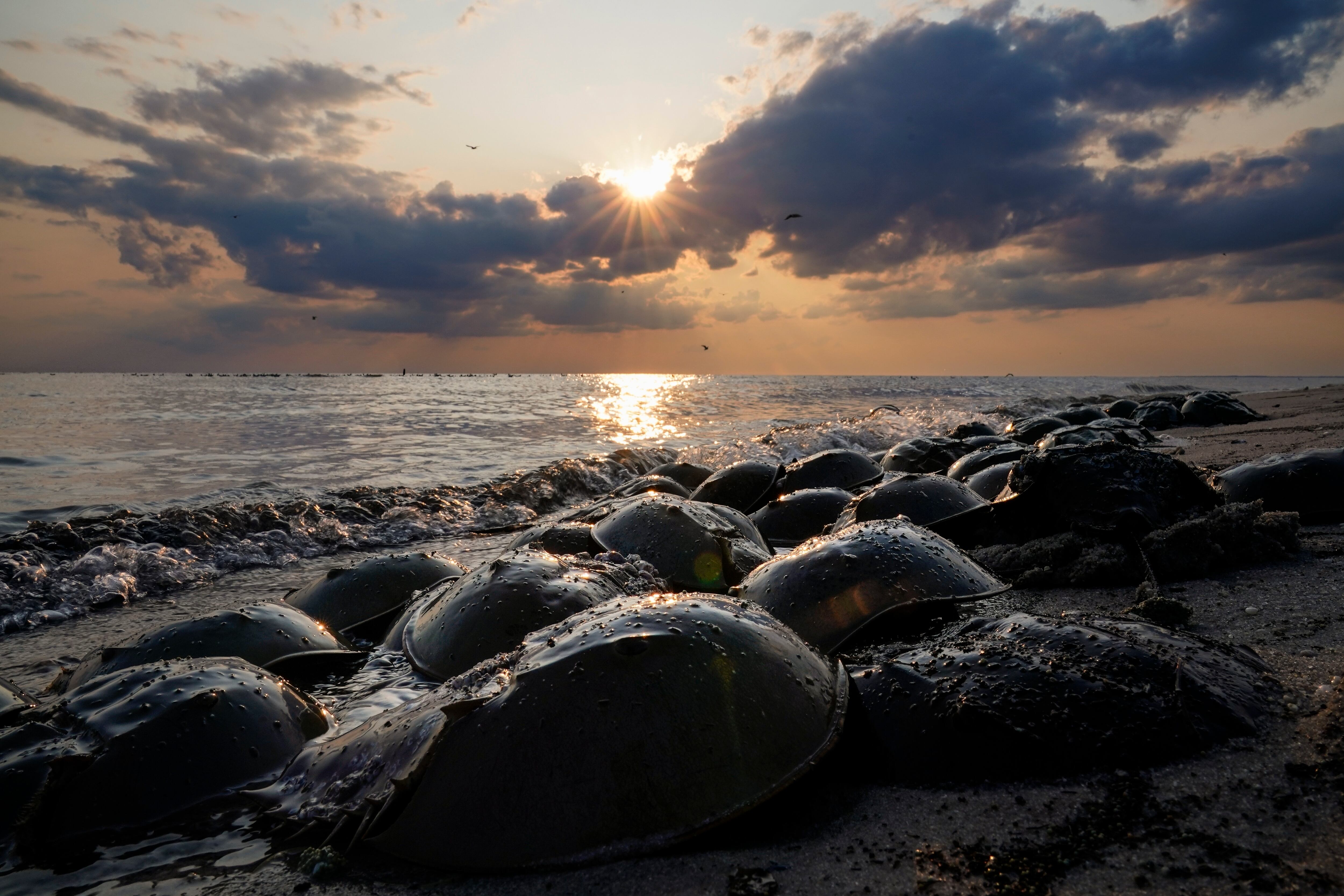
The horseshoe crab has been scuttling in the ocean and tidal pools for more than 400 million years, playing a vital role in the East Coast ecosystem along with being a prized item for fishing bait and medical research.
Its blue blood is harvested for medical researchers and used by drug and medical device makers to test for dangerous impurities in vaccines, prosthetics and intravenous drugs. The crabs are used by fishing crews as bait to catch eels and sea snails. And their eggs are a critical food for a declining subspecies of bird called the red knot – a rust-colored, migratory shorebird listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act.
The competing interests have set up a clash among researchers, fishing crews and environmentalists over new protections designed to keep more of the crabs in the environment. The animals are drained of some of their blood and returned to the shore, but many die from the bleeding. And a drive to create synthetic alternatives has yet to succeed in phasing out the crabs from use.
Recent revisions to guidelines for handling the animals should keep more alive through the process, regulators said. The animals — not really true crabs but rather more closely related to land-dwelling invertebrates such as spiders and scorpions — are declining in some of their East Coast range.
"They were here before the dinosaurs," said Glenn Gauvry, president of Ecological Research & Development Group, a Delaware-based nonprofit that advocates for horseshoe crab conservation. "And they’re having problems because the new kids on the block, us, haven’t learned to appreciate the elders."
The harvest of horseshoe crabs has emerged as a critical issue for conservationists in recent years because of the red knot. The birds, which migrate some 19,000 miles (30,577 kilometers) roundtrip from South America to Canada and must stop to eat along the way, need stronger protection of horseshoe crabs to survive, said Bethany Kraft, senior director for coastal conservation with the Audubon Society.
Kraft and other wildlife advocates said the fact the guidelines for handling crabs are voluntary and not mandatory leaves the red knot at risk.
“Making sure there is enough to fuel these birds on this massive, insanely long flight is just critical,” Kraft said. “There's very clear linkage between horseshoe crabs and the survival of the red knot in the coming decades.”
The horseshoe crabs are valuable because their blood can be manufactured into limulus amebocyte lysate, or LAL, that is used to detect pathogens in indispensable medicines such as injectable antibiotics. The crabs are collected by fishermen by hand or via trawlers for use by biomedical companies, then their blood is separated and proteins within their white blood cells are processed. It takes dozens of the crabs to produce enough blood to fill a single glass tube with its blood, which contains immune cells sensitive to bacteria.
There are only five federally licensed manufacturers on the East Coast that process horseshoe crab blood. The blood is often described by activist groups as worth $15,000 a quart (liter), though some members of the industry say that figure is impossible to verify.
Regulators estimate about 15% of the crabs die in the bleeding process. In 2021, that meant about 112,000 crabs died, said Caitlin Starks, a senior fishery management plan coordinator with the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission. The bait fishery for horseshoe crabs, which are used as bait for eels and sea snails, killed more than six times that, she said.
Still, the fisheries commission in May approved new best management practices for the biomedical industry's harvesting and handling of the crabs. Those include minimizing exposure to sunlight and keeping crabs cool and moist, Starks said.
“The goal is to give the crabs that are bled a better chance of surviving and contributing to the ecosystem after they are released,” she said.
That's exactly what the new guidelines will do, said Nora Blair, quality operations manager with Charles River Laboratories, one of the companies that manufactures LAL from horseshoe crab blood. Blair was a member of a working group that crafted the updated guidelines alongside other industry members, conservationists, fishery managers, fishermen and others.
Blair said the industry is working toward synthetic alternatives — an outcome conservationists have been pushing for years. Lonza, a Switzerland-based company that is one of the LAL manufacturers, offers animal-free testing solution, and the company has touted it as a way to test for toxins while protecting natural resources, said Victoria Morgan, a spokesperson for the company.
However, for now the wild harvest of horseshoe crabs remains critically important to drug safety, Blair said.
“The critical role of horseshoe crab in the biopharmaceutical supply chain and coastal ecosystem makes their conservation imperative,” he said.
The Atlantic horseshoe crab, the species harvested on the East Coast, ranges from the Gulf of Maine to Florida. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists the species as being “vulnerable” based on a 2016 assessment.
One of the most important ecosystems for horseshoe crabs is the Delaware Bay, an estuary of the Delaware River between Delaware and New Jersey. The bay is where the crabs breed and the red knots feed.
The density of horseshoe crab eggs in the bay is nowhere near what it was in the 1990s, said Lawrence Niles, an independent wildlife biologist who once headed New Jersey's state endangered species program. Meanwhile, the population of the rufa red knot, the threatened subspecies, has declined by 75% since the 1980s, according to the National Park Service.
The birds need meaningful protection of horseshoe crab eggs to be able to recover, Niles said. He tracks the health of red knots and horseshoe crabs and has organized a group called Horseshoe Crab Recovery Coalition to advocate for conservation measures.
Niles and volunteers he organizes have been counting the horseshoe crab eggs since the 1980s and tagging birds since the 1990s. In mid-June, as he was wrapping up this year's tracking in southern New Jersey, he described the eggs as “good and consistent” through the month.
“What we want is the harvest to stop, the killing to stop, and let the stock rebuild to its carrying capacity,” Niles said.
The horseshoe crabs have been harvested for use as bait and medicine from Florida to Maine over the years, though the largest harvests are in Maryland, Delaware, Massachusetts and Virginia. According to federal fishery statistics, the crabs were worth about $1.1 million in total at the docks in 2021.
That figure is dwarfed by seafood species such as lobsters and scallops, which are routinely worth hundreds of millions of dollars. However, horseshoe crab fishers are dedicated stewards of a fishery that supplies a vital product, said George Topping, a Maryland fisherman.
“Everything you do in life comes from horseshoe crab blood. Vaccines, antibiotics,” he said. “The horseshoe crab stocks are healthy."