By Scott Bauer and Harm Venhuizen
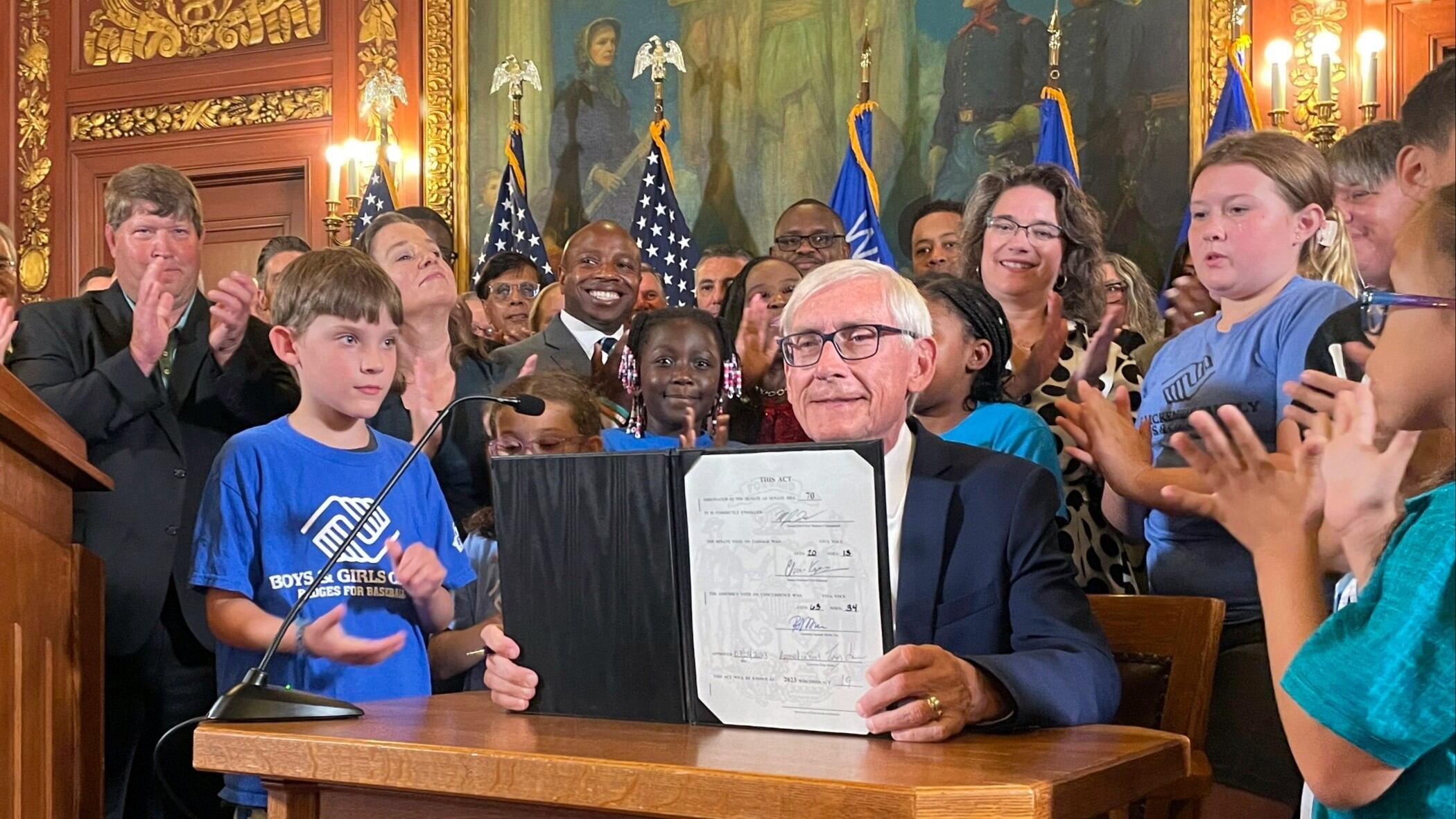
Wisconsin Gov. Tony Evers signed off on a two-year spending plan Wednesday after gutting a Republican tax cut and using his broad veto powers to increase school funding for centuries.
Evers angered Republicans with both moves, with some saying the Democratic governor was going back on deals he had made with them.
Wisconsin governors have broad partial veto power and Evers got creative with his use of it in this budget, which is the third passed by a Republican Legislature that he's signed.
He reduced the GOP income tax cut from $3.5 billion to $175 million, and did away entirely with lower rates for the two highest earning brackets. He also struck a hyphen and two numerals to increase how much revenue K-12 public schools can raise per student by $325 a year until 2425.
Evers, a former state education secretary and teacher, had proposed allowing revenue limits to increase with inflation. Under his veto, unless it's undone by a future Legislature and governor, Evers said schools will have “predictable long-term spending authority.”
“There are lots of wins here,” Evers said of the budget at a signing ceremony surrounded by Democratic lawmakers, local leaders, members of his Cabinet and others.
Republicans blasted the vetoes.
Republican Assembly Speaker Robin Vos said allowing the school revenue limit to increase effectively forever would result in “massive property tax increases” because schools will have the authority to raise those taxes if state aid isn't enough to meet the per-pupil cost. He also said scaling back the tax cut put Wisconsin at an economic disadvantage to neighboring states that have lower rates.
“Legislative Republicans worked tirelessly over the last few months to block Governor Evers’ liberal tax and spending agenda," Vos said in a statement. “Unfortunately, because of his powerful veto authority, he reinstated some of it today.”
Vos did not say if Republicans would attempt veto overrides, an effort that is almost certain to fail because they would need Democratic votes in the Assembly to get the two-thirds majority required by state law.
Republicans proposed tapping nearly half of the state's projected $7 billion budget surplus to cut income taxes across the board and reduce the number of brackets from four to three.
Evers kept all four brackets. The remaining $175 million in tax cuts over the next two years are directed to the lowest two tax rates, paid by households earning less than $36,840 a year or individuals who make less than $27,630. Wealthier payers will also benefit from the cuts but must continue to pay higher rates on income that exceeds those limits.
Evers was unable to undo the $32 million cut to the University of Wisconsin, which was funding that Republicans said would have gone toward diversity, equity and inclusion — or DEI — programming and staff. The budget Evers signed does allow for the university to get the funding later if it can show it would go toward workforce development and not DEI.
Evers previously threatened to veto the entire budget over the UW cut. But on Wednesday, he used his partial veto to protect 188 DEI positions at UW that were slated for elimination under the Republican plan.
Evers called cuts to UW funding “shortsighted, misguided and wrong for the workforce and wrong for our state." But he also said he was confident UW would be able to work with lawmakers to get the $32 million later.
Another of Evers' vetoes removed a measure that would have prohibited Medicaid payments for gender-affirming care. The governor accused Republicans of “perpetuating hateful, discriminatory, and anti-LGBTQ policies and rhetoric” with the proposal.
No Democratic lawmaker voted for the budget, but most stopped short of calling for a total veto.
Evers ignored a call from 15 liberal advocacy and government watchdog groups that had urged him to “fight like hell for our collective future” and veto the entire budget, which they argued would further racial and economic inequality.
Evers said vetoing the entire budget would have left schools in the lurch and meant rejecting $125 million in funding to combat water pollution caused by so-called forever chemicals known as PFAS, along with turning down $525 million for affordable housing and pay raises for state workers.
No governor has vetoed the budget in its entirety since 1930. This marks the third time that Evers has signed a budget into law that was passed by a Republican-controlled Legislature. In 2019, he issued 78 partial vetoes and in 2021 he made 50. That year, Evers took credit for the income tax cut written by Republicans and used it as a key part of his successful 2022 reelection campaign.
This year he made 51 partial vetoes.
The budget also increases pay for all state employees by 6% over the next two years, with higher increases for guards at the state's understaffed state prisons.
Harm Venhuizen is a corps member for the Associated Press/Report for America Statehouse News Initiative. Report for America is a nonprofit national service program that places journalists in local newsrooms to report on undercovered issues. Follow Harm on Twitter.