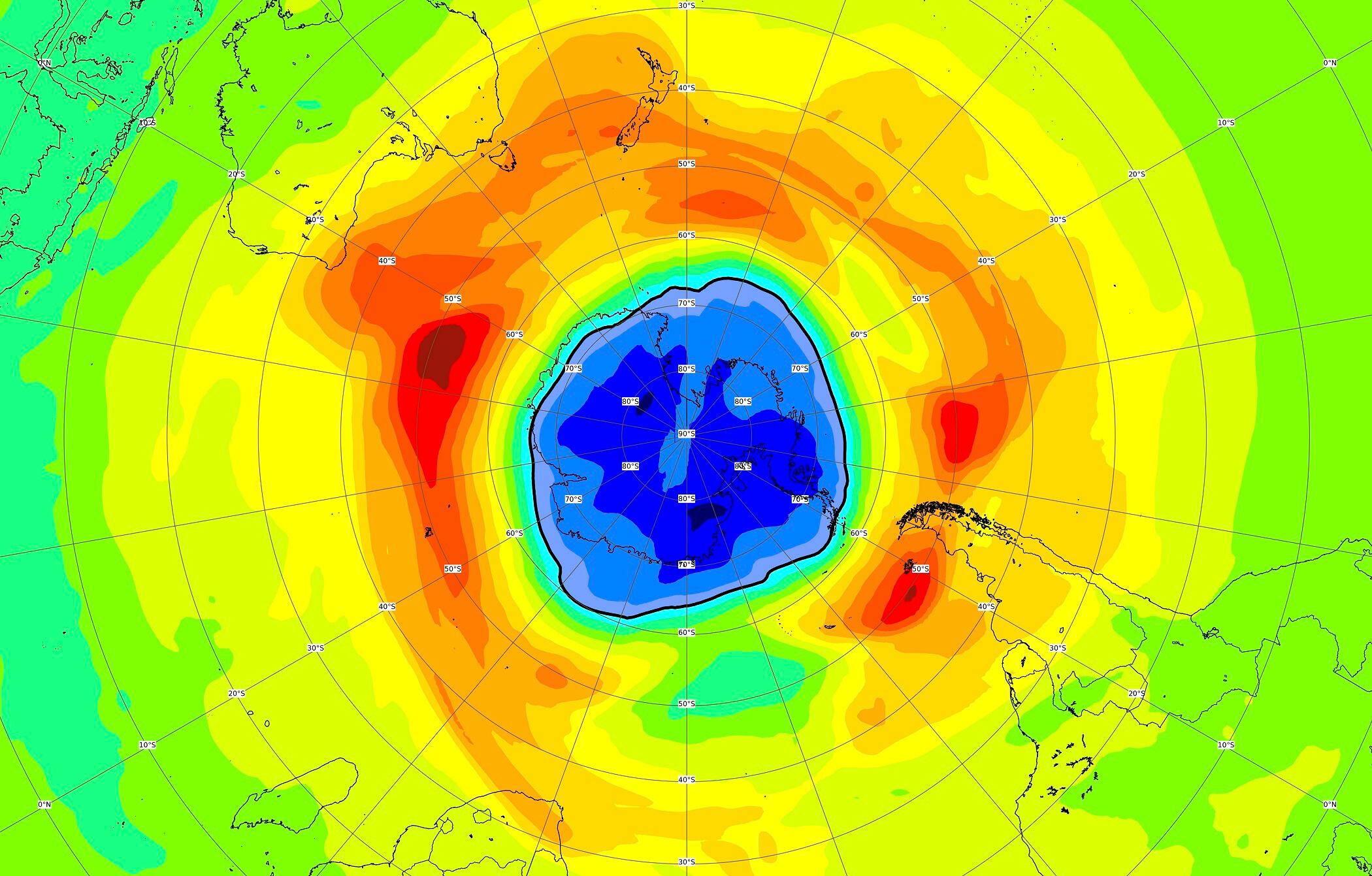
Scientists say the hole in the Earth’s protective ozone layer over the Southern Hemisphere is larger than usual this year and already surpasses the size of Antarctica.
The European Union’s Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service said Thursday that the so-called ozone hole, which appears every year during the Southern Hemisphere spring, has grown considerably in the past week following an average start.
“Forecasts show that this year´s hole has evolved into a rather larger than usual one,” said Vincent-Henri Peuch, who heads the EU's satellite monitoring service.
“We are looking at a quite big and potentially also deep ozone hole,” he said.
Atmospheric ozone absorbs ultraviolet light coming from the sun. Its absence means more of this high-energy radiation reaches the Earth, where it can harm living cells.
Peuch noted that last year's ozone hole also started out unremarkably but then turned into one of the longest-lasting ones on record.
The Montreal Protocol, signed in 1987, led to a ban on a group of chemicals called halocarbons that were blamed for exacerbating the annual ozone hole.
Experts say that while the ozone layer is beginning to recover, it's likely to take until the 2060s for the ozone-depleting substances used in refrigerants and spray cans to completely disappear from the atmosphere.
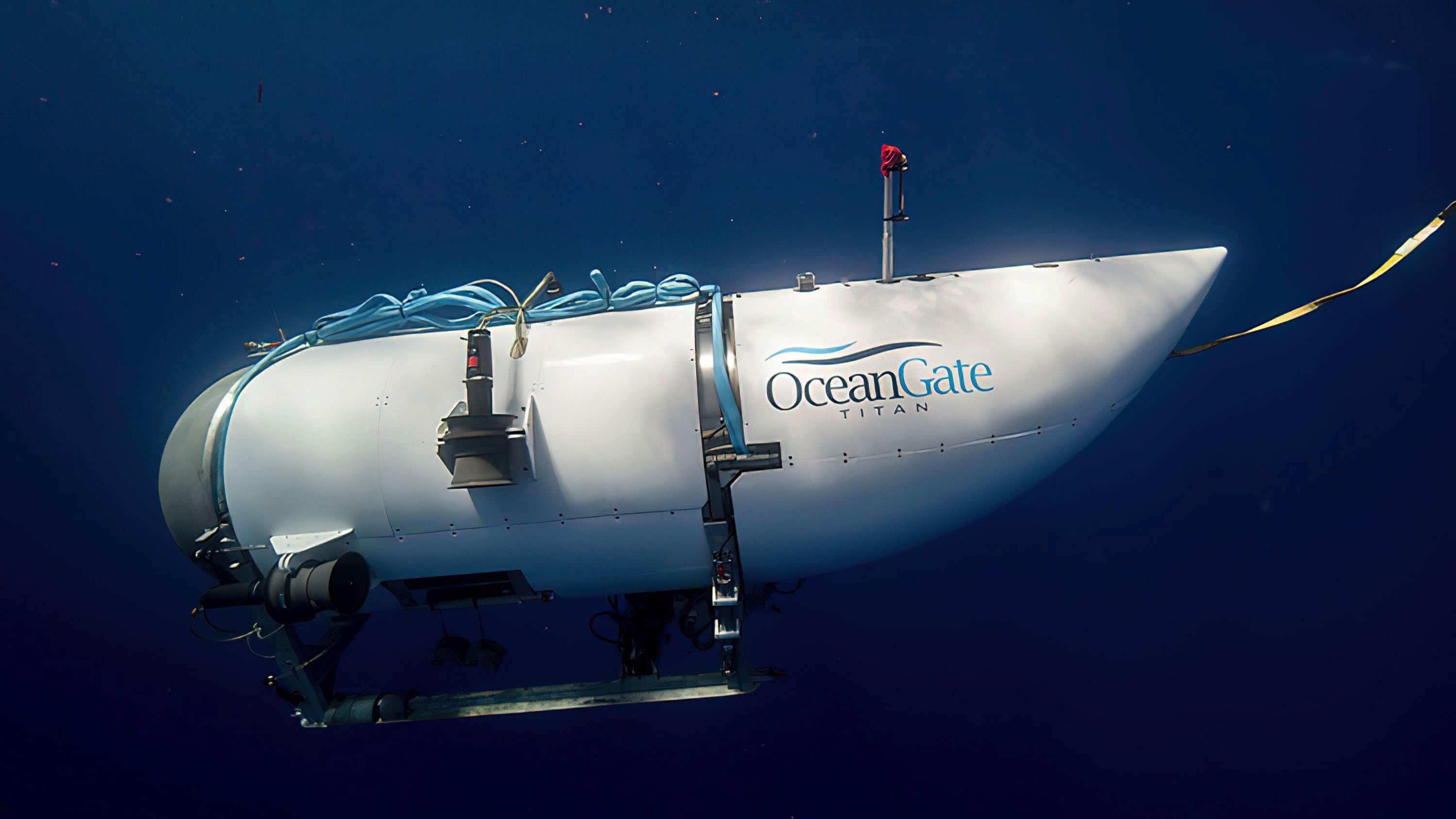
OceanGate Expeditions on Thursday said pilot and chief executive Stockton Rush, along with passengers Shahzada Dawood and his son Suleman Dawood, Hamish Harding, and Paul-Henri Nargeolet “have sadly been lost.”
A new study on loneliness is showing it may not only affect mental health, but it may also be bad for the bones. However, the study found it impacts one group in particular: men. Amid concerns about the rising epidemic of loneliness, researchers wanted to take a closer look at its effects.
Be Well: 2-Minute Morning Stretch Routine
Be Well: Celebrity Trainer Bob Harper Talks Heart Health
A new study from Finland found that "night owls," or people who tend to stay up late, don't live as long as those who go to bed early and wake up early as well.
Confidence in the scientific community declined among U.S. adults in 2022, a major survey shows, driven by a partisan divide in views of both science and medicine that emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The American Cancer Society estimates that over 20,000 new cancer cases in Connecticut this year alone. But there's a concerning shortage of chemotherapy drugs in the state and across the country. News 12 reporter Mark Sudol tells us why and what can be done.
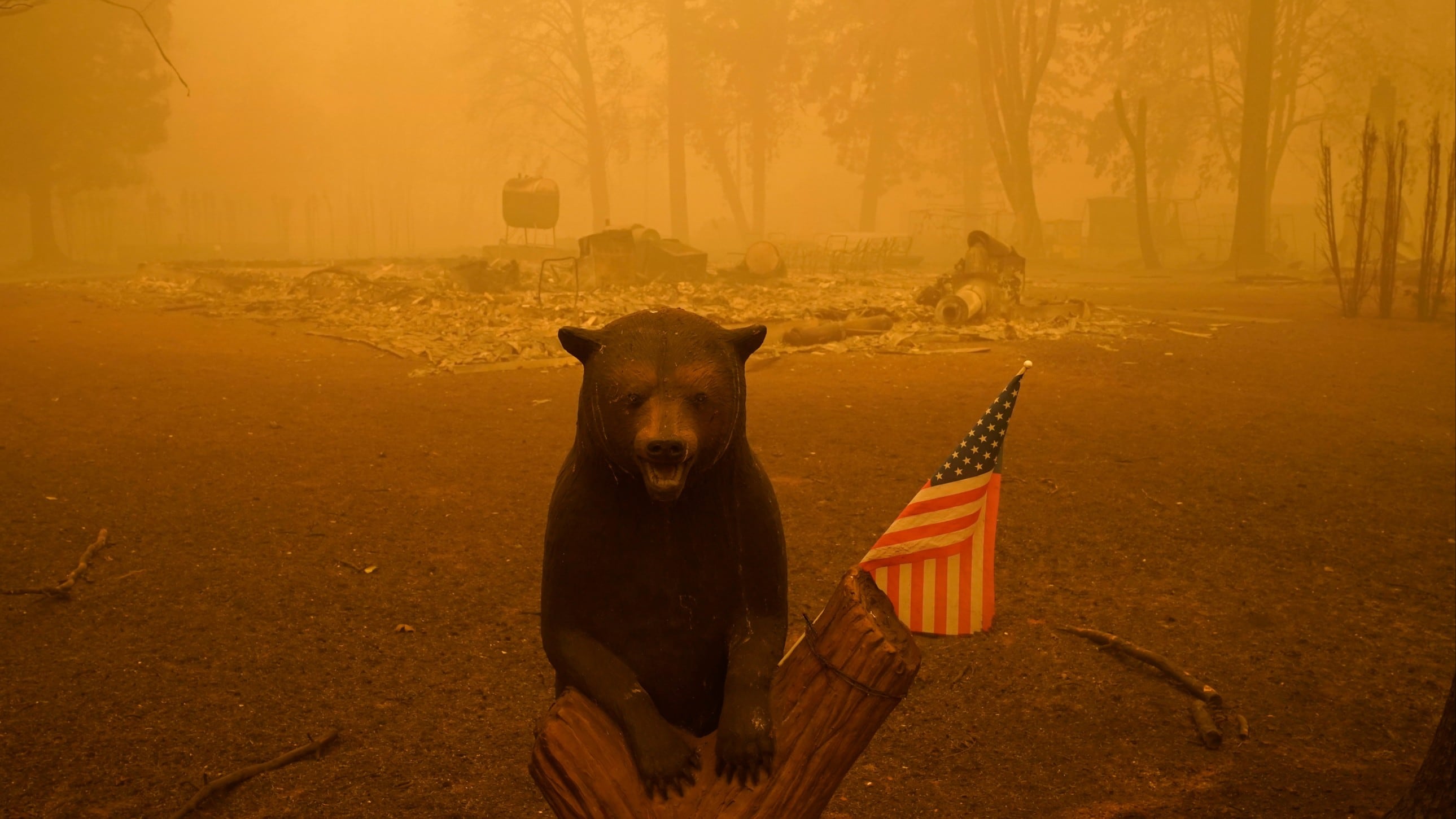
A jury in Oregon says the electric utility PacifiCorp must pay punitive damages for causing devastating wildfires in 2020 — on top of an earlier verdict already expected to amount to billions of dollars.
Pfizer is warning that an antibiotic used to treat syphilis and other bacterial infections in young people are likely to run out by the end of this quarter.
Be Well: Alex Rodriguez on the Importance of Dental Hygiene Following Gum Disease Diagnosis