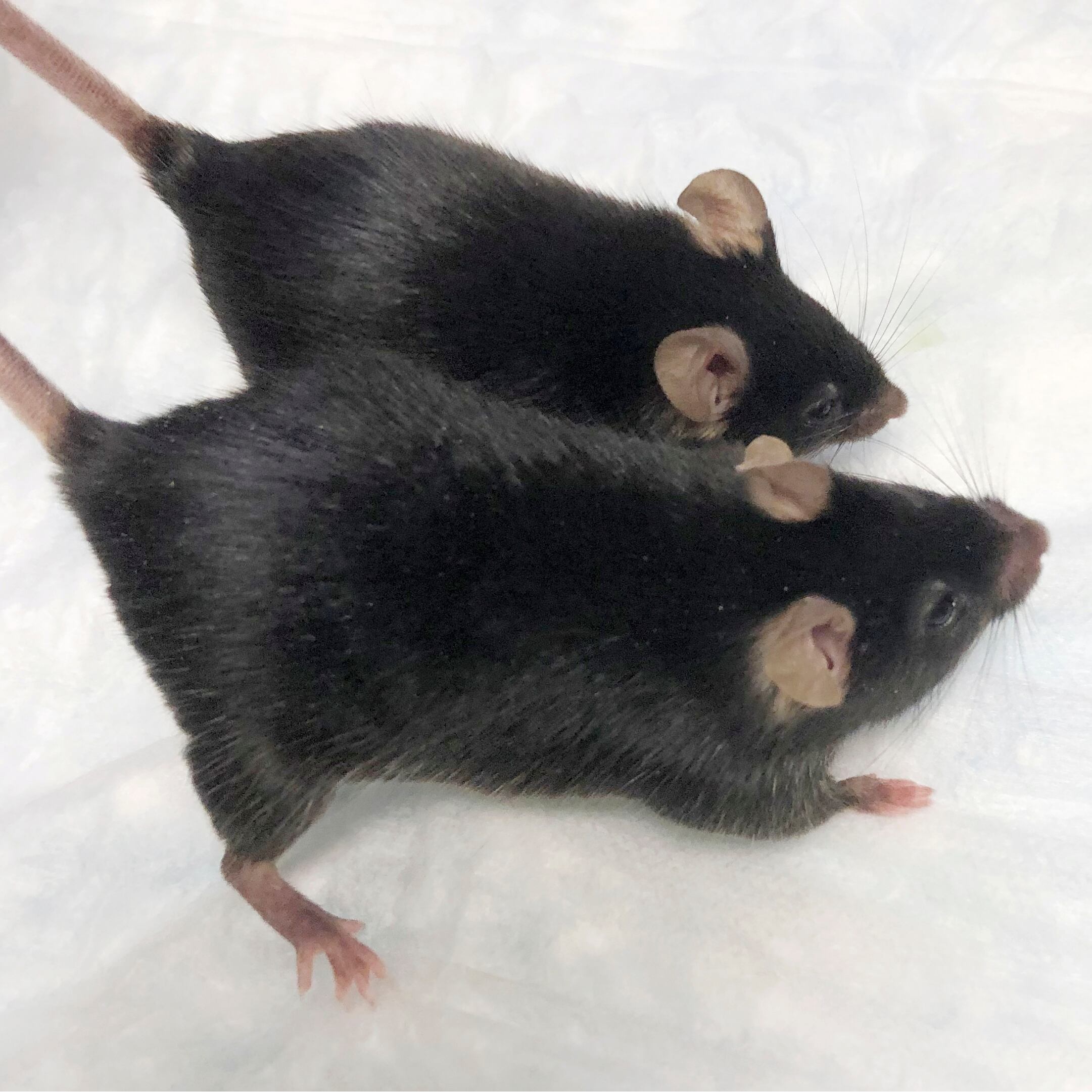
Scientists who sent bulked-up, mutant “mighty mice” to the International Space Station say the animals held onto their muscle during the monthlong flight.