By Laura Ungar and Jonathan Mattise
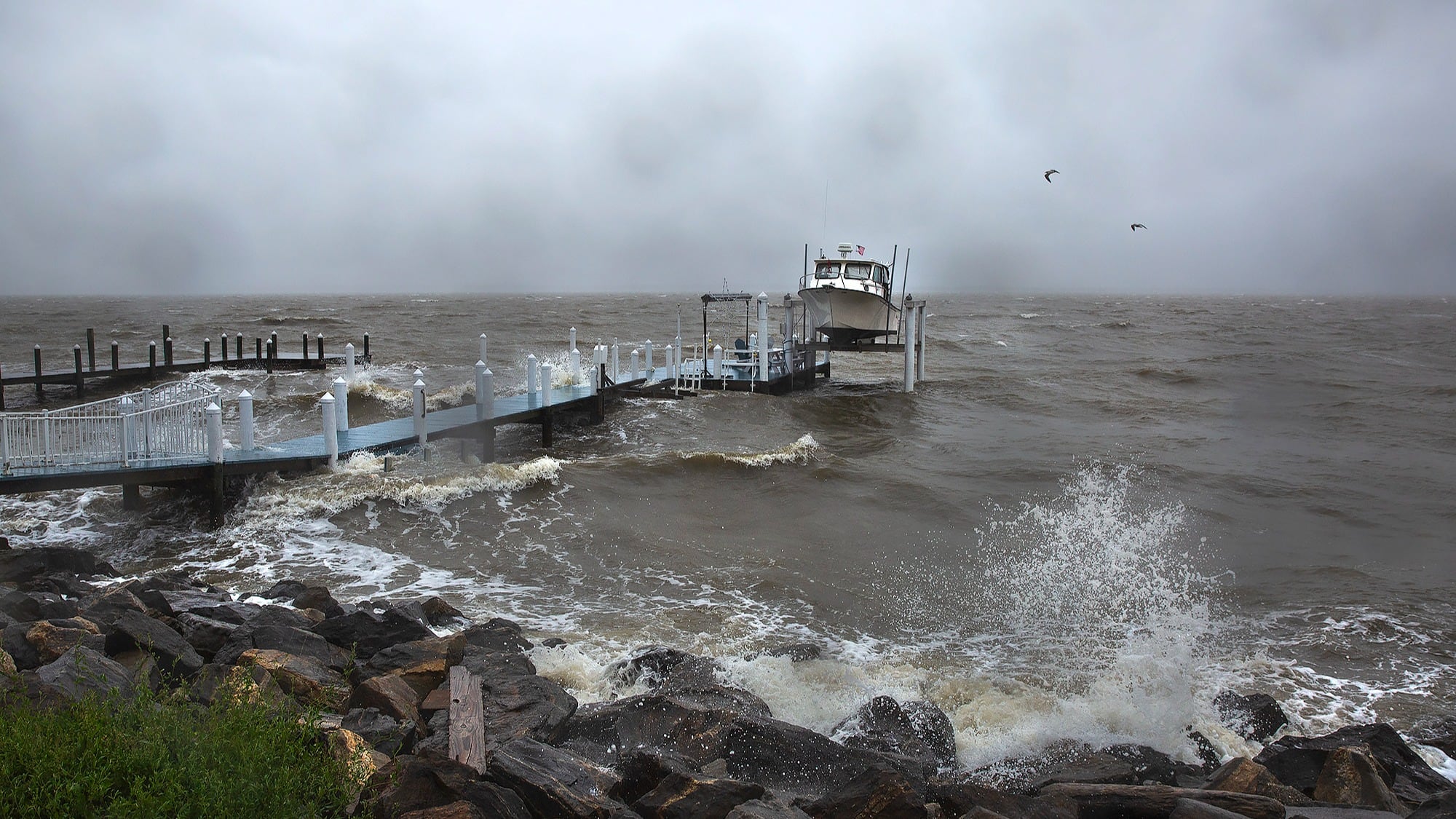
Nearly a day after being downgraded from a tropical storm, Ophelia still threatened parts of the Northeast on Sunday with coastal flooding, life-threatening waves and heavy rain from Washington to New York City, the National Hurricane Center said.
As Ophelia weakened, a new tropical storm named Philippe brewed in the Atlantic.
Even though Ophelia was downgraded Saturday night, meteorologists warned that swells generated by the storm would affect the East Coast for the rest of the weekend, likely causing dangerous surf conditions and rip currents. Ophelia was also expected to drop 1 to 3 inches (2.5 to 7.6 centimeters) of additional rain over parts of the Mid-Atlantic and New England. Isolated river flooding was also possible.
Ophelia was south of Washington on Sunday morning and was expected to continue moving northeast before turning east and then weakening more over the next two days, according to the hurricane center. Meanwhile, Philippe was 1,175 miles (1,890 kilometers) west of the Cabo Verde Islands, which are off the west coast of Africa. That storm had maximum sustained winds of 50 mph (75 kph).
The National Weather Service said numerous New Jersey communities reported coastal flooding, including, including Sea Isle City and Brielle. Thousands of people in the state remained without power Sunday. NJ.com reported more than 6,000 customers were without electricity Sunday morning, down from a high of 13,000.
Flooding and road closures were also reported in coastal Delaware.
The storm came ashore Saturday near Emerald Isle, North Carolina, with near-hurricane-strength winds of 70 mph (113 kph), but the winds weakened as the system traveled north, the hurricane center said.
Videos from social media showed significant flooding in the state's riverfront communities such as New Bern, Belhaven and Washington. A few thousand North Carolina homes and businesses remained without electricity Sunday morning, according to poweroutage.us, which tracks utility reports.
Even before making landfall, Ophelia proved treacherous enough that five people, including three children, had to be rescued Friday night by the Coast Guard. They were aboard a 38-foot (12-meter) catamaran stuck in choppy water and strong winds while anchored off Cape Lookout, North Carolina.
On Saturday, Greenville police posted a video on Facebook of an officer rescuing a small pit bull from floodwaters. Police said the dog was tied to a fence and “just inches from drowning” when an officer responded after someone called authorities. Animal protection authorities opened an investigation.
Elsewhere, a rescue team helped the Beaufort County Sheriff’s Office evacuate 15 people from a campground between the Pamlico River and the Chocowinity Bay, according to Brian Haines, a spokesperson for the North Carolina Division of Emergency Management.
At the southern tip of North Carolina’s Outer Banks, organizers on Sunday were finally able to open the long-running Beaufort Pirate Invasion, a weekend event centered on the 1747 Spanish attack on the town. Winds tore down the big tent for a banquet planned for Saturday, and several other tents were damaged or shredded.
In other developments, high winds forced New York City officials to suspend ferry service to Rockaway. Other ferries were operating on schedule.
The governors of North Carolina, Virginia and Maryland each declared a state of emergency on Friday.
Scientists say climate change could result in hurricanes expanding their reach into mid-latitude regions more often, making storms like this month’s Hurricane Lee more common.
One study simulated tropical cyclone tracks from pre-industrial times, modern times and a future with higher emissions. It found that hurricanes would track closer to the coasts, including around Boston, New York City and Virginia, and would be more likely to form along the Southeast coast.
In some areas where the storm struck Saturday, the effects were modest.
Aaron Montgomery, 38, said he noticed a leak in the roof of his family's new home in Williamsburg, Virginia. They were still able to make the hour-long drive for his wife’s birthday to Virginia Beach, where he said the surf and wind were strong but the rain had stopped.
“No leak in a roof is insignificant, so it’s certainly something we have to deal with Monday morning,” he said.
Ungar reported from Louisville, Kentucky. Mattise reported from Nashville, Tennessee. AP Radio reporter Jackie Quinn in Washington and AP writers Brian Witte in Annapolis, Maryland, Ron Todt in Philadelphia, Sudhin Thanawala in Atlanta, Christopher Weber in Los Angeles and David Collins in Hartford, Connecticut, contributed to this report.