By David Keyton, Christina Larson, and Frank Jordans
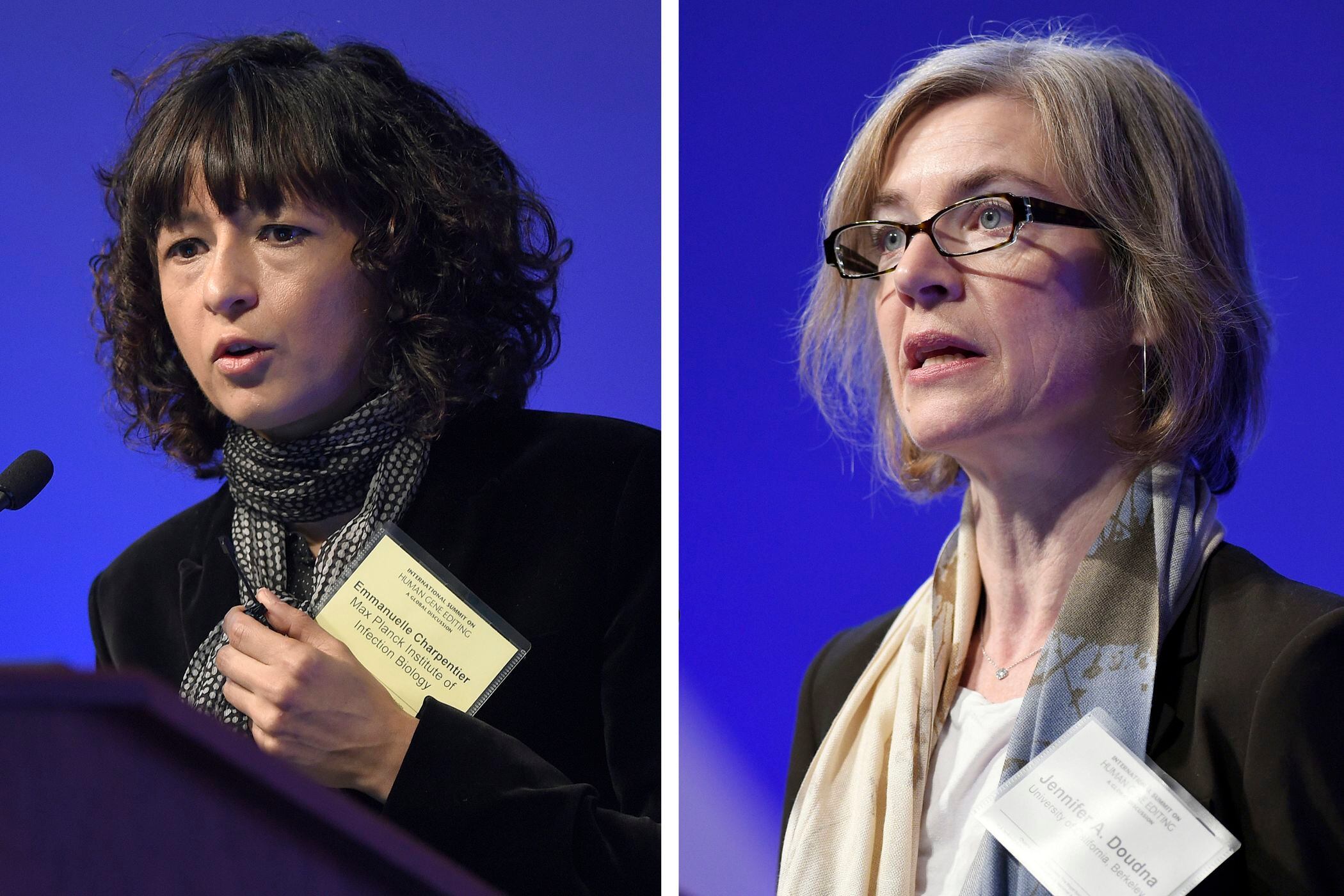
Two scientists won the Nobel Prize in chemistry Wednesday for developing "molecular scissors" to edit genes, offering the promise of one day curing a host of inherited diseases.
Working on opposite sides of the Atlantic, Frenchwoman Emmanuelle Charpentier and American Jennifer A. Doudna developed a method known as CRISPR-cas9 that can be used to alter the DNA of animals, plants, and microorganisms.
The award marked only the fourth time in the 119-year history of the prizes that a Nobel in the sciences was given exclusively to women.
Charpentier and Doudna's work allows for laser-sharp snips in the long strings of DNA that make up the code of life, enabling scientists to precisely edit specific genes to remove errors that lead to diseases.
"There is enormous power in this genetic tool," said Claes Gustafsson, chair of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry. "It has not only revolutionized basic science but also resulted in innovative crops and will lead to groundbreaking new medical treatments."
Dr. Francis Collins, who led the drive to map the human genome, said the technology "has changed everything" about how to approach diseases with a genetic cause.
"You can draw a direct line from the success of the human genome project to the power of CRISPR-cas to make changes in the instruction book," said Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, which helped fund Doudna's work.
More than 100 clinical trials are underway to study using CRISPR in treatments for inherited diseases, and "many are very promising," said Victor Dzau, president of the National Academy of Medicine.
But many also cautioned that the technology raises serious ethical questions and must be used carefully.
Much of the world became more aware of CRISPR in 2018, when Chinese scientist He Jiankui revealed he had helped make the world's first gene-edited babies, to try to engineer resistance to infection with the AIDS virus. His work was denounced as unsafe human experimentation because of the risk of causing unintended changes that could pass to future generations, and he has been sentenced to prison in China.
In September, an international panel of experts issued a report saying it is still too soon to try to make genetically edited babies because the science isn't advanced enough to ensure safety, but they mapped a pathway for countries that want to consider it.
"Being able to selectively edit genes means that you are playing God in a way," said American Chemistry Society President Luis Echegoyen, a chemistry professor at the University of Texas El Paso.
George Daley, dean of Harvard Medical School, said: "New technology often presents this dichotomy — there is immense potential for human benefit, especially for disease treatment, but also the risk of misapplication."
When asked about the significance of two women winning, Charpentier, 51, said that while she considers herself first and foremost a scientist, "it's reflective of the fact that science becomes more modern and involves more female leaders."
"I do hope that it will remain and even develop more in this direction," she said, adding that it is "more cumbersome to be a woman in science than to be a man in science."
Three times a woman has won a Nobel in the sciences by herself; this is the first time an all-female team won a science prize. In 1911, Marie Curie was the sole recipient of the chemistry award, as was Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin in 1964. In 1983, Barbara McClintock won the Nobel in medicine.
The breakthrough research done by Charpentier and Doudna was published in 2012, making the discovery very recent compared with a lot of other Nobel-winning research, which is often honored only after decades have passed.
"My greatest hope is that it's used for good, to uncover new mysteries in biology and to benefit humankind," said Doudna, who is affiliated with the University of California, Berkeley, and is paid by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, which also supports The Associated Press' Health and Science Department.
Speaking to reporters from the Max Planck Unit for the Science of Pathogens in Berlin, which she leads, Charpentier said that despite how recently it was developed, the method is now widely used by scientists researching diseases, developing drugs, and engineering new plants.
Among the most promising therapies being studied are those to treat eye diseases and blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia, she said.
In addition to transforming medicine, CRISPR has the potential to be used to engineer plants to store more carbon or to withstand extremes of climate change, Doudna said from Berkeley. CRISPR opens the door for researchers to "address urgent problems humanity is facing," she said.
The Broad Institute at Harvard and MIT have been in a long court fight over patents on CRISPR technology, and many other scientists did important work on it, but Doudna and Charpentier have been most consistently honored with prizes for turning it into an easily usable tool.
The Nobel comes with a gold medal and 10 million kronor (more than $1.1 million), courtesy of a bequest left more than a century ago by the prize's creator, Swedish inventor Alfred Nobel.
On Monday, the Nobel in medicine was awarded for the discovery of the liver-ravaging hepatitis C virus. Tuesday's prize in physics honored breakthroughs in understanding black holes.
The other prizes are for outstanding work in the fields of literature, peace, and economics.
___
Larson reported from Washington, and Jordans from Berlin. AP Chief Medical Writer Marilynn Marchione in Milwaukee and AP Science Writer Seth Borenstein in Kensington, Maryland, contributed to this report.