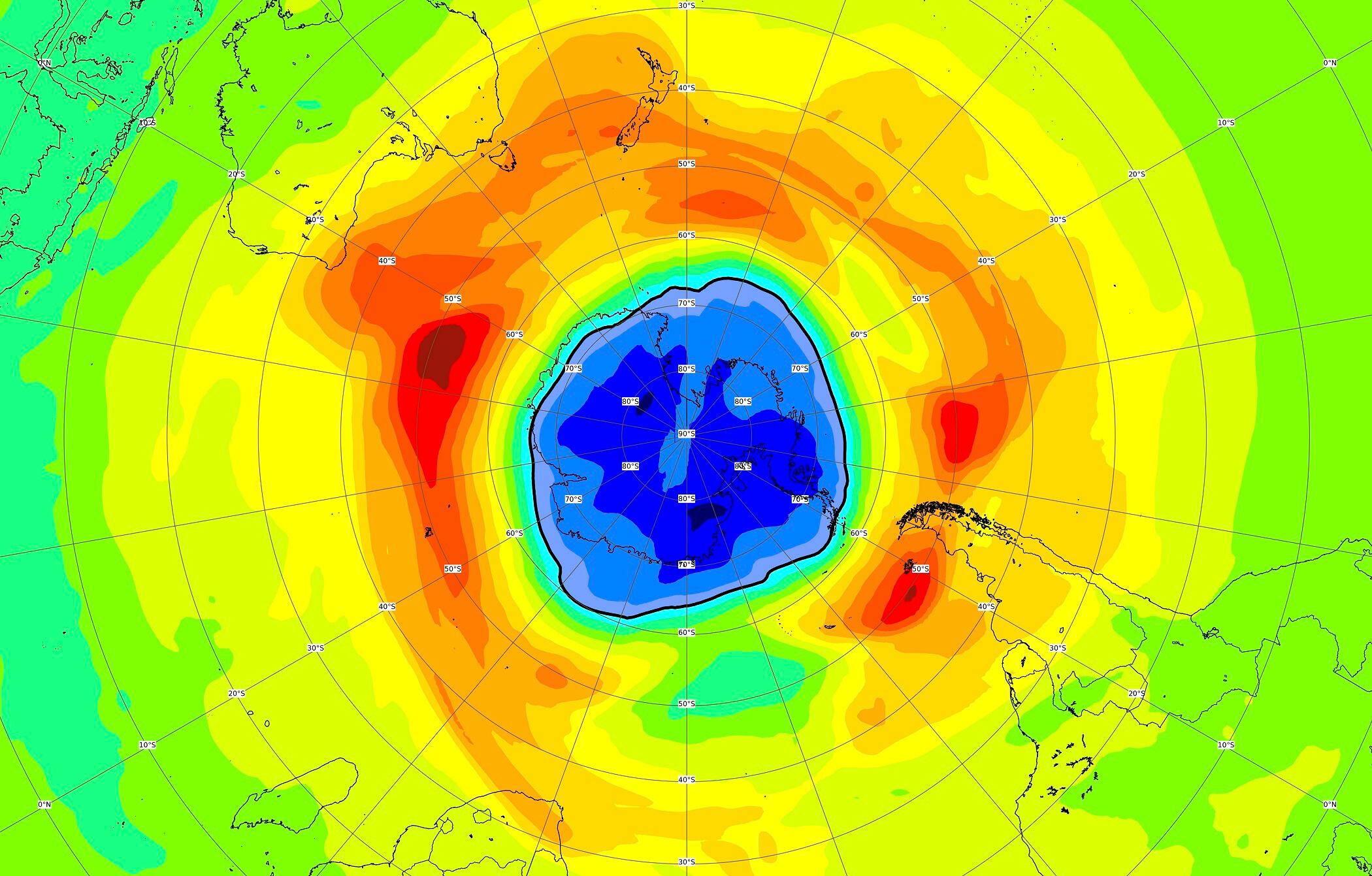
Scientists say the hole in the Earth’s protective ozone layer over the Southern Hemisphere is larger than usual this year and already surpasses the size of Antarctica.
The European Union’s Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service said Thursday that the so-called ozone hole, which appears every year during the Southern Hemisphere spring, has grown considerably in the past week following an average start.
“Forecasts show that this year´s hole has evolved into a rather larger than usual one,” said Vincent-Henri Peuch, who heads the EU's satellite monitoring service.
“We are looking at a quite big and potentially also deep ozone hole,” he said.
Atmospheric ozone absorbs ultraviolet light coming from the sun. Its absence means more of this high-energy radiation reaches the Earth, where it can harm living cells.
Peuch noted that last year's ozone hole also started out unremarkably but then turned into one of the longest-lasting ones on record.
The Montreal Protocol, signed in 1987, led to a ban on a group of chemicals called halocarbons that were blamed for exacerbating the annual ozone hole.
Experts say that while the ozone layer is beginning to recover, it's likely to take until the 2060s for the ozone-depleting substances used in refrigerants and spray cans to completely disappear from the atmosphere.
A 29-year-old Cincinnati woman was awakened by her Apple Watch, which alerted her about an elevated heart rate, prompting her to head to a doctor who notified her of a blood clot.
Cheddar News checks in with a coast-to-coast forecast of the weather.
A quarantine is in place for a section of Broward county in Florida due to a rise in African land snails, which are harmful to agriculture and can eat their way through about 500 plant species.
Climate change is on trial in Montana. In a landmark case, 16 young people are suing the state over effects like smoke, heat, and drought. It's just the first in a series of cases intended to pressure lawmakers into taking action on the environment. Here with more is Cheddar News Senior Reporter Chloe Aiello.
Be Well: 2-Minute Breathing and Stretching Routine
Be Well: Keeping Your Kids Safe During Summer Sports & Activities
Members of the United Nations adopted the first-ever treaty to protect marine life in the high seas on Monday, with the U.N.'s chief hailing the historic agreement as giving the ocean “a fighting chance.”
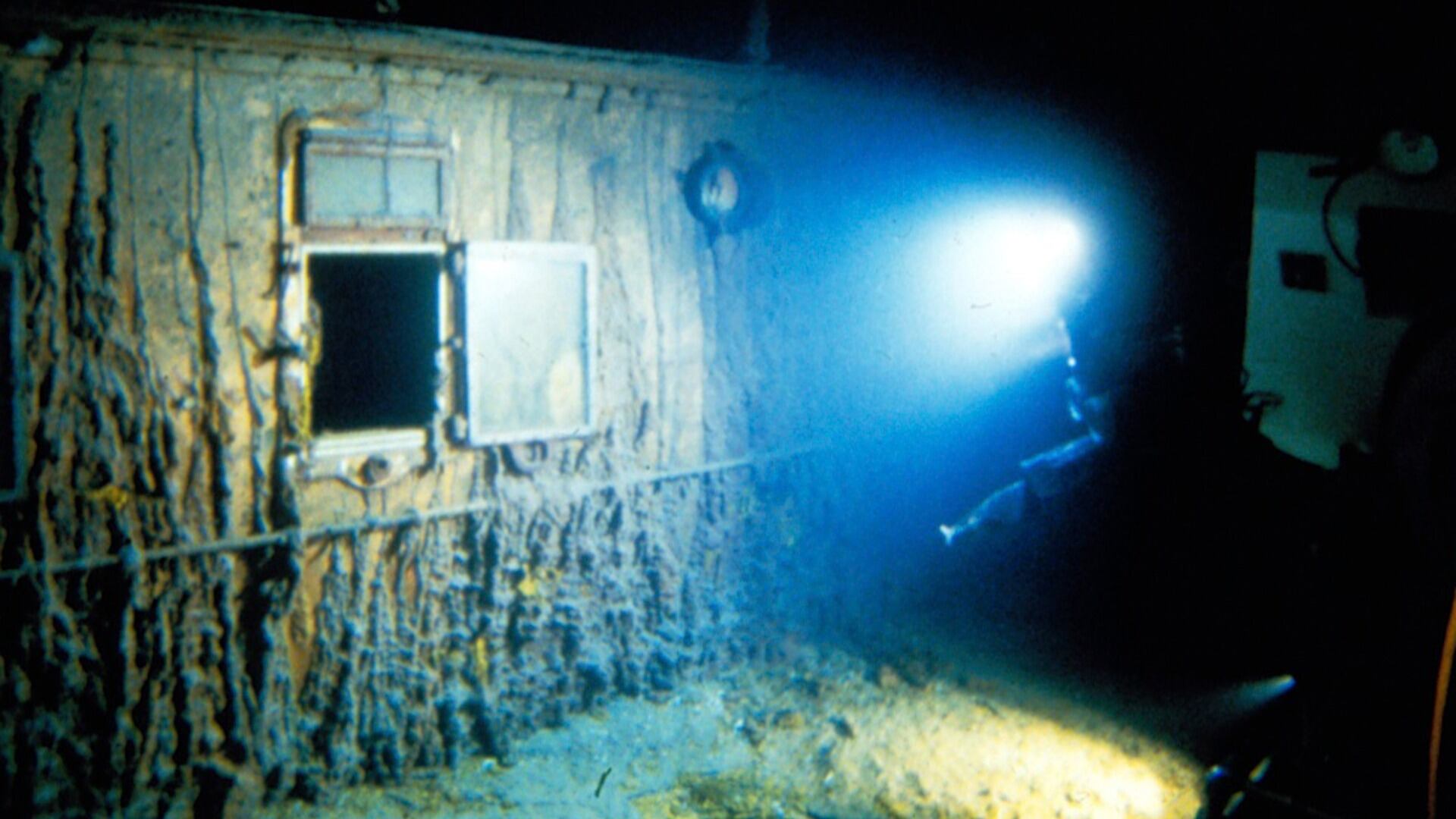
A search is underway for a deep-sea vessel that went missing with five people aboard after it dived toward the deteriorating wreck site of the Titanic ocean liner. What we know so far.
U.S. Hit With Record Breaking Heat Waves
It's only June and already scientists are saying it could be the hottest year on record, as the warming effects of El Niño will continue to strengthen into the fall and winter. Here with more is Cheddar News Senior Reporter Chloe Aiello.