By Seth Borenstein
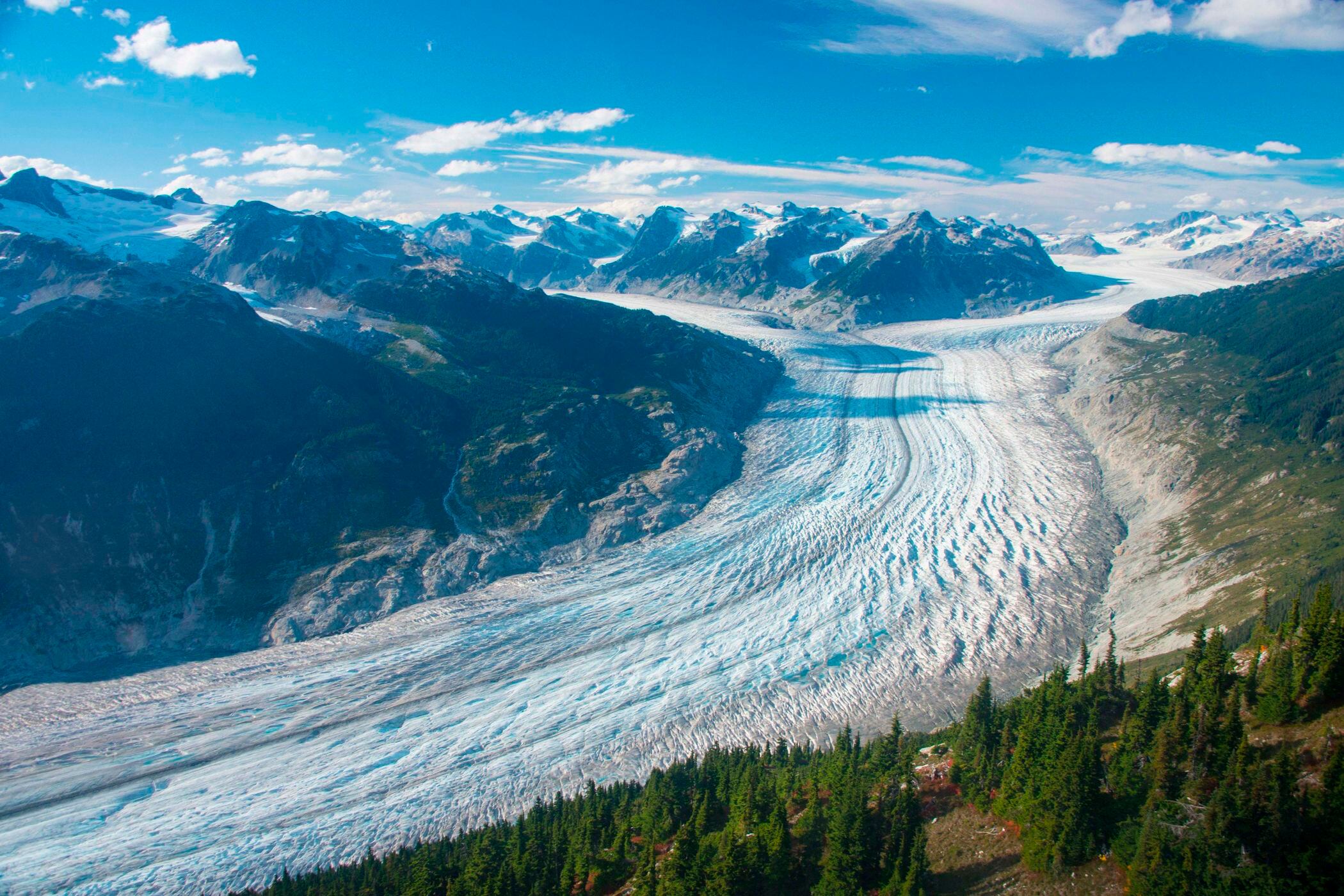
Glaciers are melting faster, losing 31% more snow and ice per year than they did 15 years earlier, according to three-dimensional satellite measurements of all the world’s mountain glaciers.
Scientists blame human-caused climate change.
Using 20 years of recently declassified satellite data, scientists calculated that the world’s 220,000 mountain glaciers are losing more than 328 billion tons (298 billion metric tons) of ice and snow per year since 2015, according to a study in Wednesday’s journal Nature. That’s enough melt flowing into the world’s rising oceans to put Switzerland under almost 24 feet (7.2 meters) of water each year.
The annual melt rate from 2015 to 2019 is 78 billion more tons (71 billion metric tons) a year than it was from 2000 to 2004. Global thinning rates, different than volume of water lost, doubled in the last 20 years and “that’s enormous,” said Romain Hugonnet, a glaciologist at ETH Zurich and the University of Toulouse in France who led the study.
Half the world’s glacial loss is coming from the United States and Canada.
Alaska’s melt rates are “among the highest on the planet," with the Columbia glacier retreating about 115 feet (35 meters) a year, Hugonnet said.
Almost all the world’s glaciers are melting, even ones in Tibet that used to be stable, the study found. Except for a few in Iceland and Scandinavia that are fed by increased precipitation, the melt rates are accelerating around the world.
The near-uniform melting “mirrors the global increase in temperature” and is from the burning of coal, oil and gas, Hugonnet said. Some smaller glaciers are disappearing entirely. Two years ago, scientists, activists and government officials in Iceland held a funeral for a small glacier.
“Ten years ago, we were saying that the glaciers are the indicator of climate change, but now actually they’ve become a memorial of the climate crisis,” said World Glacier Monitoring Service Director Michael Zemp, who wasn’t part of the study.
The study is the first to use this 3D satellite imagery to examine all of Earth’s glaciers not connected to ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctic. Past studies either only used a fraction of the glaciers or estimated the loss of Earth’s glaciers using gravity measurements from orbit. Those gravity readings have large margins of error and aren't as useful, Zemp said.
Ohio State University’s Lonnie Thompson said the new study painted an “alarming picture."
Shrinking glaciers are a problem for millions of people who rely on seasonal glacial melt for daily water and rapid melting can cause deadly outbursts from glacial lakes in places like India, Hugonnet said.
But the largest threat is sea level rise. The world’s oceans are already rising because warm water expands and because of melting ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, but glaciers are responsible for 21% of sea level rise, more than the ice sheets, the study said. The ice sheets are larger longer term threats for sea level rise.
“It’s becoming increasingly clear that sea level rise is going to be a bigger and bigger problem as we move through the 21st century,” said National Snow and Ice Data Center Director Mark Serreze.
___
Read more stories on climate by The Associated Press at https://www.apnews.com/Climate
Follow Seth Borenstein on Twitter at https://twitter.com/borenbears
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.