By Seth Borenstein
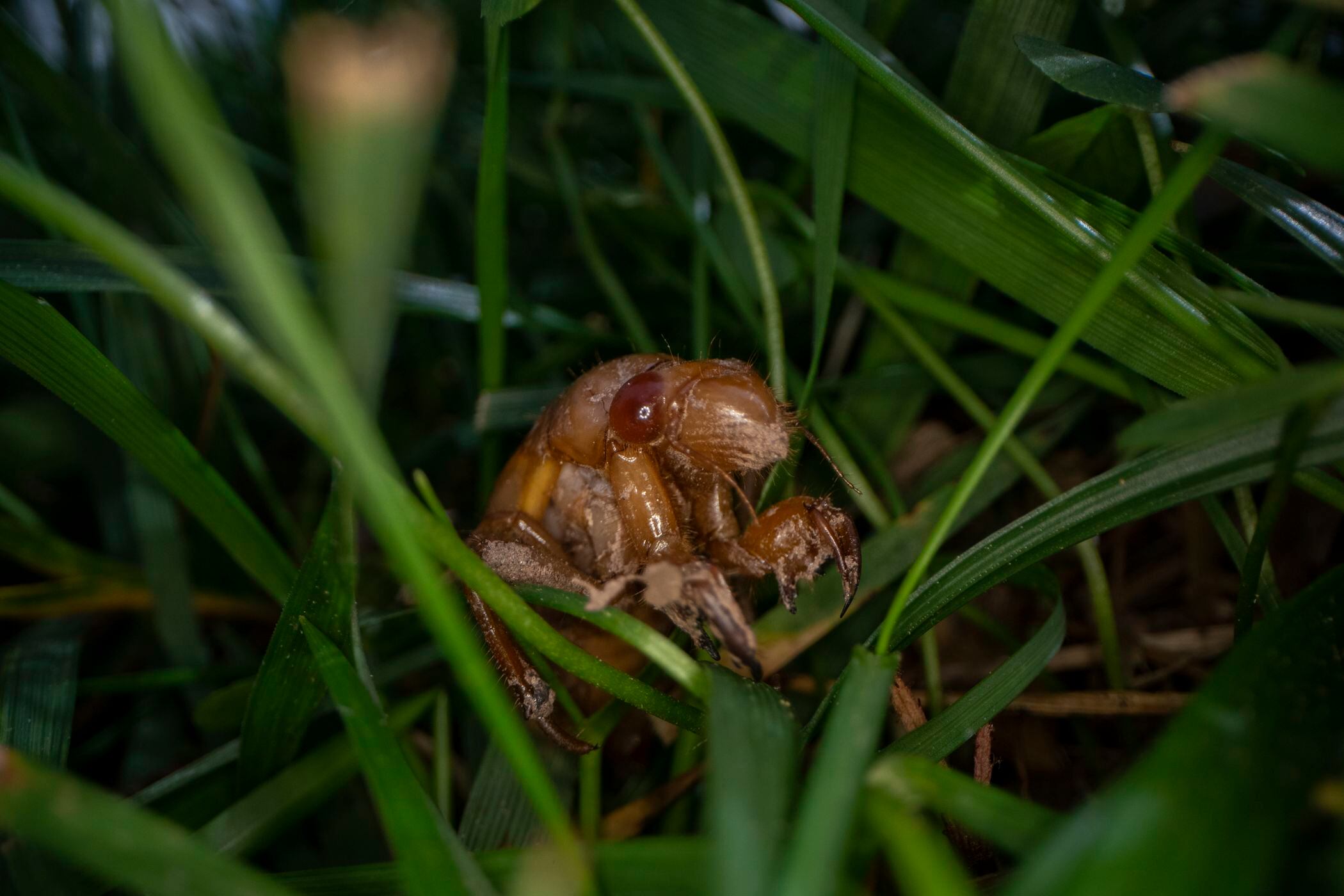
Sifting through a shovel load of dirt in a suburban backyard, Michael Raupp and Paula Shrewsbury find their quarry: a cicada nymph.
And then another. And another. And four more.
In maybe a third of a square foot of dirt, the University of Maryland entomologists find at least seven cicadas -- a rate just shy of a million per acre. A nearby yard yielded a rate closer to 1.5 million.
And there's much more afoot. Trillions of the red-eyed black bugs are coming, scientists say.
Within days, a couple weeks at most, the cicadas of Brood X (the X is the Roman numeral for 10) will emerge after 17 years underground. There are many broods of periodic cicadas that appear on rigid schedules in different years, but this is one of the largest and most noticeable. They’ll be in 15 states from Indiana to Georgia to New York; they’re coming out now in mass numbers in Tennessee and North Carolina.
When the entire brood emerges, backyards can look like undulating waves, and the bug chorus is lawnmower loud.
The cicadas will mostly come out at dusk to try to avoid everything that wants to eat them, squiggling out of holes in the ground. They’ll try to climb up trees or anything vertical, including Raupp and Shrewsbury. Once off the ground, they shed their skins and try to survive that vulnerable stage before they become dinner to a host of critters including ants, birds, dogs, cats and Raupp.
It’s one of nature’s weirdest events, featuring sex, a race against death, evolution and what can sound like a bad science fiction movie soundtrack.
Some people may be repulsed. Psychiatrists are calling entomologists worrying about their patients, Shrewsbury said. But scientists say the arrival of Brood X is a sign that despite pollution, climate change and dramatic biodiversity loss, something is still right with nature. And it’s quite a show.
Raupp presents the narrative of cicada’s lifespan with all the verve of a Hollywood blockbuster:
“You’ve got a creature that spends 17 years in a COVID-like existence, isolated underground sucking on plant sap, right? In the 17th year these teenagers are going to come out of the earth by the billions if not trillions. They’re going to try to best everything on the planet that wants to eat them during this critical period of the nighttime when they’re just trying to grow up, they’re just trying to be adults, shed that skin, get their wings, go up into the treetops, escape their predators,” he says.
“Once in the treetops, hey, it’s all going to be about romance. It’s only the males that sing. It’s going to be a big boy band up there as the males try to woo those females, try to convince that special someone that she should be the mother of his nymphs. He’s going to perform, sing songs. If she likes it, she’s going to click her wings. They’re going to have some wild sex in the treetop.
“Then she’s going to move out to the small branches, lay their eggs. Then it’s all going to be over in a matter of weeks. They’re going to tumble down. They’re going to basically fertilize the very plants from which they were spawned. Six weeks later the tiny nymphs are going to tumble 80 feet from the treetops, bounce twice, burrow down into the soil, go back underground for another 17 years.”
“This,” Raupp says, “is one of the craziest life cycles of any creature on the planet.”
America is the only place in the world that has periodic cicadas that stay underground for either 13 or 17 years, says entomologist John Cooley of the University of Connecticut.
The bugs only emerge in large numbers when the ground temperature reaches 64 degrees. That’s happening earlier in the calendar in recent years because of climate change, says entomologist Gene Kritsky. Before 1950 they used to emerge at the end of May; now they’re coming out weeks earlier.
Though there have been some early bugs In Maryland and Ohio, soil temperatures have been in the low 60s. So Raupp and other scientists believe the big emergence is days away -- a week or two, max.
Cicadas who come out early don’t survive. They’re quickly eaten by predators. Cicadas evolved a key survival technique: overwhelming numbers. There’s just too many of them to all get eaten when they all emerge at once, so some will survive and reproduce, Raupp says.
This is not an invasion. The cicadas have been here the entire time, quietly feeding off tree roots underground, not asleep, just moving slowly waiting for their body clocks tell them it is time to come out and breed. They’ve been in America for millions of years, far longer than people.
When they emerge, it gets noisy -- 105 decibels noisy, like “a singles bar gone horribly, horribly wrong,” Cooley says. There are three distinct cicada species and each has its own mating song.
They aren’t locusts and the only plants they damage are young trees, which can be netted. The year after a big batch of cicadas, trees actually do better because dead bugs serve as fertilizer, Kritsky says.
People tend to be scared of the wrong insects, says University of Illinois entomologist May Berenbaum. The mosquito kills more people than any other animals because of malaria and other diseases. Yet some people really dread the cicada emergence, she said.
“I think it’s the fact that they’re an inconvenience. Also, when they die in mass numbers they smell bad,” Berenbaum says. “They really disrupt our sense of order.”
But others are fond of cicadas -- and even munch on them, using recipes like those in a University of Maryland cookbook. And for scientists like Cooley, there is a real beauty in their life cycle.
“This is a feel-good story, folks. It really is and it’s in a year we need more,” he says. “When they come out, it’s a great sign that forests are in good shape. All is as it is supposed to be.”
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.