By Christina Larson
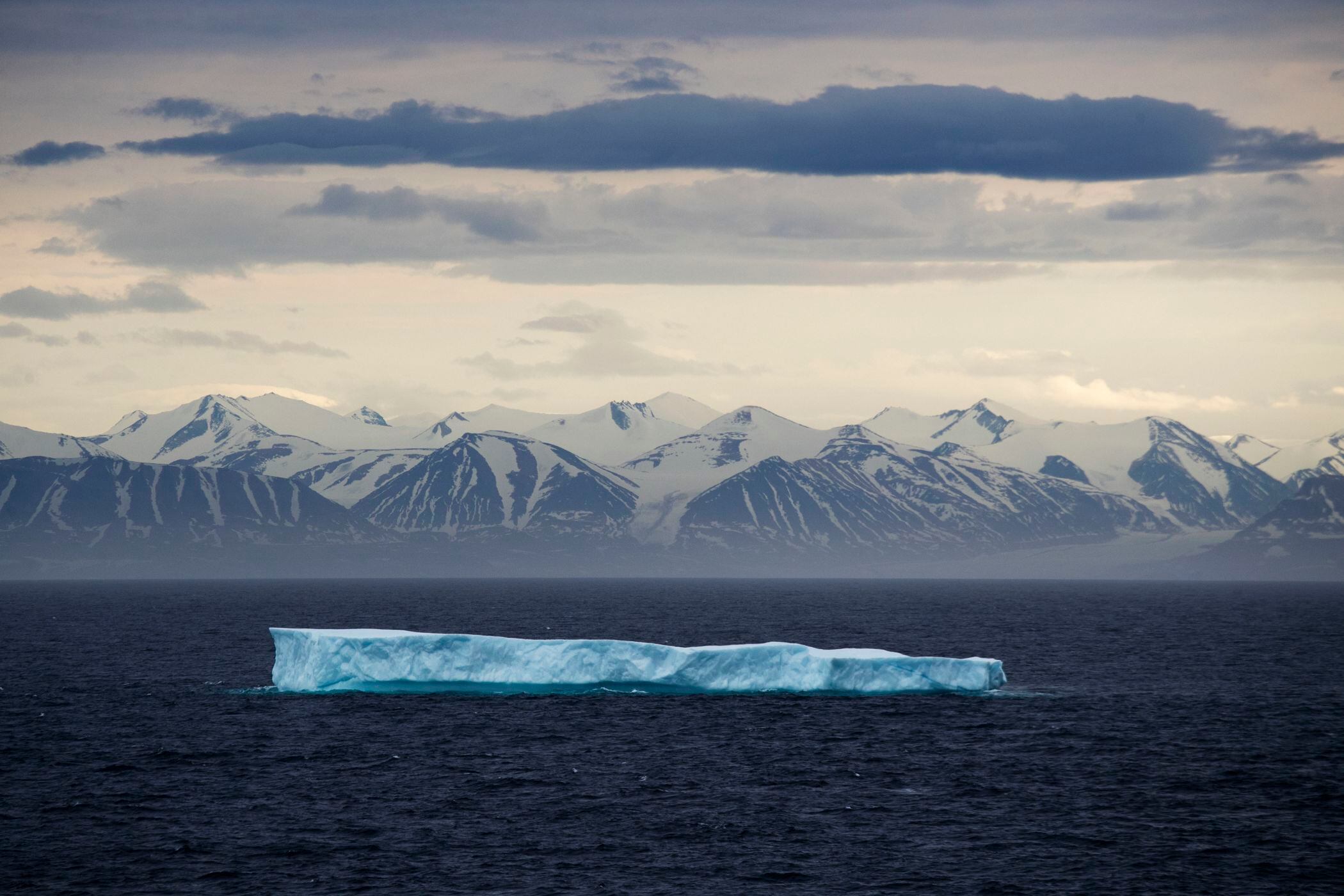
This year's vast wildfires in far northeastern Russia were linked to broader changes in a warming Arctic, according to a report Tuesday by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Wildfires are a natural part of many boreal ecosystems. But the extent of flames during the 2020 fire season was unprecedented in the 2001-2020 satellite record, and is consistent with the predicted effects of climate change, said Alison York, a University of Alaska Fairbanks fire scientist and a contributor to the annual Arctic Report Card.
The recent wildfires were exacerbated by elevated air temperatures and decreased snow cover on the ground in the Arctic region, the report found.
The past year — from October 2019 to September 2020 — was the second warmest on record in the Arctic, the report said. And the extent of snow on the ground in June across the Eurasian Arctic was the lowest recorded in 54 years.
Under those conditions, trees and plants “are just more flammable,” said York.
“The Arctic isn’t just this collection of components, it’s really an integrated system,” said Dartmouth sea ice scientist Don Perovich, who contributed to the report. "When something happens to one part of the system, it has cascading effects," he said.
Satellites recorded the second lowest extent of sea ice in September since record-keeping began 42 years ago, the report found.
Melting ice is both a result of increased temperatures and an accelerator of further changes, Perovich said. “As sea ice thins, more light can penetrate into the ocean, with unclear impacts for ecosystems,” he said.
As snow and ice cover decreases, the land and ocean surfaces also absorb more heat.
“Changes in the Arctic climate are important because the Arctic acts as a refrigerator for the rest of the world — it helps cool the planet,” said Lawrence Mudryk, a report contributor and a climate scientist at Environment and Climate Change Canada, a governmental research group.
“How much of the Arctic continues to be covered by snow and sea ice reflects part of how efficiently that refrigerator is working,” he said.
Last year's report included essays and research contributed by the Arctic's Indigenous communities for the first time. But in 2020, close collaboration between visiting scientists and Indigenous communities was not possible because of travel restrictions related to COVID-19.
Report contributor Matthew Druckenmiller, a climate scientist at the University of Colorado Boulder, said efforts to involve Indigenous communities would resume after the pandemic subsides.
The consequences of a warming Arctic are already felt far beyond the region.
“The Arctic continues to be a warning siren of how our Earth system is changing and it is important for policymakers and the public to understand that the impacts don’t stay in the Arctic with the polar bears,” said University of Georgia meteorology professor Marshall Shepherd, who was not involved in the report.
“We feel them, too, through changes in our weather patterns, sea level rise, and fisheries."
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.