By John Leicester
Because of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, Europe is going to have to wait at least several more years and may need NASA's help before its first planned Mars rover can drill into the planet's dusty surface, seeking signs of whether it ever hosted life.
The European Space Agency said Thursday that it will no longer attempt to send the ExoMars rover aloft this year on a Russian rocket and may now have to strip out the mission's many Russian components.
A launch with Russia’s state space corporation, Roscosmos, is now “practically impossible but also politically impossible,” the agency’s director, Josef Aschbacher, said. “This year, the launch is gone.”
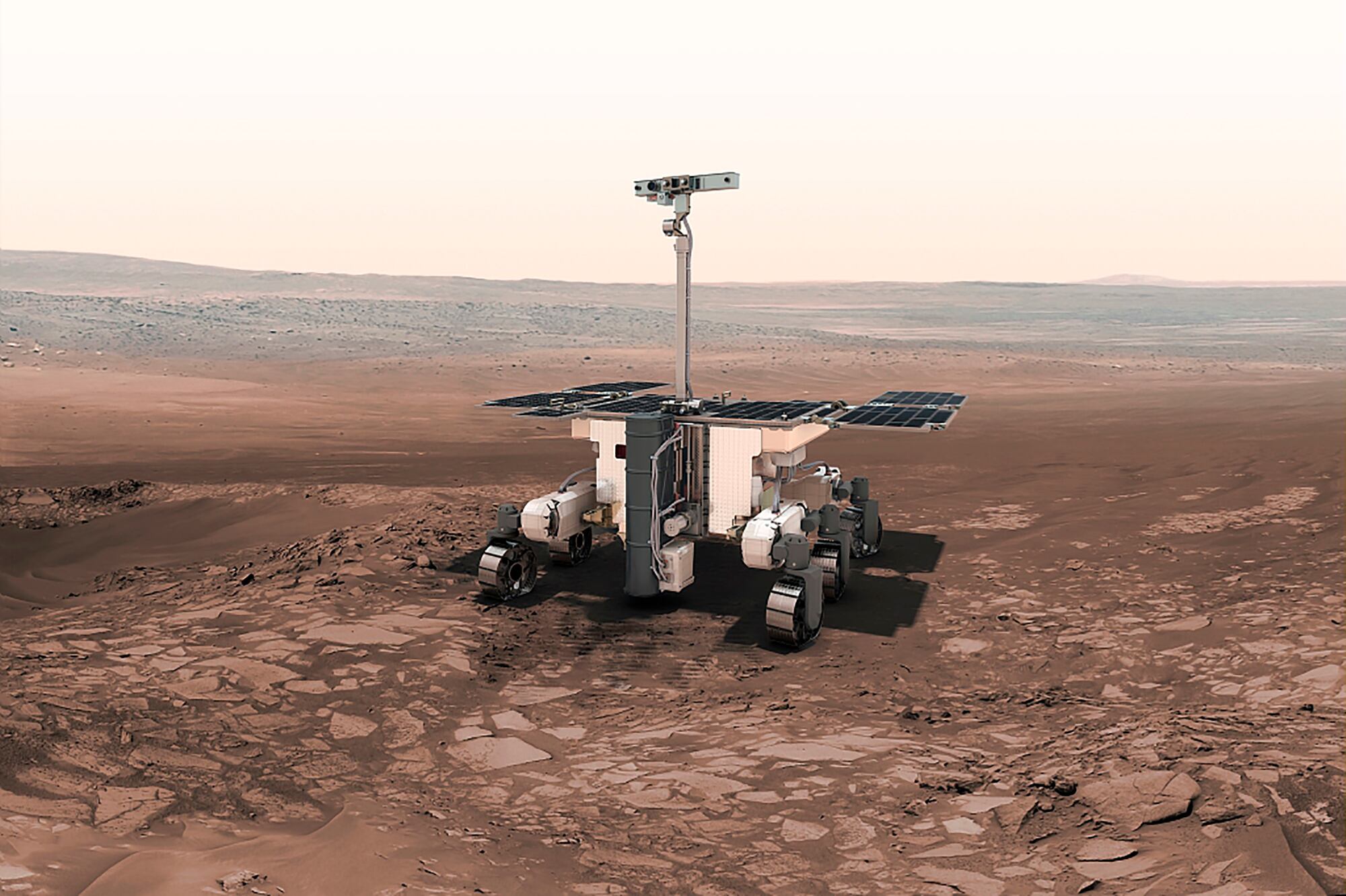
Like trying to untangle spaghetti, experts will now try and figure out how to do without the Russian technology that's woven into the mission. A heater that was meant to keep the rover from freezing on Mars is, for example, Russian. So, too, is the bulk of the mission's Kazachok landing platform, which means "little Cossack" in Russian. The largely European six-wheeled rover was meant to roll off that platform onto the Martian surface.
In an interview with The Associated Press, Aschbacher said the space agency will now sift “bit by bit and component by component” through the mission, to determine how much time is needed “to really do it without the Russians.” Alternatives might be sourced from Europe and with the help of NASA, he said.
Because of the Russian invasion, “we need to untangle all this cooperation which we had, and this is a very complex process, a painful one I can also tell you, but also a very complex one, and we have to do it,” he said.
He described the breakdown of cooperation as “a wake up call” for Europe to further develop its own space technologies.
“We need to make sure that we have our independent access to space,” he said.
Because of their respective orbits around the Sun, Mars is only readily reachable from Earth every two years. The earliest next launch window would be 2024. But if sanctions on Russia haven’t been lifted by then, enabling ESA cooperation with Roscosmos to resume, then that window could be missed, too.
The earliest a fully European or Europe-NASA version of the ExoMars rover could be launched would be 2026 or, failing that, 2028, Aschbacher said.
The rover itself is named Rosalind Franklin and equipped with a drill, to search for signs of life at depths up to two meters (6 feet) below the Martian surface, where they could be well preserved — if they exist.
The ESA had previously said that the mission was “very unlikely" because of Russia's war against Ukraine. The decision to suspend cooperation with Roscosmos was taken by ESA’s ruling council at a meeting in Paris.
“We deeply deplore the human casualties and tragic consequences of the aggression towards Ukraine,” an ESA statement said. “While recognizing the impact on scientific exploration of space, ESA is fully aligned with the sanctions imposed on Russia by its member states.”
The ExoMars mission has already been pushed back from 2020, because of the coronavirus pandemic and the need for more tests on the spacecraft.
The mission was to have blasted off on a Russian Proton-M rocket from the Baikonur launch site in Kazakhstan in September, and had been scheduled to land on the red planet some nine months later.
Already on Mars are NASA’s Perseverance rover and China’s first Mars rover, Zhurong, named after the Chinese god of fire. Both landed on the red planet last year. Two other NASA spacecraft are still active on the surface: Curiosity and InSight.