By Matthew Perrone
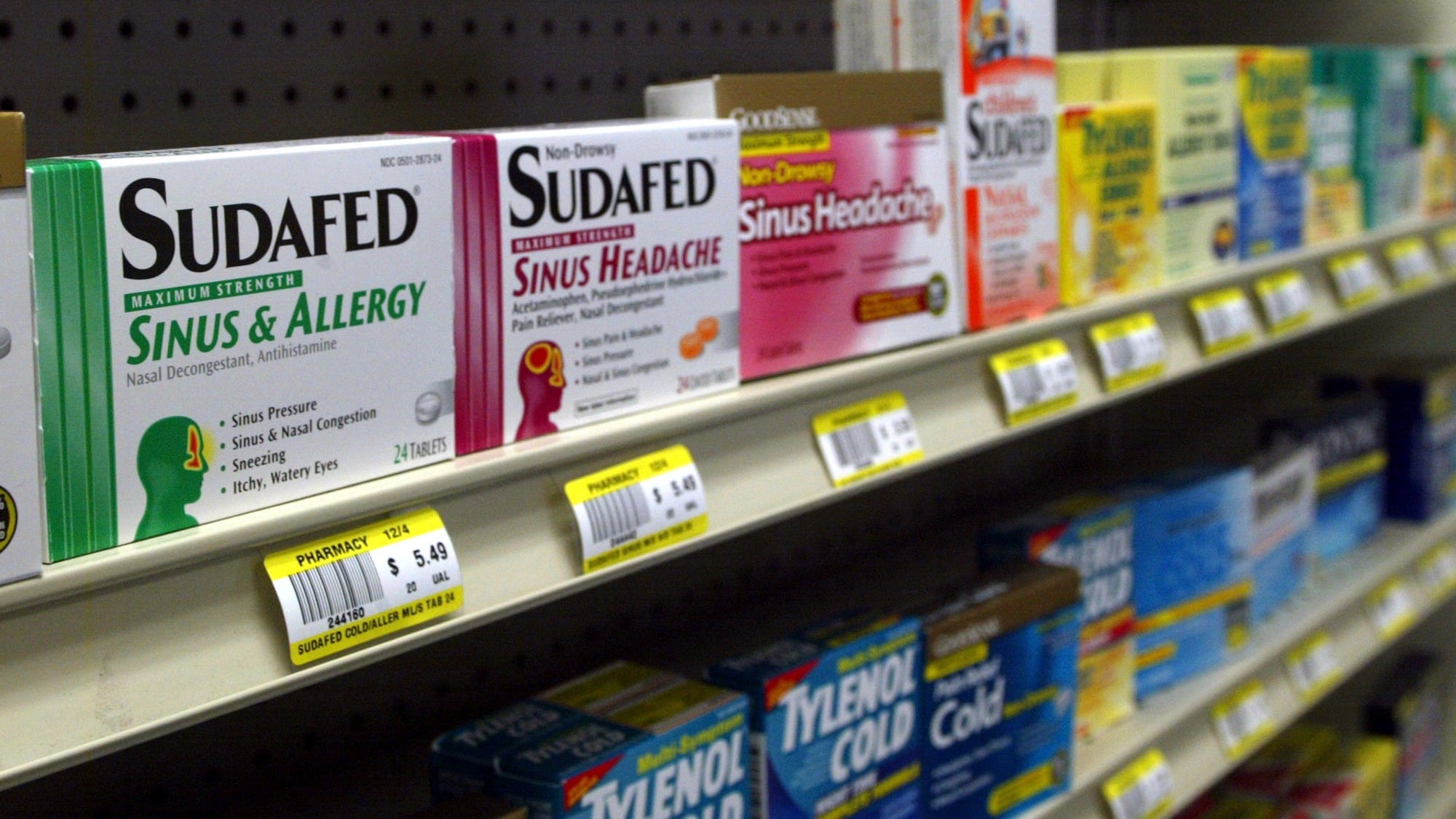
The leading decongestant used by millions of Americans looking for relief from a stuffy nose is no better than a dummy pill, according to government experts who reviewed the latest research on the long-questioned drug ingredient.
Advisers to the Food and Drug Administration voted unanimously on Tuesday against the effectiveness of the key drug found in popular versions of Sudafed, Allegra, Dayquil and other medications stocked on store shelves.
“Modern studies, when well conducted, are not showing any improvement in congestion with phenylephrine,” said Dr. Mark Dykewicz, an allergy specialist at the Saint Louis University School of Medicine.
The FDA assembled its outside advisers to take another look at phenylephrine, which became the main drug in over-the-counter decongestants when medicines with an older ingredient — pseudoephedrine — were moved behind pharmacy counters. A 2006 law had forced the move because pseudoephedrine can be illegally processed into methamphetamine.
Those original versions of Sudafed and other medicines remain available without a prescription, but they're less popular and account for about one-fifth of the $2.2 billion market for oral decongestants. Phenylephrine versions — sometimes labeled “PE” on packaging — make up the rest.
If the FDA follows through on the panel’s recommendations, Johnson & Johnson, Bayer and other drugmakers could be required to pull their oral medications containing phenylephrine from store shelves. That would likely force consumers to switch to the behind-the-counter pseudoephedrine products or to phenylephrine-based nasal sprays and drops.
In that scenario, the FDA would have to work with drugstores, pharmacists and other health providers to educate consumers about the remaining options for treating congestion, panelists said Tuesday.
The group also told the FDA that studying phenylephrine at higher doses was not an option because it can push blood pressure to potentially dangerous levels.
“I think there’s a safety issue there,” said Dr. Paul Pisaric of Archwell Health in Oklahoma. “I think this is a done deal as far as I’m concerned. It doesn’t work.”
This week’s two-day meeting was prompted by University of Florida researchers who petitioned the FDA to remove most phenylephrine products based on recent studies showing they failed to outperform placebo pills in patients with cold and allergy congestion. The same researchers also challenged the drug’s effectiveness in 2007, but the FDA allowed the products to remain on the market pending additional research.
That was also the recommendation of FDA's outside experts at the time, who met for a similar meeting on the drug in 2007.
This time, the 16 members of the FDA panel unanimously agreed that current evidence doesn't show a benefit for the drug.
“I feel this drug in this oral dose should have been removed from the market a long time ago,” said Jennifer Schwartzott, the patient representative on the panel. “Patients require and deserve medications that treat their symptoms safely and effectively and I don’t believe that this medication does that.”
The advisers essentially backed the conclusions of an FDA scientific review published ahead of this week’s meeting, which found numerous flaws in the 1960s and 1970s studies that supported phenylephrine’s original approval. The studies were “extremely small” and used statistical and research techniques no longer accepted by the agency, regulators said.
“The bottom line is that none of the original studies stand up to modern standards of study design or conduct,” said Dr. Peter Starke, the agency’s lead medical reviewer.
Additionally, three larger, rigorously conducted studies published since 2016 showed no difference between phenylephrine medications and placebos for relieving congestion. Those studies were conducted by Merck and Johnson & Johnson and enrolled hundreds of patients.
A trade group representing nonprescription drugmakers, the Consumer Healthcare Products Association, argued that the new studies had limitations and that consumers should continue to have “easy access” to phenylephrine.
Like many other over-the-counter ingredients, phenylephrine was essentially grandfathered into approval during a sweeping FDA review begun in 1972. It has been sold in various forms for more than 75 years, predating the agency's own regulations on drug effectiveness.
“Any time a product has been on the market that long, it’s human nature to make assumptions about what we think we know about the product,” said Dr. Theresa Michele, who leads the FDA’s office of nonprescription drugs.
But FDA reviewers said their latest assessment reflects new testing insights into how quickly phenylephrine is metabolized when taken by mouth, leaving only trace levels that reach nasal passages to relieve congestion. The drug appears more effective when applied directly to the nose, in sprays or drops, and those products are not under review.
There’s unlikely to be any immediate impact from Tuesday’s panel vote, which is not binding.
The group’s negative opinion opens the door for the FDA to pull phenylephrine from a federal list of decongestants deemed effective for over-the-counter pills and liquids. The FDA said removing the products would eliminate “unnecessary costs and delay in care of taking a drug that has no benefit.”
The FDA's nasal decongestants drug list, or monograph, has not been updated since 1995. The process for changing a monograph has traditionally taken years or decades, requiring multiple rounds of review and public comment. But a 2020 law passed by Congress streamlines the process, which should allow the FDA to accelerate the publication of new standards for nonprescription ingredients.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.