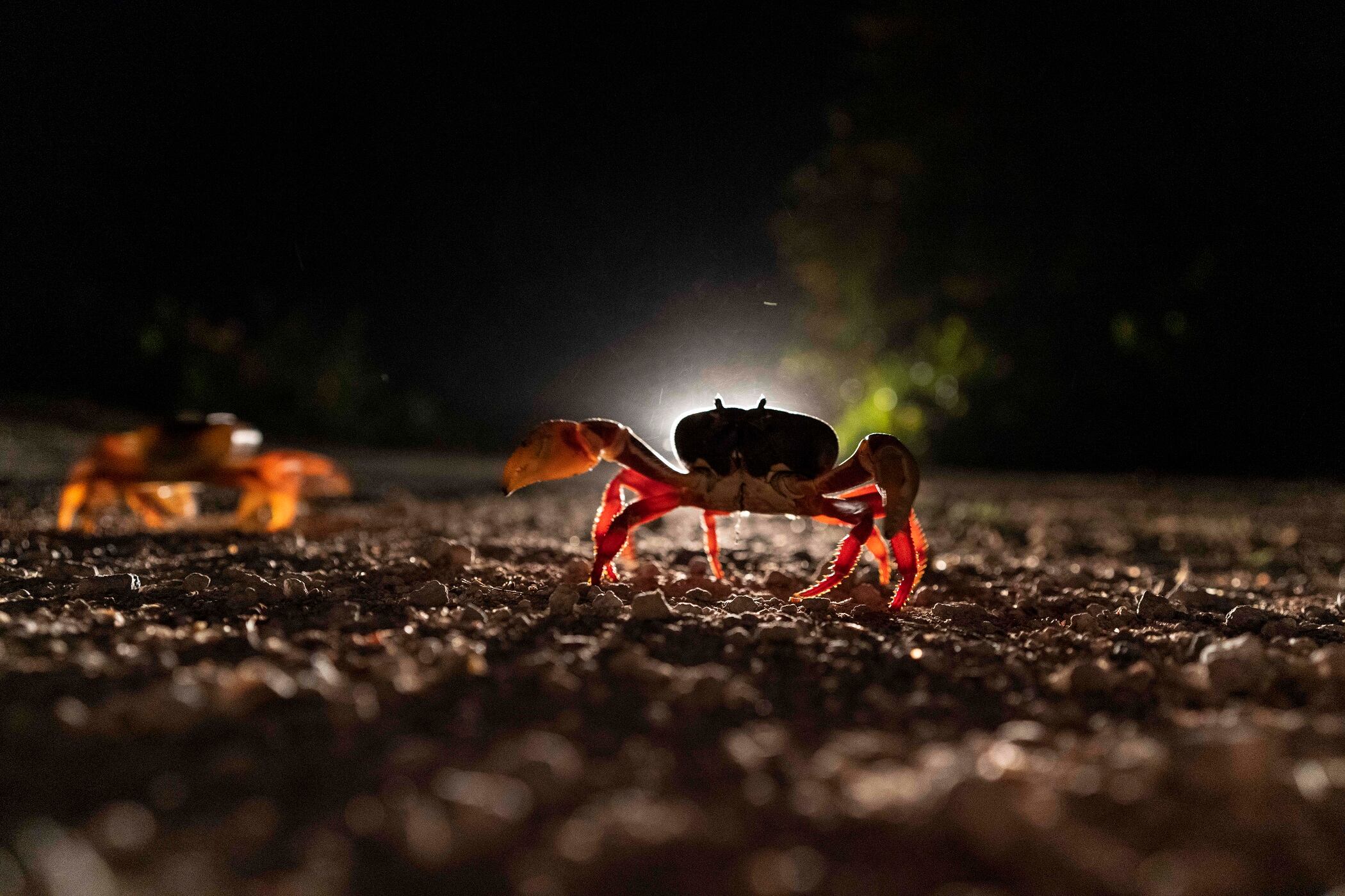
Every year in Cuba, millions of crabs emerge from the forest at the beginning of the spring rains and head for the waters of the Bay of Pigs, crossing streets and highways on a perilous journey to mate and reproduce.
Now underway, the migration causes concern to drivers who try to swerve in an often futile attempt not to kill the crustaceans. The crabs are a nuisance to residents but the sight of their road-crossing is a wonder for tourists and other first-time onlookers.
“They got here before us,” said Amaury Urra, a 50-year-old hiking guide who spent his entire life in this part of the Ciénega de Zapata, the largest wetland in the Caribbean, particularly picturesque for the backdrop of turquoise sea waters and the coastal cliffs. ″We’re used to this.″
“Where I live, which is in the center of the town of Girón, the crabs don’t get there as much,″ though there are plenty on the outskirts, he said.
Located about 180 kilometers (110 miles) southeast of Havana, the area was the scene of a 1961 failed invasion by Cuban exiles who signed up for a covertly CIA-funded operation to overthrow Fidel Castro.
This year, the crabs started their journey early. At the end of March, the municipal authorities issued a warning to drivers to avoid traveling in the morning and evening hours - the favorite crossing times for the crabs. Environmentalists usually demand the closure of the main road, especially at key migration times.
The passage of the red crustaceans — the species is called gecarcinus ruricola — could last until July. The largest amount of traffic occurs between April and May. Residents have to be careful: When the crabs feel threatened, they can puncture car tires with their pincers.
Official figures estimate that some 3.5 million crabs die each season on the road, many crushed by passing vehicles. They take a minute and a half to cross.
This type of crab lives and migrates in the Bahamas, Nicaragua, Jamaica and Dominica. But only here, and perhaps in another sector of the coast towards the neighboring province of Cienfuegos, does its path collide so dramatically with human traffic.