A search is underway for a deep-sea vessel that went missing with five people aboard after it dived toward the deteriorating wreck site of the Titanic ocean liner.
The U.S. Coast Guard is leading the search for the small craft, named Titan, in the North Atlantic Ocean. The remote area is where the Titanic struck an iceberg and sank in 1912, killing all but about 700 of the roughly 2,200 passengers and crew.
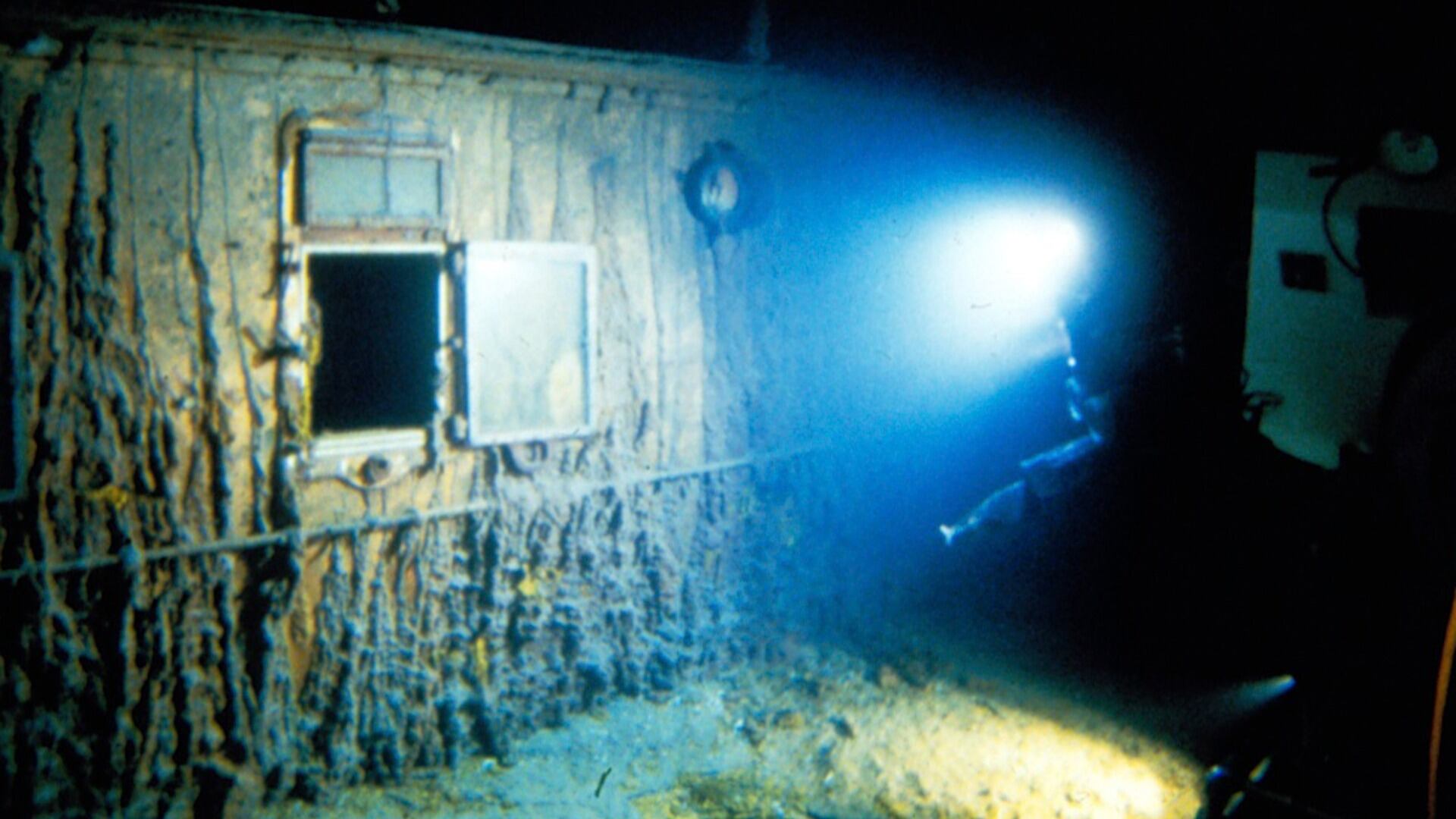
This was OceanGate Expeditions' third annual voyage to chronicle the deterioration of Titanic since 2021. The sunken ship is about 2.4 miles (3.8 kilometers) below the surface.
The undersea exploration company has been chronicling the ship's decay as well as the underwater ecosystem that has sprung up around it over the last century.
What we know so far:
WHEN AND WHERE DID THE TITAN GO MISSING?
The craft submerged Sunday morning, and its support vessel lost contact with it about an hour and 45 minutes later, according to the Coast Guard.
The vessel was reported overdue about 435 miles (700 kilometers) south of St. John’s, Newfoundland, according to Canada’s Joint Rescue Coordination Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia.
The Titan was being launched from an icebreaker that was hired by OceanGate and formerly operated by the Canadian Coast Guard. The ship ferried dozens of people and the submersible craft to the North Atlantic wreck site, where the Titan makes multiple dives.
David Concannon, an adviser to OceanGate, told The Associated Press on Monday that the submersible had a 96-hour oxygen supply. He said officials are working to get a remotely operated vehicle that can reach a depth of six kilometers (3.7 miles) to the site as soon as possible.
WHO WAS ON BOARD?
The Coast Guard said there was one pilot and four “mission specialists” aboard. “Mission specialists” are people who pay to come along on OceanGate’s expeditions. They take turns operating sonar equipment and performing other tasks in the five-person submersible.
An initial group of tourists in 2021 paid $100,000 to $150,000 apiece to go on the trip. OceanGate’s website described the “mission support fee” for the 2023 expedition as $250,000 a person.
British businessman Hamish Harding, who lives in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, was one of the mission specialists, according to Action Aviation, a company for which Harding serves as chairman.
Harding is an adventurer who holds three Guinness World Records, including the longest duration at full ocean depth by a crewed vessel. In March 2021, he and ocean explorer Victor Vescovo dived to the lowest depth of the Mariana Trench. In June 2022, he went into space on Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket.
Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman, members of one of Pakistan's most prominent families, were also on board, according to a family statement sent to the AP. Their eponymous firm invests in agriculture, industries and the health sector. Shahzada Dawood also is on the board of trustees for the California-based SETI Institute that searches for extraterrestrial intelligence.
WHAT KIND OF DEEP-SEA VESSEL WAS IT?
Titan is capable of diving four kilometers (2.4 miles) “with a comfortable safety margin,” according to documents filed by the company in April with a U.S. District Court in Virginia that oversees Titanic matters.
In a May 2021 court filing, OceanGate said the Titan had an “unparalleled safety feature” that assesses the integrity of the hull throughout every dive. At the time of the filing, Titan had undergone more than 50 test dives, including to the equivalent depth of the Titanic, in deep waters off the Bahamas and in a pressure chamber, the company said.
During its 2022 expedition, OceanGate reported that the submersible had a battery issue on its first dive and had to be manually attached to its lifting platform, according to a November court filing.
WHAT WAS THE TITAN'S MISSION?
The goal of OceanGate's expeditions has been chronicling the Titanic's deterioration as well as the underwater ecosystem that shipwrecks often spawn.
What's left of the Titanic is slowly succumbing to metal-eating bacteria that consumes hundreds of pounds of iron a day. Holes pervade the wreckage, while the crow’s nest is already gone. Some have predicted the ship could vanish in a matter of decades as holes yawn in the hull and sections disintegrate.
The company outfitted the Titan with high-definition cameras and multi-beam sonar equipment. Charting the wreck's decomposition can help scientists predict the fate of other deep-sea wrecks, including those that sank during the world wars. Another focus is the sea life: Hundreds of species have only been seen at the wreck.
"The ocean is taking this thing, and we need to document it before it all disappears or becomes unrecognizable,” Stockton Rush, president of OceanGate Expeditions, told the AP in 2021.