By Seth Borenstein
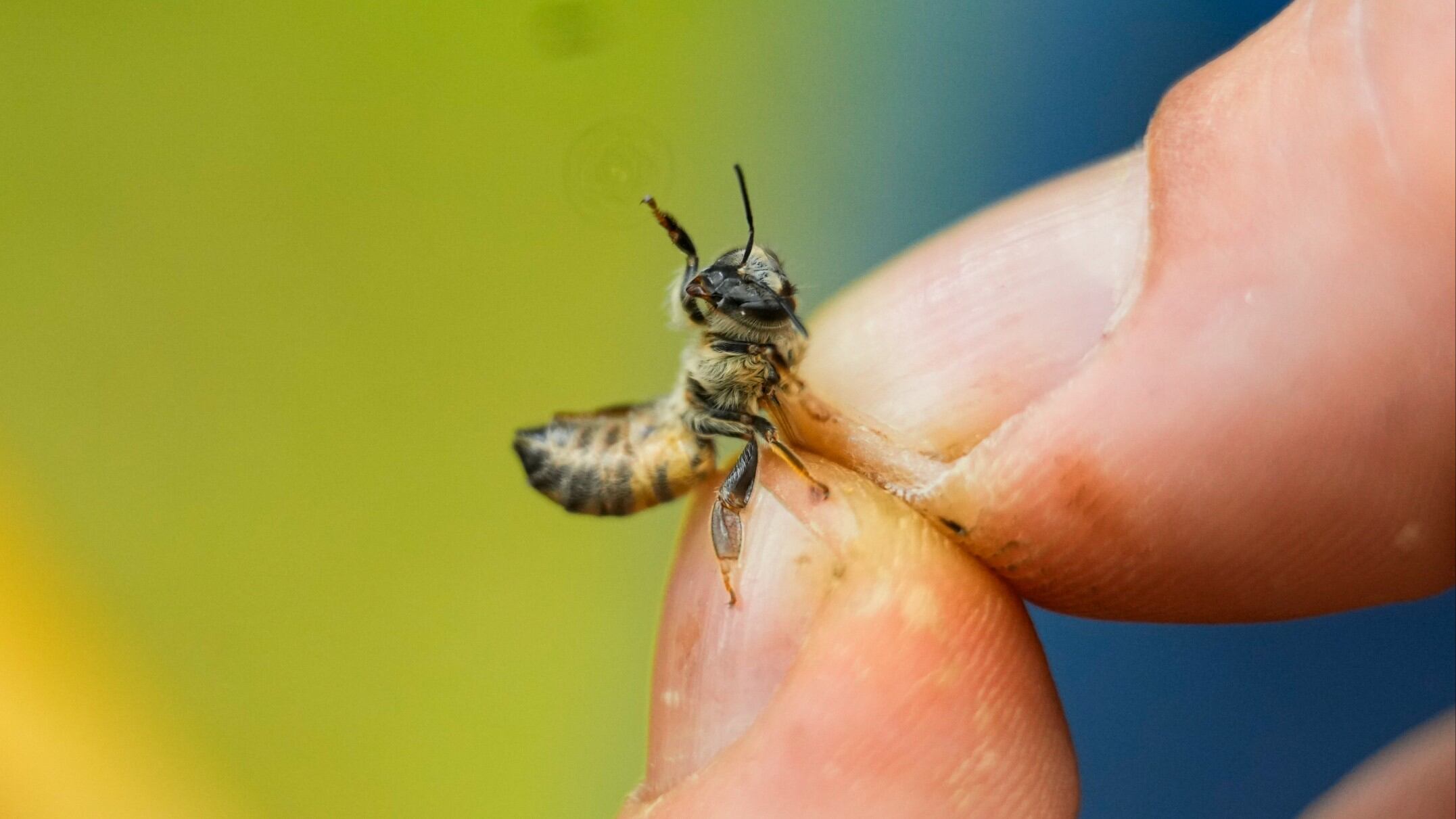
America’s honeybee hives just staggered through the second highest death rate on record, with beekeepers losing nearly half of their managed colonies, an annual bee survey found.
But using costly and Herculean measures to create new colonies, beekeepers are somehow keeping afloat. Thursday’s University of Maryland and Auburn University survey found that even though 48% of colonies were lost in the year that ended April 1, the number of United States honeybee colonies "remained relatively stable.”
Honeybees are crucial to the food supply, pollinating more than 100 of the crops we eat, including nuts, vegetables, berries, citrus and melons. Scientists said a combination of parasites, pesticides, starvation and climate change keep causing large die-offs.
Last year’s 48% annual loss is up from the previous year’s loss of 39% and the 12-year average of 39.6%, but it’s not as high as 2020-2021’s 50.8% mortality rate, the survey found. Beekeepers told the surveying scientists that 21% loss over the winter is acceptable and more than three-fifths of beekeepers surveyed said their losses were higher than that.
“This is a very troubling loss number when we barely manage sufficient colonies to meet pollination demands in the U.S.,” said former government bee scientist Jeff Pettis, president of the global beekeeper association Apimondia that wasn’t part of the study. “It also highlights the hard work that beekeepers must do to rebuild their colony numbers each year."
The overall bee colony population is relatively steady because commercial beekeepers split and restock their hives, finding or buying new queens, or even starter packs for colonies, said University of Maryland bee researcher Nathalie Steinhauer, the survey’s lead author. It's an expensive and time consuming process.
The prognosis is not as bad as 15 years ago because beekeepers have learned how to rebound from big losses, she said.
“The situation is not really getting worse, but it’s also not really getting better,” Steinhauer said. “It is not a bee apocalypse.”
Despite big annual losses the situation is a far cry from 2007 when many bee experts expected an end to managed pollination said U.S. Department Agriculture research entomologist Jay Evans, who wasn’t part of the survey.
“There are threats certainly in the environment and honeybees have persisted,” Evans said. “I don’t think honeybees will go extinct but I think they will always have these sort of challenges.”
Some commercial beekeepers who have succeeded in the past lost as much as 80% of their colonies this past year, while other beekeepers did well, it varied so much, Evans said. Pettis, who has 150 colonies on Maryland’s Eastern shore, had less than 18% loss, saying he used organic acids for mite control.
The parasitic mite Varroa destructor that helps transmit viruses is the chief culprit, but bad weather and queen issues were also big problems in the past year, Steinhauer said. Pesticides also make things worse because it makes bees more vulnerable to diseases and less likely to seek food, she said.
“It really can be like death by a thousand cuts with the most obvious one being varroa,” Steinhauer said.
The mite varroa is a flat creature that crawls on the bee – it would be the equivalent of a frisbee or flat softball on human bodies – Evans said. The mite seems to make it easier for viruses to attack and kill bees, he and Steinhauer said.
It used to take large amounts of varroa, such as in 60% of a colony, to cause virus problems, but now even small infestations at 1% or 2% in a colony can cause massive problems, Steinhauer said.
“We are fighting this evolving enemy,” Steinhauer said.
Another problem is landscapes that have only one crop or homogenous landscapes which deprive bees of food, while pesticides and bouts of extreme weather also have caused problems.
For example in the Washington, D.C. area unusual 80-degree warmth in January brought some bees out of their normal winter routine and then when it turned cool again, they had problems, Evans said.
“The impact of climate change on bee colony survival is real and can go undetected,” Pettis said in an email.
The demand for pollination from commercial bee colonies is growing even as the beekeepers have to work harder to make up for losses, Steinhauer said. The U.S. Department of Agriculture says 35% of the human diet comes from insect-pollinated plants and the honeybee is responsible for 80% of that pollination.
“There is this whole side of our agricultural industry that relies on these colonies,” Steinhauer said. “And the fact that every year the commercial beekeepers have to invest so much more effort to keep those numbers up because they have to fulfill those pollination contracts puts a lot of stress on those beekeepers and the bees.” ___