By Linda A. Johnson and Frank Jordans
Pfizer said Wednesday that new test results show its coronavirus vaccine is 95% effective, is safe and also protects older people most at risk of dying — last data needed to seek emergency use of limited shot supplies even as the catastrophic outbreak worsens across the globe.
The announcement from Pfizer and its German partner BioNTech, just a week after they revealed the first promising preliminary results, comes as the team is preparing within days to formally ask U.S. regulators to allow emergency use of the vaccine.
They also have begun “rolling submissions” for the vaccine with regulators in Europe, the U.K. and Canada and soon will add this new data.
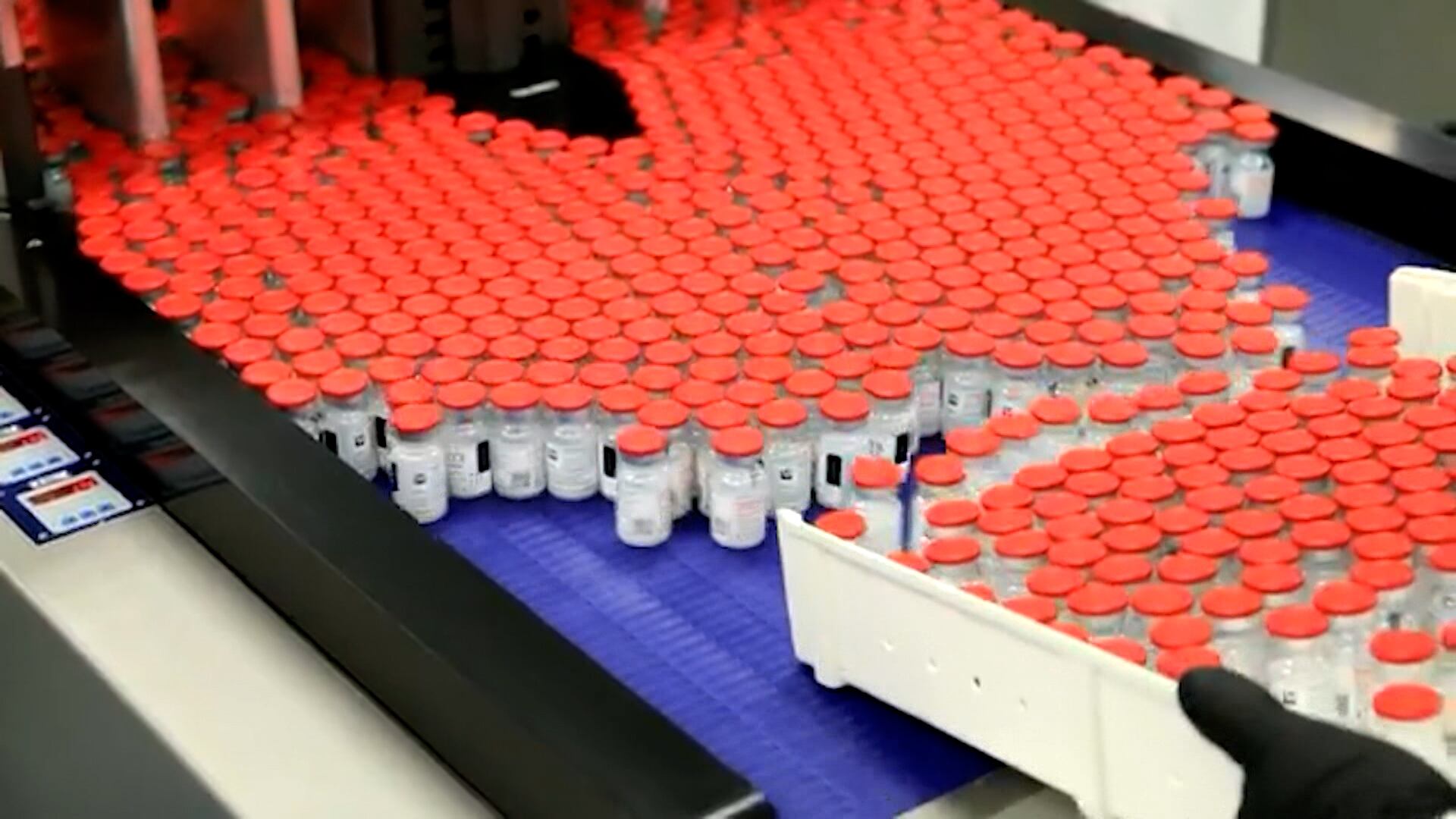
Pfizer and BioNTech had initially estimated the vaccine was more than 90% effective after 94 infections had been counted in a study that included 44,000 people. With the new announcement, the company now has accumulated 170 infections in the study -- and said only eight of them occurred in volunteers who got the actual vaccine rather than a dummy shot. One of those eight developed severe disease, the company said.
“This is an extraordinarily strong protection,” Dr. Ugur Sahin, BioNTech's CEO and co-founder, told The Associated Press.
The companies have not yet released detailed data on its study, and results have not been analyzed by independent experts. Also still to be determined are important questions such as how long protection lasts and whether people might need boosters.
But all eyes are on the progress of potential vaccines as the grim infection rate jumps in the U.S. and abroad as winter weather forces people indoors, in the close quarters that fuels viral spread.
Pfizer and BioNTech said the vaccine was more than 94% effective in adults over age 65, though it is not clear exactly how that was determined with only eight infections in the vaccinated group to analyze and no breakdown provided of those people’s ages.
Sahin said there were enough older adults enrolled in the study and among the placebo recipients who became infected that he is confident “this vaccine appears to work in the higher-risk population.”
Earlier this week Moderna, Inc. announced that its experimental vaccine appears to be 94.5% effective after an interim analysis of its late-stage study.
Similar results from two vaccines both made with a brand-new technology — using a snippet of the genetic code of the coronavirus to train the body to recognize if the real virus comes along — likely will add to experts' reassurance about the novel approach.
While initial supplies will be scarce and rationed, as the supply grows Sahin said the companies have a responsibility to help ensure access for lower-income countries as well.
Pfizer and BioNTech also say now have the required data on the vaccine’s safety needed to seek emergency authorization from the Food and Drug Administration.
The companies didn’t disclose safety details but said no serious vaccine side effects have been reported, with the most common problem being fatigue after the second vaccine dose, affecting about 4% of participants.
The study has enrolled nearly 44,000 people in the U.S. and five other countries. The trial will continue to collect safety and effectiveness data on volunteers for two more years.
Pfizer and BioNTech said they expect to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses globally in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021.
U.S. officials have said they hope to have about 20 million vaccine doses each from Moderna and Pfizer available for distribution in late December. The first shots are expected to be offered to vulnerable groups like medical and nursing home workers, and people with serious health conditions.
AP medical writer Lauran Neergaard contributed to this report.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.